INFORMATION:
Researchers use AI to estimate focal mechanism parameters of earthquake
2021-03-22
(Press-News.org) The research team led by Prof. ZHANG Jie from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences made progress on real-time determination of earthquake focal mechanism through deep learning. The work was published in Nature Communications.
Since there are connections between characteristics of the rupture surface of the source fault and seismic wave radiated by the source, it's vital to monitor the earthquake by immediate determination of the source focal mechanism which inferred from multiple ground seismic records.
However, it's hard to calculate the mechanism from the simple records. The parameters about focal mechanism are either merely reported or reported after a few minutes even longer.
In this study, Prof. ZHANG's team applied a novel convolutional neural network to solve this problem effectively, paving the way for the acceleration of the investigation of details about earthquake.
The neural network, named as Focal Mechanism Network (FMNet), was first trained to estimate the source focal mechanism rapidly using full waveforms. Then, the neural network model was trained by comprehensive dataset, which modified the report system. After the earthquake, the real-dataset are introduced into the training system, the estimated parameters about the earthquake source can be calculated within one second with a minimum requirement of computing resources and memory storage.
A large number of practical data tests have proved the effectiveness of the method.
The results of this study are now being translated into practical functions and will soon be put into trial operation on the intelligent ground motion artificial intelligence earthquake monitoring system jointly developed by USTC and China Earthquake Administration.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Atomic techniques reveal the evolution of a bacterial protein
2021-03-22
A combination of an array of atomic-level techniques has allowed researchers to show how changes in an environment-sensing protein enable bacteria to survive in different habitats, from the human gut to deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
"The study gives us unprecedented atomic-level insight into how bacteria adapt to changing conditions," says Stefan Arold, professor of bioscience at KAUST. "To obtain these insights, we pushed the limits of three different methods of investigation and combined their results into a unified picture."
The histone-like nucleoid-structuring (H-NS) protein allows bacteria to sense changes in their environment, such as changes in temperature and salinity. Previously, the team had shown how the intestinal pathogen Salmonella typhimurium ...
Human fondness, faith in machines grows during pandemic
2021-03-22
People are not very nice to machines. The disdain goes beyond the slot machine that emptied your wallet, a dispenser that failed to deliver a Coke or a navigation system that took you on an unwanted detour.
Yet USC researchers report that people affected by COVID-19 are showing more goodwill -- to humans and to human-like autonomous machines.
"The new discovery here is that when people are distracted by something distressing, they treat machines socially like they would treat other people. We found greater faith in technology due to the pandemic and a closing of the gap between humans and machines," said Jonathan Gratch, senior author of the study and director for virtual humans research at the USC Institute for Creative Technologies.
The findings, which appeared recently ...
Bacteria may aid anti-cancer immune response
2021-03-22
Cancer immunotherapy may get a boost from an unexpected direction: bacteria residing within tumor cells. In a new study published in Nature, researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science and their collaborators have discovered that the immune system "sees" these bacteria and shown they can be harnessed to provoke an immune reaction against the tumor. The study may also help clarify the connection between immunotherapy and the gut microbiome, explaining the findings of previous research that the microbiome affects the success of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy treatments of the past decade or so have dramatically improved recovery rates from certain ...
United States ranks lowest in overall policies to help parents support children
2021-03-22
National work-family policies that give lower-income families more time together while allowing them paid time off are more effective for children's psychological health than cash transfers, according to a study of developed nations led by Baylor University.
In a study of about 200,000 children in 20 developed nations, the United States ranked lowest in overall policies aimed at helping parents support children.
The study, published in the journal Social Forces, supports the view of critics who say that the United States government does not do enough to mandate ...
Does 'harsh parenting' lead to smaller brains?
2021-03-22
Repeatedly getting angry, hitting, shaking or yelling at children is linked with smaller brain structures in adolescence, according to a new study published in Development and Psychology. It was conducted by Sabrina Suffren, PhD, at Université de Montréal and the CHU Sainte?Justine Research Centre in partnership with researchers from Stanford University.
The harsh parenting practices covered by the study are common and even considered socially acceptable by most people in Canada and around the world.
"The implications go beyond changes in the brain. I think what's ...
Lung cancer resistance: the key is glucose
2021-03-22
Cancers are not only made of tumor cells. In fact, as they grow, they develop an entire cellular ecosystem within and around them. This "tumor microenvironment" is made up of multiple cell types, including cells of the immune system, like T lymphocytes and neutrophils.
The tumor microenvironment has predictably drawn a lot of interest from cancer researchers, who are constantly searching for potential therapeutic targets. When it comes to the immune cells, most research focuses on T lymphocytes, which have become primary targets of cancer immunotherapy ...
Global biodiversity awareness tracked with Wikipedia page views
2021-03-22
Wikipedia page views could be used to monitor global awareness of biodiversity, proposes a research team from UCL, ZSL, and the RSPB.
Using their new metric, the research team found that awareness of biodiversity is marginally increasing, but the rate of change varies greatly between different groups of animals, as they report in a paper included in an upcoming special section of Conversation Biology.
Lead author, PhD student Joe Millard (UCL Centre for Biodiversity & Environment Research, UCL Biosciences and Institute of Zoology, ZSL) said: "As extinctions and biodiversity losses ramp up worldwide, largely due to climate change and other human actions, it's vital that ...
Motherless gorillas beat the odds
2021-03-22
A study by the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund shows that gorilla families come together to support young gorillas that lose their mothers.
The findings, published in the journal eLife, use the Fossey Fund's more than 50-year dataset to discover how maternal loss influences young gorillas' social relationships, survival and future reproduction. The study shows when young mountain gorillas lose their mothers, the rest of the group helps buffer the loss by strengthening their relationships with the orphans.
"Mothers are incredibly important for survival early in life--this is something that is shared across all mammals," said lead author Dr. Robin Morrison. "But in social mammals, like ourselves, mothers often continue to provide vital support up to adulthood and even beyond."
"In ...
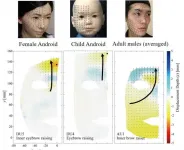
Expressing some doubts about android faces
2021-03-22
Osaka, Japan - Researchers from the Graduate School of Engineering and Symbiotic Intelligent Systems Research Center at Osaka University used motion capture cameras to compare the expressions of android and human faces. They found that the mechanical facial movements of the robots, especially in the upper regions, did not fully reproduce the curved flow lines seen in the faces of actual people. This research may lead to more lifelike and expressive artificial faces.
The field of robotics has advanced a great deal over the past decades. However, while current androids can appear very humanlike at first, their active facial expressions may still be unnatural and slightly unsettling to us. The exact reasons ...
Study estimates rising global burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer
2021-03-22
Although cancers that occur in the gallbladder or bile ducts are rare, their rates are increasing. A recent study provides details on the burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer (GBTC) across 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017. The findings are published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Determining GBTC estimates and trends in different global regions can help to guide research priorities and policies for prevention and treatment. With this in mind, a team of scientists examined publicly available information ...