Upgrade for CRISPR/Cas: Researchers knock out multiple genes in plants at once
2021-03-22
(Press-News.org) Using an improved version of the gene editing tool CRISPR/Cas9, researchers knocked out up to twelve genes in plants in a single blow. Until now, this had only been possible for single or small groups of genes. The approach was developed by researchers at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Leibniz Institute of Plant Biochemistry (IPB). The method makes it easier to investigate the interaction of various genes. The study appeared in The Plant Journal.
The inheritance of traits in plants is rarely as simple and straightforward as Gregor Mendel described. The monk, whose experiments in the 19th century on trait inheritance in peas laid the foundation of genetics, in fact got lucky. "In the traits that Mendel studied, the rule that only one gene determines a specific trait, for example the colour of the peas, happened to apply," says plant geneticist Dr Johannes Stuttmann from the Institute of Biology at MLU. According to the researcher, things are often much more complicated. Frequently there are different genes that, through their interaction with one another, result in certain traits or they are partly redundant, in other words they result in the same trait. In this case, when only one of these genes is switched off, the effects are not visible in the plants.
The scientists at MLU and IPB have now developed a way to study this complex phenomenon in a more targeted way by improving CRISPR/Cas9. These gene editing tools can be used to cut the DNA of organisms at specific sites. The team built on the work of biologist Dr Sylvestre Marillonnet who developed an optimised building block for the CRISPR/Cas9 system at the IPB. "This building block helps to produce significantly more Cas9 enzyme in the plants, which acts as a scissor for the genetic material," explains Stuttmann. The researchers added up to 24 different guide RNAs which guide the scissor enzyme to the desired locations in the genetic material. Experiments on thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana) and the wild tobacco plant Nicotiana benthamiana proved that the approach works. Up to eight genes could be switched off simultaneously in the tobacco plants while, in the thale cress, up to twelve genes could be switched off in some cases. According to Stuttmann, this is a major progress: "As far as I know, our group has been the first to successfully address so many target genes at once. This may make it possible to overcome the redundancy of genes," says the biologist.
Until now, creating multiple mutations was a much more complex process. The plants had to be bred in stages with a single mutation each and then crossed with one another. "This is not only time-consuming, it's also not possible in every case," says Stuttmann. The new approach developed at the MLU and the IPB overcomes these disadvantages and could prove to be a more efficient method of research. In future, it will also be possible to test random combinations of several genes in order to identify redundancies. Only in the case of conspicuous changes in the plant's traits would it then be necessary to specifically analyse the genetic material of the new plants.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation).
Study: Stuttmann J. et al. Highly efficient multiplex editing: One?shot generation of 8x Nicotiana benthamiana and 12x Arabidopsis mutants. The Plant Journal (2021). Doi: 10.1111/tpj.15197
https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15197
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-22
Patricia Bernal, a Ramón y Cajal researcher at the Department of Microbiology of the University of Seville's Faculty of Biology, is working with the bacterium Pseudomonas putida, a biological control agent found in the soil and in plant roots and which, as such, has the ability to protect plants from pathogen attacks (organisms that cause diseases) also known as phytopathogens. Specifically, the US researcher is studying a molecular weapon that bacteria use (Type VI Secretion System or T6SS) to eliminate their competitors.
The T6SS could be compared to a harpoon with a poisonous tip that bacteria throw at their enemies to annihilate them. In a recent paper, which has just been published in the scientific journal PNAS and for ...
2021-03-22
Igor Stagljar made his career building molecular tools to combat cancer. But when the pandemic hit last March, he aimed his expertise at a new adversary, SARS-CoV-2.
Stagljar is a professor of biochemistry and molecular genetics in the Donnelly Centre for Cellular and Biomolecular Research at U of T's Temerty Faculty of Medicine. Last spring, with support from U of T's Toronto COVID-19 Action Fund, his team began developing a new method for measuring immunity to coronavirus in those who recovered from COVID-19.
They are now ready to reveal their creation -- a pinprick test that accurately measures ...
2021-03-22
"You have to win the battle against depression", "what counts is not surrendering" and "this is not a short road" are examples of conceptual metaphors typically used to describe experiences and issues associated with disorders like depression. Such expressions allude to abstract concepts but do so using familiar terms that enable better understanding of the experience. This kind of metaphor is often used unconsciously, going unnoticed by both speaker and listener. However, the study of metaphors can help access and understand the thinking, beliefs and feelings of individuals with mental disorders.
The conceptual metaphors of depression found in 23 blogs written by people with major depressive disorders were analysed by a multidisciplinary UOC team composed of Marta Coll-Florit and Salvador ...
2021-03-22
The results argue for a comprehensive approach to disease prevention. The scientists have now published their findings in the journal Nature Medicine.
Many elderly people suffer simultaneously from several, frequently very different diseases, a condition also known as multimorbidity. Their quality of life is severely restricted, and they receive medication from different doctors, a process which is difficult and often insufficiently coordinated. Observations indicate that certain diseases commonly occur together, but the causes of this are largely ...
2021-03-22
It's well known that mentoring opportunities are critical for development and career advancement, and are associated with greater job satisfaction and increased earnings and promotions.
Yet a recent study co-authored by RMIT University's Professor Andrew R. Timming found women may be missing out on these opportunities due to fears by male managers of potential misconduct allegations.
"Workplace relations between males and females have changed over the past two years. Male managers are significantly less likely than female managers to mentor or interact one-on-one with female employees," Timming said.
"We found that male managers were less likely to work one-on-one in an office with the door closed and less likely to have ...
2021-03-22
WASHINGTON, March 22, 2021 -- What's better at finding a hidden bomb -- a dog or an electronic chemical detector? In this episode, the Reactions team travels to the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory to find out: https://youtu.be/TRwqOFHOjac.
INFORMATION:
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions and follow us on Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS' mission is to advance the broader ...
2021-03-22
March 22, 2021 (BRONX, NY)-- Most people with cancer who are infected by the novel coronavirus produce antibodies at a rate comparable to the rest of the population--but their ability to do so depends on their type of cancer and the treatments they've received, according to a new study by researchers at Montefiore Health System and Albert Einstein College of Medicine. The findings, published online today in Nature Cancer, may lead to better care for cancer patients, who face a heightened risk of dying from COVID-19, and suggests that cancer patients should ...
2021-03-22
PHILADELPHIA--Hormone drugs that reduce androgen levels may help disarm the coronavirus spike protein used to infect cells and stop the progression of severe COVID-19 disease, suggests a new preclinical study from researchers in the Abramson Cancer Center at the University of Pennsylvania and published online in Cell Press's iScience.
Researchers show how two receptors--known as ACE2 and TMPRSS2--are regulated by the androgen hormone and used by SARS-CoV-2 to gain entry into host cells. Blocking the receptors with the clinically proven inhibitor Camostat and other anti-androgen therapies prevented viral entry and replication, they also showed in lab studies.
The findings provide more insight into the molecular mechanisms of the virus but also support ...
2021-03-22
There are some tasks that traditional robots -- the rigid and metallic kind -- simply aren't cut out for. Soft-bodied robots, on the other hand, may be able to interact with people more safely or slip into tight spaces with ease. But for robots to reliably complete their programmed duties, they need to know the whereabouts of all their body parts. That's a tall task for a soft robot that can deform in a virtually infinite number of ways.
MIT researchers have developed an algorithm to help engineers design soft robots that collect more useful information about their surroundings. The deep-learning algorithm suggests an optimized placement of sensors within the robot's body, allowing it to better interact with ...
2021-03-22
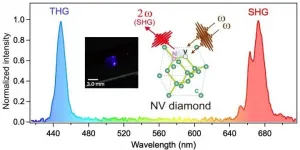
Tsukuba, Japan - Researchers from the Department of Applied Physics at the University of Tsukuba demonstrated second-order nonlinear optical effects in diamonds by taking advantage of internal color center defects that break inversion symmetry of diamond crystal. This research may lead to faster internet communications, all-optical computers, and even open a route to next generation quantum sensing technologies.
Current fiber optical technology uses light pulses to transfer broad-bandwidth data that let you check your email, watch videos, and everything else on the Internet. The main drawback is that light pulses hardly interact with each other, so the information must be converted into electrical signals to allow your computer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Upgrade for CRISPR/Cas: Researchers knock out multiple genes in plants at once