(Press-News.org) It's well known that mentoring opportunities are critical for development and career advancement, and are associated with greater job satisfaction and increased earnings and promotions.
Yet a recent study co-authored by RMIT University's Professor Andrew R. Timming found women may be missing out on these opportunities due to fears by male managers of potential misconduct allegations.
"Workplace relations between males and females have changed over the past two years. Male managers are significantly less likely than female managers to mentor or interact one-on-one with female employees," Timming said.
"We found that male managers were less likely to work one-on-one in an office with the door closed and less likely to have a late-night dinner with female employees."
Despite this trend, the study also found a large portion of female employees reporting a willingness to be mentored by an older male co-worker, many of whom hold senior positions.
The study was co-authored with Professors Michael T. French and Karoline Mortensen at the University of Miami.
More than 2,000 participants in the United States completed the surveys, but Timming said the findings were highly relevant in Australia and other similar countries that have experienced their own #MeToo movements.
"Aside from cultural similarities between the US and Australia, both countries have recently experienced allegations of rape and sexual misconduct," Timming said.
"This research is critical for everyone in the workplace, male and female alike, across Australia."
"We need to ensure that women don't miss out on workplace mentoring opportunities because males fear misconduct allegations."
The study involved two surveys: one administered to female employees and another distributed to both male and female managers.
The surveys were conducted in the summer of 2018 - roughly one year after Hollywood celebrities began accusing powerful men in the film industry of sexual assault and harassment, starting the #MeToo movement.
More than 1,800 female employees were asked to answer questions relating to their level of comfort and willingness to be mentored by an older male co-worker.
From this survey, 38% of females under 35 years of age reported that their interactions with males were very to somewhat different today than they were 1-2 years ago - prior to the #MeToo movement.
Only 11% of female participants overall reported an unwillingness to be mentored by an older male co-worker.
"Women are clearly still willing to be mentored by older males, but opportunities for such mentoring may not be as forthcoming - as seen in our second survey."
The second survey presented 12 photographs of employees to more than 200 male and female managers, where they were asked three mentoring questions for each photographed individual.
The female managers reported a greater willingness and likelihood to mentor female employees than male employees.
In contrast, male managers were significantly less likely to mentor female employees, less likely to work one-on-one with female employees behind closed doors, and less likely to have a late-night dinner with female employees.
"Although we can't say with absolute certainty whether the #MeToo movement caused this reluctance, it seems reasonable to conclude that it may have played a role."
INFORMATION:
'A Multivariate Analysis of Workplace Mentoring and Socializing in the Wake of #MeToo' is published in Applied Economics (DOI: 10.1080/00036846.2021.1896673)
WASHINGTON, March 22, 2021 -- What's better at finding a hidden bomb -- a dog or an electronic chemical detector? In this episode, the Reactions team travels to the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory to find out: https://youtu.be/TRwqOFHOjac.
INFORMATION:
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions and follow us on Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS' mission is to advance the broader ...
March 22, 2021 (BRONX, NY)-- Most people with cancer who are infected by the novel coronavirus produce antibodies at a rate comparable to the rest of the population--but their ability to do so depends on their type of cancer and the treatments they've received, according to a new study by researchers at Montefiore Health System and Albert Einstein College of Medicine. The findings, published online today in Nature Cancer, may lead to better care for cancer patients, who face a heightened risk of dying from COVID-19, and suggests that cancer patients should ...
PHILADELPHIA--Hormone drugs that reduce androgen levels may help disarm the coronavirus spike protein used to infect cells and stop the progression of severe COVID-19 disease, suggests a new preclinical study from researchers in the Abramson Cancer Center at the University of Pennsylvania and published online in Cell Press's iScience.
Researchers show how two receptors--known as ACE2 and TMPRSS2--are regulated by the androgen hormone and used by SARS-CoV-2 to gain entry into host cells. Blocking the receptors with the clinically proven inhibitor Camostat and other anti-androgen therapies prevented viral entry and replication, they also showed in lab studies.
The findings provide more insight into the molecular mechanisms of the virus but also support ...
There are some tasks that traditional robots -- the rigid and metallic kind -- simply aren't cut out for. Soft-bodied robots, on the other hand, may be able to interact with people more safely or slip into tight spaces with ease. But for robots to reliably complete their programmed duties, they need to know the whereabouts of all their body parts. That's a tall task for a soft robot that can deform in a virtually infinite number of ways.
MIT researchers have developed an algorithm to help engineers design soft robots that collect more useful information about their surroundings. The deep-learning algorithm suggests an optimized placement of sensors within the robot's body, allowing it to better interact with ...
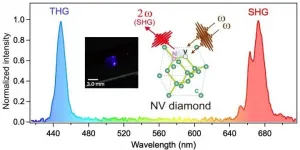
Tsukuba, Japan - Researchers from the Department of Applied Physics at the University of Tsukuba demonstrated second-order nonlinear optical effects in diamonds by taking advantage of internal color center defects that break inversion symmetry of diamond crystal. This research may lead to faster internet communications, all-optical computers, and even open a route to next generation quantum sensing technologies.
Current fiber optical technology uses light pulses to transfer broad-bandwidth data that let you check your email, watch videos, and everything else on the Internet. The main drawback is that light pulses hardly interact with each other, so the information must be converted into electrical signals to allow your computer ...
In a recent study testing the effects of exercise on overall metabolism, researchers at Oregon State University found that even a single session of moderate aerobic exercise makes a difference in the cells of otherwise sedentary people.
Mitochondria are the part of the cell responsible for the biological process of respiration, which turns fuels such as sugars and fats into energy, so the researchers focused only on mitochondria function.
"What we found is that, regardless of what fuel the mitochondria were using, there were mild increases in the ability to burn off the fuels," said Matt Robinson, lead author on the study and an assistant professor ...
Melbourne researchers have revealed how melanoma cells are flooded with DNA changes as this skin cancer progresses from early, treatable stages through to fatal end-stage disease.
Using genomics, the team tracked DNA changes occurring in melanoma samples donated by patients as their disease progressed, right through to the time the patient died. This revealed dramatic and chaotic genetic changes that accumulated in the melanoma cells as the cancers progressed, providing clues to potential new approaches to treating this disease.
The research, published in Nature Communications, was led by Professor Mark Shackleton, Professor Director of Oncology at Alfred Health and Monash University; Professor ...
Clinically, multiple lines of evidence show that chronic pain and depressive symptoms are frequently encountered. Patients suffered from both pain and depression are likely to become insensitive to drug treatment, indicating a refractory disease. The neural mechanism under this comorbidity remains unclear.
In a study published in Nature Neuroscience, the research team led by Prof. ZHANG Zhi and Dr. LI Juan from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), reported the discrete thalamocortical circuits underlying the pain symptom caused by tissue injury and depression-like states.
Being the gateway towards cerebral cortex and considered as the major source of 'nociceptive ...
The research team led by Prof. ZHANG Jie from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences made progress on real-time determination of earthquake focal mechanism through deep learning. The work was published in Nature Communications.
Since there are connections between characteristics of the rupture surface of the source fault and seismic wave radiated by the source, it's vital to monitor the earthquake by immediate determination of the source focal mechanism which inferred from multiple ground seismic records.
However, it's hard to calculate the mechanism from the simple ...
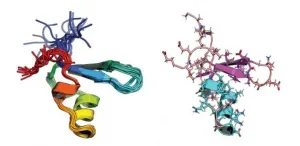
A combination of an array of atomic-level techniques has allowed researchers to show how changes in an environment-sensing protein enable bacteria to survive in different habitats, from the human gut to deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
"The study gives us unprecedented atomic-level insight into how bacteria adapt to changing conditions," says Stefan Arold, professor of bioscience at KAUST. "To obtain these insights, we pushed the limits of three different methods of investigation and combined their results into a unified picture."
The histone-like nucleoid-structuring (H-NS) protein allows bacteria to sense changes in their environment, such as changes in temperature and salinity. Previously, the team had shown how the intestinal pathogen Salmonella typhimurium ...