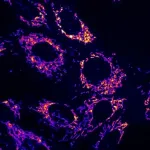
A new dye shakes up solar cells
2021-03-19
(Press-News.org) In 1991, scientists Brian O'Regan and Michael Grätzel at EPFL published a seminal paper describing a new type of solar cell: the dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC), also known as "Grätzel cell". Simple and cheap to build while being flexible and versatile, DSSCs are already manufactured on a multi-megawatt scale, cutting a significant slice of the photovoltaic market, which currently supplies almost 3% of all the world's electricity, well in the race to reduce carbon emissions.
Now, Dan Zhang and Marko Stojanovic, two PhD students in Grätzel's lab at EPFL's School of Basic Sciences, have led the development of a simple dye for DSSCs, called MS5. In devices, this new sensitizer can either be used as single dye, and produce an open-circuit voltage - the maximum voltage a solar cell can reach in full sunlight - of 1.24 Volts or as co-sensitizer, along with the commercial dye XY1b, and enable a power conversion efficiency of 13.5 %. Both are among the highest in the field of DSSCs.
The work is published in Nature Communications.
The team used this new dye in combination with another organic sensitizer coded XY1b. Apart from absorbing photons from the blue and yellow domain of the solar emission, the role of the new dye in this tandem is to boost the voltage output of the device by retarding the recombination of charge carriers generated by light. Called MS5, the photosensitizer was used with a copper (II/I) electrolyte to enable the DSSC achieve its impressive efficiency.
"Our work constitutes an important breakthrough in the work of DSSCs and especially dye design," says Michael Grätzel. "It shows that high performances are achievable with a relatively simple dye through judicious molecular engineering of the sensitizer's molecular structure."
Tested under ambient light conditions, the dye showed impressive performance, which is crucial for photovoltaics to be effective under cloudy conditions, or in-door applications to power electronic devices applied e.g. for the internet of things. And last but not least, MS5 is easy to synthesize up to the gram scale using a one-step procedure that researchers describe in their paper.
"Our results not only push the field of dye-sensitized solar cells further, but demonstrate EPFL's leading expertise in the field," says Marko Stojanovic.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-19
Researchers from Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with their colleagues from the Czech Republic have found a method to synthesize cyclic carbonates from atmospheric CO2. Cyclic carbonates are organic compounds, used as electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries, green solvents as well as in pharmaceutical drugs manufacturing. The scientists managed to synthetize carbonates under sunlight and at room temperature, while conventional methods require synthesis under high pressure and temperatures. The research findings are published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A (IF:11,301; Q1).
"The increase in CO2 levels in the atmosphere is a global environmental problem. The solutions of the problem are usually focused on measures to reduce CO2 emissions. An alternative method is to use the CO2 already ...
2021-03-19
Flashlight fish have the ability to generate situation-specific blink patterns resembling a visual Morse code. Researchers at Ruhr-Universität Bochum have shown in laboratory and field experiments that the animals use these light signals to coordinate their behaviour in the school when visibility is limited. Both the light intensity and the blinking frequency affected the animals' behaviour. The team headed by Peter Jägers and Professor Stefan Herlitze from the Department of General Zoology and Neurobiology has shared their findings in the journal Scientific Reports, published online on 19 ...
2021-03-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Recent generations show a worrying decline in health compared to their parents and grandparents when they were the same age, a new national study reveals.
Researchers found that, compared to previous generations, members of Generation X and Generation Y showed poorer physical health, higher levels of unhealthy behaviors such as alcohol use and smoking, and more depression and anxiety.
The results suggest the likelihood of higher levels of diseases and more deaths in younger generations than we have seen in the past, said Hui Zheng, ...
2021-03-19
Most drugs operate via the membranes that surround the body's cells. A study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden has now mapped the structure and mechanism of MGST2, a membrane enzyme that, amongst other things, plays a part in chronic inflammation and cancer. The study, which is published in the journal Nature Communications, can make a significant contribution to the development of future drugs.
All our cells are enclosed in a fat-rich membrane. The cells' equivalent to organs, the organelles, are also enclosed by membranes. Embedded in the cell's internal and external membranes are proteins that regulate a large number of vital functions. ...
2021-03-19
Parkinson's disease is the second most common, age-related, neurodegenerative disease: In Germany alone, about 300,000 people are affected and experience sometimes major limitations to their quality of life. Although Parkinson's is so widespread, there is still no treatment that targets the cause of the disease and can stop it in its tracks.
However, current research provides new hope: A research team at the University of Konstanz led by Professor Marcus Groettrup describes a new approach for developing future treatments for Parkinson's. The biologists demonstrated that the ubiquitin-like ...
2021-03-19
Boston, Mass. - In a paper published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, physician-researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) assessed the relative impact of COVID-19 on patients hospitalized with the viral infection in March and April 2020, versus patients hospitalized with influenza during the last five flu seasons at the medical center. Overall, the team demonstrated that COVID-19 cases resulted in significantly more weekly hospitalizations, more use of mechanical ventilation and higher mortality rates than influenza.
COVID-19 and influenza are both contagious respiratory viral diseases that can lead to pneumonia and acute respiratory failure in severe cases. However, detailed comparison of the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 ...
2021-03-19
Researchers at Aalto University and the Niilo Mäki Institute have used neuroimaging to pinpoint where the brain activates - or doesn't activate - among children identified as having a high risk of dyslexia. Magnetoencephalography (MEG) has rarely been used to study the reading disorder in children.
The brain study was carried out at Aalto University by measuring brain activity with MEG, which measures the weak magnetic fields arising from electrical activity in the brain, over a period of two days. Earlier studies have shown that difficulties in processing sounds may be partly responsible for dyslexia, and that these challenges may relate to the left auditory cortex which processes language.
During the study, the children listened to nonsensical ...
2021-03-19
At the start of Neurodiversity Celebration Week, new research from Cranfield University demonstrates the importance of organisations becoming more inclusive employers when it comes to neurodiversity.
It has been estimated that one in seven of the population of the UK is neurodiverse. However, according to research by the Institute of Leadership and Management, only half of managers would employ a neurodiverse person.
Last week, in an interview with The Times, The Second Sea Lord Vice Admiral Nick Hine, revealed that ten years ago he was diagnosed with autism.
Speaking to The Times, the Vice Admiral, said: ""The world is made for neuro-typical people by neuro-typical people, and therefore it's not surprising that people who are not neuro-typical have a ...
2021-03-19
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- Army-funded researchers created nanosized robots that could enable locomotion, novel metamaterial design and high-fidelity sensors.
Cornell University researchers created micron-sized shape memory actuators that fold themselves into 3D configurations and allow atomically thin 2D materials with just a quick jolt of voltage. Once the material is bent, it holds its shape, even after the voltage is removed.
To demonstrate the technology, the team created what is potentially the world's smallest self-folding origami bird.
"The research team is pushing the boundary of how quickly and precisely we can control motion at the micro- and even nano-scales," said Dr. Dean Culver, program manager for Complex Dynamics and Systems at Army Research Office, ...
2021-03-19
Infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in pregnancy is associated with preeclampsia, stillbirth, preterm birth and other adverse outcomes, found new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) .
"Our findings suggest that pregnant people with COVID-19 have an increased risk of high blood pressure, stillbirth and preterm birth. Their newborns are more likely to need intensive care. Pregnant people with severe COVID-19 symptoms have a particularly high risk of these complications," says Dr. Nathalie ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new dye shakes up solar cells