Where unconscious memories form
2010-12-16
(Press-News.org) A small area deep in the brain called the perirhinal cortex is critical for forming unconscious conceptual memories, researchers at the UC Davis Center for Mind and Brain have found.
The perirhinal cortex was thought to be involved, like the neighboring hippocampus, in "declarative" or conscious memories, but the new results show that the picture is more complex, said lead author Wei-chun Wang, a graduate student at UC Davis.
The results were published Dec. 9 in the journal Neuron.
We're all familiar with memories that rise from the unconscious mind. Imagine looking at a beach scene, said Wang. A little later, someone mentions surfing, and the beach scene pops back into your head.
Declarative memories, in contrast, are those where we recall being on that beach and watching that surf competition: "I remember being there."
Damage to a structure called the hippocampus affects such declarative "I remember" memories, but not conceptual memories, Wang said. Neuroscientists had previously thought the same was true for the perirhinal cortex, which is located immediately next to the hippocampus.
Wang and colleagues carried out memory tests on people diagnosed with amnesia, who had known damage to the perirhinal cortex or other brain areas. They also carried out functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans of healthy volunteers while they performed memory tests.
In a typical test, they gave the subjects a long list of words, such as chair, table or spoon, and asked them to think about how pleasant they were.
Later, they asked the subjects to think up words in different categories, such as "furniture."
Amnesiacs with damage to the perirhinal cortex performed poorly on the tests, while the same brain area lit up in fMRI scans of the healthy control subjects.
The study helps us understand how memories are assembled in the brain and how different types of brain damage might impair memory, Wang said. For example, Alzheimer's disease often attacks the hippocampus and perirhinal cortex before other brain areas.
###
Co-authors on the study are Andy Yonelinas, professor of psychology and at the Center for Mind and Brain; Charan Ranganath, professor at the Center for Neuroscience; former UC Davis graduate student Michele Lazzara, now project coordinator at the University of Illinois at Chicago; and Robert Knight, professor of psychology at UC Berkeley.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-12-16
Dolphins along coast of Argentina could experience a significant loss of genetic diversity because some of the animals that accidently die when tangled in fishing nets are related. According to a new genetic analysis published this week in the journal PLoS One, Franciscana dolphins that die as by-catch are more than a collection of random individuals: many are most likely mother-offspring pairs. This result, which suggests reduced genetic diversity and reproductive potential, could have significant implications for the conservation of small marine mammals.
"It has always ...
2010-12-16
Polar bears were added to the threatened species list nearly three years ago when their icy habitat showed steady, precipitous decline because of a warming climate.
But it appears the Arctic icons aren't necessarily doomed after all, according to results of a study published in this week's issue of the journal Nature.
The findings indicate that there is no "tipping point" that would result in unstoppable loss of summer sea ice when greenhouse gas-driven warming rises above a certain threshold.
Scientists from several institutions, including the U.S. Geological Survey ...
2010-12-16
New York, NY, December 15, 2010 – There is burgeoning public interest in possible wide-ranging health benefits from vitamin D, including cardiovascular health. In a study published in the December 2010 issue of The American Journal of Medicine, investigators found that there was no independent association between serum levels of vitamin D or parathyroid hormone and cardiovascular mortality in this prospective study, the first in a population of older community-dwelling adults with a low prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and a broad range of kidney function.
Researchers ...
2010-12-16
Madison, WI DECEMBER 15, 2010 -- The manufacturing of nanomaterials has been steadily on the rise in the medical, industrial, and scientific fields. Nanomaterials are materials that are engineered to have dimensions less than 100 nanometers and have very unique properties as a result of their small size.
In a study funded by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, a team of scientists from the University of Kentucky determined that earthworms could absorb copper nanoparticles present in soil.
One crucial step in determining the uptake of nanomaterials was discerning ...
2010-12-16
MADISON — It's one of the more frustrating parts of summer. You check the weather forecast, see nothing dramatic, and go hiking or biking. Then, four hours later, a thunderstorm appears out of nowhere and ruins your afternoon.
Thunderstorms can bring intense rain, hail, lightning and even tornadoes, but "predicting them a few hours out is one of the great problems of meteorology," says Chian-Yi Liu, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
And the consequences can be more serious than a rained-out hike — even major storms can be missed, Liu ...
2010-12-16
New research findings appearing in the January Journal of Lipid Research indicate that compounds called oxysterols are not present in any significant amount in multiple sclerosis patients, contradicting a previous study that suggested that some of these cholesterol metabolites were associated with MS and could be used as diagnostic tools in the clinic.
Oxysterols are somewhat controversial in science; while some laboratory experiments suggest these steroid molecules may be biologically important, they are present in only trace amounts in the blood, and studies in living ...
2010-12-16
URBANA – Is red seaweed a viable future biofuel? Now that a University of Illinois metabolic engineer has developed a strain of yeast that can make short work of fermenting galactose, the answer is an unequivocal yes.
"When Americans think about biofuel crops, they think of corn, miscanthus, and switchgrass. ln small island or peninsular nations, though, the natural, obvious choice is marine biomass," said Yong-Su Jin, a U of I assistant professor of microbial genomics and a faculty member in its Institute for Genomic Biology.
Producers of biofuels made from terrestrial ...
2010-12-16
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Despite increased racial and ethnic diversity, American neighborhoods continue to be segregated, and some of the progress made toward integration since 1980 has come to a halt this decade, according to a new report by Brown University sociologist John Logan. The report, co-authored by Florida State University sociologist Brian Stults, marks the launch of the US2010 project, a program of research on changes in American society, supported by the Russell Sage Foundation and Brown University.
"This is a surprising result," said Logan, ...
2010-12-16
Not a happy holiday thought, but an important one: The number of babies who die of SIDS, or sudden infant death syndrome, surges by 33 percent on New Year's Day. The suspected reason? Alcohol consumption by caretakers the night before.
Led by sociologist David Phillips of the University of California, San Diego, the study documenting the dramatic rise in SIDS deaths on New Year's is published in the journal Addiction. The spike, write Phillips and his coauthors, is beyond the normal winter increase in SIDS.
The study examined 129,090 SIDS cases from 1973 to 2006 using ...
2010-12-16
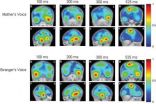
A mother's voice will preferentially activate the parts of the brain responsible for language learning, say researchers from the University of Montreal and the Sainte-Justine University Hospital Research Centre. The research team made the discovery after performing electrical recordings on the infants within the 24 hours following their birth. The brain signals also revealed that while the infants did react to other women's voices, these sounds only activated the voice recognition parts of the brains. "This is exciting research that proves for the first time that the newborn's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Where unconscious memories form