(Press-News.org) Durham, NC - The standard of treatment for bone tumors is often two-fold: surgery to remove the cancerous section followed by radiation therapy to ensure all the cancerous cells have been killed off. This is an effective way to defeat bone tumors; however, it often results in large bone defects and hampers wound healing because of extensive tissue cutoff and irradiation-induced tissue damage. A new study published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine demonstrates how stem cells primed with ferulic acid can repair such bone damage and how this occurs. The information this study provides could aid in the development of new treatments for irradiated bone injuries.
Heng Zhu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine (BIRM), and Li Ding, M.D., Ph.D., of the Air Force Medical Center in the People's Republic of China, were co-corresponding authors of the paper. BIRM colleagues Jia-Wu Liang, M.D, and Pei-Lin Li, M.D., were co-first authors.
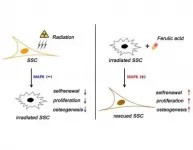
"One prime concern of radiation therapy is that it impairs the 'stemness' of skeletal stem cells (SSCs), meaning that it affects their ability to self-renew and differentiate, which are assets critical to bone regeneration and repair," said Dr. Zhu. "Despite this, little information is available regarding the change in SSC stemness after irradiation and the related underlying regulatory factors. This limits our level of understanding regarding SSC-based bone regeneration."
While seeking a way to restrict radiation's harmful effects on SSCs, Dr. Zhu and his team became interested in ferulic acid (FA). FA is a potent antioxidant commonly found in fruits and vegetables that exhibits strong anti-inflammatory properties and has been widely applied in the prevention of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer and more. It is also known to alleviate radiation-induced stem cell damage.
"Given the fundamental role of SSCs in bone regeneration and the potential role of FA in irradiation protection, we hypothesized that FA combined with SSCs might be effective in reconstructing irradiated bone defects. We explored this idea using an in vitro cell model and an in vivo animal model. Moreover, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the protective effects of FA on SSCs were also investigated," Dr. Ding said.
For the in vitro phase of their study, the researchers seeded irradiated SSCs and nonirradiated SCCs onto culture plates and then added FA at different concentrations to determine the potential effects of FA on SSC proliferation, differentiation and self-renewal.
To explore the repairing capacity of SSC on irradiated bone defects in an animal model, the hind limbs and lower abdomens of mice were locally irradiated and then bone defect surgeries were conducted an hour later. Nonirradiated mice that underwent surgery served as bone defect controls. Microcryogels that had been seeded with either FA-primed SSCs or SSCs alone were then injected into the bone defect areas of the irradiated mice. The same concentration of microcryogel without SSCs was used in another group of irradiated animals, as a control. Finally, to study the effects of FA on bone repair, FA solution was injected into irradiated bone defects.
The results were then evaluated at intervals of one, two and three weeks post-radiation. They showed that FA significantly rescued the radiation-induced impairment of SSCs by activating the p38/MAPK and ERK/MAPK pathways, which are chains of proteins in cells that communicate signals from receptors on a cell's surface to its DNA. As such, they play an important role in proliferation, differentiation, development, transformation, apoptosis and other complex cellular programs.
Moreover, the FA substantially enhanced the bone repair effects of SSCs in the irradiated bone defect mice.
"This work unveils that FA promotes the maintenance of skeletal stem cells' stemness after irradiation. It also defined activation of the p38/MAPK and ERK/MAPK pathways as the molecular underlying mechanism governing FA activity," said Dr. Liang "Notably, our data shows that SSC is very sensitive to irradiation and exhibits impaired stemness, which adds new information to understanding bone osteoporosis and hindered bone repair post-radiation."
"While several studies previously published have shown that FA can enhance and improve stem cell self-renewal and that its activity is mediated through activation of p38/MAPK and ERK/MAPK pathways, ours is the first to demonstrate that FA enhances the bone repair effects of SSCs," Dr. Li added. "As such, we believe that targeting SSCs has potential as a novel strategy in treating irradiated bone injury."
"In the current study, promising data demonstrates that stem cells combined with ferulic acid, a potent antioxidant agent, enhanced the bone repair effects of skeletal stem cells in an irradiated bone defect," said Anthony Atala, M.D., Editor-in-Chief of STEM CELLS Translational Medicine and Director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine. "These findings could someday lead to new treatment standards for bone tumors."
INFORMATION:
The full article, "Ferulic acid promotes bone defect repair after radiation by maintaining the stemness of skeletal stem cells," can be accessed at https://stemcellsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/sctm.20-0536.
About STEM CELLS Translational Medicine: STEM CELLS Translational Medicine (SCTM), co-published by AlphaMed Press and Wiley, is a monthly peer-reviewed publication dedicated to significantly advancing the clinical utilization of stem cell molecular and cellular biology. By bridging stem cell research and clinical trials, SCTM will help move applications of these critical investigations closer to accepted best practices. SCTM is the official journal partner of Regenerative Medicine Foundation.
About AlphaMed Press: Established in 1983, AlphaMed Press with offices in Durham, NC, San Francisco, CA, and Belfast, Northern Ireland, publishes two other internationally renowned peer-reviewed journals: STEM CELLS®, celebrating its 39th year, is the world's first journal devoted to this fast paced field of research. The Oncologist®, also a monthly peer-reviewed publication, entering its 26th year, is devoted to community and hospital-based oncologists and physicians entrusted with cancer patient care. All three journals are premier periodicals with globally recognized editorial boards dedicated to advancing knowledge and education in their focused disciplines.
About Wiley: Wiley, a global company, helps people and organizations develop the skills and knowledge they need to succeed. Our online scientific, technical, medical and scholarly journals, combined with our digital learning, assessment and certification solutions, help universities, learned societies, businesses, governments and individuals increase the academic and professional impact of their work. For more than 200 years, we have delivered consistent performance to our stakeholders. The company's website can be accessed at http://www.wiley.com.
About Regenerative Medicine Foundation (RMF): The non-profit Regenerative Medicine Foundation fosters strategic collaborations to accelerate the development of regenerative medicine to improve health and deliver cures. RMF pursues its mission by producing its flagship World Stem Cell Summit, honouring leaders through the Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Action Awards, and promoting educational initiatives.
As World Water Day is observed around the globe, new research from UBC Okanagan suggests a systematic approach to forest and water supply research may yield an improved assessment and understanding of connections between the two.
Healthy forests play a vital role in providing a clean, stable water supply, says eco-hydrologist Dr. Adam Wei.
Acting as natural reservoirs, forests in watersheds release and purify water by slowing erosion and delaying its release into streams. But forests are changing--in part because of human activity--and that's having an impact on forests' interaction with hydrological ...
Latino undergraduate male college students are involved in many leadership roles, yet how this leadership evolves in higher education has been understudied. Researchers from Florida Atlantic University in collaboration with San Diego State University and Texas A&M University explored how Latino male college students make meaning of their masculinity and how this meaning shapes their understanding and performance of leadership.
The study published in the International Journal of Leadership Education, utilized a qualitative method to delve deep into the understandings of the masculinities, gender socialization, leadership and transfer experiences of 34 Latino undergraduate male students. Using a philosophical approach, the researchers ...
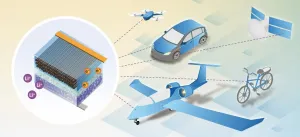
Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology have produced a structural battery that performs ten times better than all previous versions. It contains carbon fibre that serves simultaneously as an electrode, conductor, and load-bearing material. Their latest research breakthrough paves the way for essentially 'massless' energy storage in vehicles and other technology.
The batteries in today's electric cars constitute a large part of the vehicles' weight, without fulfilling any load-bearing function. A structural battery, on the other hand, is one that works as both a power source and as part of the structure - for example, in a car body. This is termed 'massless' energy storage, because in essence the battery's weight vanishes when it becomes part of ...
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this review article the authors Oliver K. Semisch-Dieter, Andy H. Choi and Martin P. Stewart from the University of Technology Sydney, Ultimo, NSW, Australia discuss the use of biomaterials in dental implants.
Biomaterials have become essential for modern implants. A suitable implant biomaterial integrates into the body to perform a key function, whilst minimizing negative immune response. Focusing on dentistry, the use of dental implants for tooth replacement requires a balance between bodily response, mechanical structure and performance, and aesthetics. ...
A team of researchers from Tübingen and Israel uncovers how brain structures can maintain function and stable dynamics even in unusual conditions. Their results might lay the foundations for better understanding and treating conditions like epilepsy and autism.
The neurons in our brains are connected with each other, forming small functional units called neural circuits. A neuron that is connected to another one via a synapsis can transmit information to the second neuron by sending a signal. This, in turn, might prompt the second neuron to transmit a signal to ...
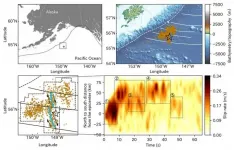
Tsukuba, Japan - An earthquake is generally viewed to be caused by a rupture along a fault that is transmitted outward from its point of origin in a uniform, predictable pattern. Of course, given the complexity of the environments where these ruptures typically occur, the reality is often much more complicated.
In a new study published in Scientific Reports, a research team led by the University of Tsukuba developed a new method to model the details of complex earthquake rupture processes affecting systems of multiple faults. They then applied this method to the magnitude ...
An international team of interdisciplinary researchers has identified mathematical metrics to characterize the fragility of financial markets. Their paper "Network geometry and market instability" sheds light on the higher-order architecture of financial systems and allows analysts to identify systemic risks like market bubbles or crashes.
With the recent rush of small investors into so-called meme stocks and reemerging interest in cryptocurrencies talk of market instability, rising volatility, and bursting bubbles is surging. However, "traditional economic theories cannot foresee events like the US subprime mortgage collapse of 2007" according ...
Point
Epithelial cell rests of Malassez derived from the periodontal ligament were transformed into progenitor stem-like cells by stimulation with epigenetic agents.
Subsequently, the progenitor stem-like cells were directly differentiated into endothelial, mesenchymal stem, and osteogenic cells that constitute the periodontal ligament.
Background
Stem cells derived from the dental pulp or periodontal ligament have been used for regenerative dentistry. Although it is relatively easy to collect the dental pulp stem cells, it is difficult to obtain adequate numbers of good quality cells; a ...
Using an improved version of the gene editing tool CRISPR/Cas9, researchers knocked out up to twelve genes in plants in a single blow. Until now, this had only been possible for single or small groups of genes. The approach was developed by researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Leibniz Institute of Plant Biochemistry (IPB). The method makes it easier to investigate the interaction of various genes. The study appeared in The Plant Journal.
The inheritance of traits in plants is rarely as simple and straightforward as Gregor Mendel described. The monk, whose experiments in the 19th century on trait inheritance in peas laid the foundation of genetics, in fact got lucky. "In the traits that ...
Patricia Bernal, a Ramón y Cajal researcher at the Department of Microbiology of the University of Seville's Faculty of Biology, is working with the bacterium Pseudomonas putida, a biological control agent found in the soil and in plant roots and which, as such, has the ability to protect plants from pathogen attacks (organisms that cause diseases) also known as phytopathogens. Specifically, the US researcher is studying a molecular weapon that bacteria use (Type VI Secretion System or T6SS) to eliminate their competitors.
The T6SS could be compared to a harpoon with a poisonous tip that bacteria throw at their enemies to annihilate them. In a recent paper, which has just been published in the scientific journal PNAS and for ...