(Press-News.org) Dolphins along coast of Argentina could experience a significant loss of genetic diversity because some of the animals that accidently die when tangled in fishing nets are related. According to a new genetic analysis published this week in the journal PLoS One, Franciscana dolphins that die as by-catch are more than a collection of random individuals: many are most likely mother-offspring pairs. This result, which suggests reduced genetic diversity and reproductive potential, could have significant implications for the conservation of small marine mammals.
"It has always been assumed that dolphins could be entangled in fishing nets with family members, but this is one of the very few analyses to demonstrate this result," says Martin Mendez, a postdoctoral researcher at the Sackler Institute for Comparative Genomics at the American Museum of Natural History who led the study. "When family members die as by-catch, a portion of genetic identity of a species is lost, and two important demographic elements of a population are removed: a reproductive female and the next generation."
Franciscana dolphins (Pontoporia blainvillei) have a range that hugs the Atlantic coast of Brazil, Uruguay, and Argentina. This species is one of the world's smallest cetaceans and is a member of the river dolphin family, although it actually lives in coastal waters and estuaries. Females probably begin to have calves between two and five years and probably stay with each calf for some time. Because researchers estimate that between two and five percent of the Fransiscana population near Argentina becomes entangled in fishing nets from small-scale operations each year, the by-catch death rate has a significant impact on the population numbers. By-catch is the biggest impact to small cetacean populations world-wide.
"The by-catch in lost Franciscana dolphins is comparable to what the population produces in terms of offspring," says Pablo Bordino of Fundación Aquamarina in Buenos Aires, Argentina. "To know that Franciscana family groups are being caught in certain areas allows us to focus our conservation strategies to try to avoid this serious impact. The use of genetic information also gives us a new window into the ecology of this species."
In the current study, Mendez, Bordino, and colleagues looked at over 250 by-catch deaths among Franciscana dolphins over 10 years and found that most of the animals entangled in groups were genetic relatives.
"Like other highly cognitive species, the Franciscana dolphin likely relies on vital bonds among related animals to survive in a challenging environment," says Howard Rosenbaum, Director of the Wildlife Conservation Society's Ocean Giants Program. "Our genetic findings confirm that these bonds—especially between mothers and calves—make the Franciscana particularly vulnerable to bycatch mortality, a significant threat to the species in some areas of its range."
"People assume that by-catch is random, but there are related animals in the sample," says Mendez. "This analysis combining high-resolution genetic data would not have been possible a decade ago. We can now use these data to recover essential biological and ecological information, and translate that into management or conservation action."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Mendez, Bordino, and Rosenbaum , the authors include Randall S. Wells of the Chicago Zoological Society in Sarasota, Florida and Andrew Stamper of Walt Disney World Resorts at Lake Buena Vista, Florida. The research was funded by Fundación Aquamarina, Chicago Zoological Society, Ecohealth Alliance, Disney Wildlife Conservation Fund, and the Sackler Institute for Comparative Genomics at the American Museum of Natural History.
New research shows dolphin by-catch includes genetic relatives
Genetics of net entanglement has implications for small cetacean conservation
2010-12-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Polar bears: On thin ice? Extinction can be averted, scientists say
2010-12-16
Polar bears were added to the threatened species list nearly three years ago when their icy habitat showed steady, precipitous decline because of a warming climate.
But it appears the Arctic icons aren't necessarily doomed after all, according to results of a study published in this week's issue of the journal Nature.
The findings indicate that there is no "tipping point" that would result in unstoppable loss of summer sea ice when greenhouse gas-driven warming rises above a certain threshold.
Scientists from several institutions, including the U.S. Geological Survey ...
Vitamin D and parathyroid hormone levels may not affect cardiovascular mortality
2010-12-16
New York, NY, December 15, 2010 – There is burgeoning public interest in possible wide-ranging health benefits from vitamin D, including cardiovascular health. In a study published in the December 2010 issue of The American Journal of Medicine, investigators found that there was no independent association between serum levels of vitamin D or parathyroid hormone and cardiovascular mortality in this prospective study, the first in a population of older community-dwelling adults with a low prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and a broad range of kidney function.
Researchers ...
Nanomaterials in our environment
2010-12-16
Madison, WI DECEMBER 15, 2010 -- The manufacturing of nanomaterials has been steadily on the rise in the medical, industrial, and scientific fields. Nanomaterials are materials that are engineered to have dimensions less than 100 nanometers and have very unique properties as a result of their small size.
In a study funded by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, a team of scientists from the University of Kentucky determined that earthworms could absorb copper nanoparticles present in soil.
One crucial step in determining the uptake of nanomaterials was discerning ...
Satellites give an eagle eye on thunderstorms
2010-12-16
MADISON — It's one of the more frustrating parts of summer. You check the weather forecast, see nothing dramatic, and go hiking or biking. Then, four hours later, a thunderstorm appears out of nowhere and ruins your afternoon.
Thunderstorms can bring intense rain, hail, lightning and even tornadoes, but "predicting them a few hours out is one of the great problems of meteorology," says Chian-Yi Liu, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
And the consequences can be more serious than a rained-out hike — even major storms can be missed, Liu ...
Link between cholesterol compound and multiple sclerosis unlikely, researchers say
2010-12-16
New research findings appearing in the January Journal of Lipid Research indicate that compounds called oxysterols are not present in any significant amount in multiple sclerosis patients, contradicting a previous study that suggested that some of these cholesterol metabolites were associated with MS and could be used as diagnostic tools in the clinic.
Oxysterols are somewhat controversial in science; while some laboratory experiments suggest these steroid molecules may be biologically important, they are present in only trace amounts in the blood, and studies in living ...
Seaweed as biofuel? Metabolic engineering makes it a viable option
2010-12-16
URBANA – Is red seaweed a viable future biofuel? Now that a University of Illinois metabolic engineer has developed a strain of yeast that can make short work of fermenting galactose, the answer is an unequivocal yes.
"When Americans think about biofuel crops, they think of corn, miscanthus, and switchgrass. ln small island or peninsular nations, though, the natural, obvious choice is marine biomass," said Yong-Su Jin, a U of I assistant professor of microbial genomics and a faculty member in its Institute for Genomic Biology.
Producers of biofuels made from terrestrial ...
Census analysis: Nation's diversity grows, but integration slows
2010-12-16
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Despite increased racial and ethnic diversity, American neighborhoods continue to be segregated, and some of the progress made toward integration since 1980 has come to a halt this decade, according to a new report by Brown University sociologist John Logan. The report, co-authored by Florida State University sociologist Brian Stults, marks the launch of the US2010 project, a program of research on changes in American society, supported by the Russell Sage Foundation and Brown University.
"This is a surprising result," said Logan, ...
SIDS spikes on New Year's Day
2010-12-16
Not a happy holiday thought, but an important one: The number of babies who die of SIDS, or sudden infant death syndrome, surges by 33 percent on New Year's Day. The suspected reason? Alcohol consumption by caretakers the night before.
Led by sociologist David Phillips of the University of California, San Diego, the study documenting the dramatic rise in SIDS deaths on New Year's is published in the journal Addiction. The spike, write Phillips and his coauthors, is beyond the normal winter increase in SIDS.
The study examined 129,090 SIDS cases from 1973 to 2006 using ...
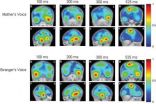
Allô allô! Mom's voice plays special role in activating newborn's brain
2010-12-16
A mother's voice will preferentially activate the parts of the brain responsible for language learning, say researchers from the University of Montreal and the Sainte-Justine University Hospital Research Centre. The research team made the discovery after performing electrical recordings on the infants within the 24 hours following their birth. The brain signals also revealed that while the infants did react to other women's voices, these sounds only activated the voice recognition parts of the brains. "This is exciting research that proves for the first time that the newborn's ...
Study shows caffeine negatively affects children
2010-12-16
Cincinnati, OH, December 16, 2010 -- Caffeine consumption in children is often blamed for sleep problems and bedwetting. Information on childhood caffeine consumption is limited, and many parents may not know the amount or effects of their child's caffeine consumption. In a study published in The Journal of Pediatrics, researchers found that 75% of children surveyed consumed caffeine on a daily basis, and the more caffeine the children consumed, the less they slept.
Dr. William Warzak and colleagues from the University of Nebraska Medical Center surveyed the parents ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
In football players with repeated head impacts, inflammation related to brain changes
Being an early bird, getting more physical activity linked to lower risk of ALS
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
[Press-News.org] New research shows dolphin by-catch includes genetic relativesGenetics of net entanglement has implications for small cetacean conservation