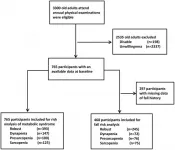
(Press-News.org) Oncotarget published "Predictors of immunotherapy benefit in Merkel cell carcinoma" which reported that the authors retrospectively analyzed electronic health records and next-generation sequencing data of 45 patients treated at our institution from 2013 to 2020 to understand clinical and genomic correlates of benefit from immunotherapy.
They reported that their cohort predominantly included individuals with stage III disease at primary disease diagnosis and individuals with stage IV disease at recurrent/metastatic disease diagnosis.
Less advanced stages at primary disease diagnosis and shorter disease-free interval between completion of initial treatment and recurrence were each associated with greater odds of response.
Single-nucleotide variants in ARID2 and NTRK1 were associated with response, while none of Merkel cell polyomavirus status, total mutational burden, ultraviolet mutational signatures, and copy-number alterations predicted outcomes.
Patients with shorter disease-free intervals may be particularly suitable immunotherapy candidates.
Dr. Glenn J. Hanna from CCR/NCI in Bethesda, MD as well as The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston Massachusetts said, "Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a relatively rare cancer, with roughly 400 cases per 100,000 persons each year in the United States."
Dr. Glenn J. Hanna from CCR/NCI in Bethesda, MD as well as The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston Massachusetts said, "Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a relatively rare cancer, with roughly 400 cases per 100,000 persons each year in the United States"
Before the age of immunotherapy, there was significant room for improvement in survival rates, with five-year survival of 60% overall and 14–21% among patients with distant disease.
Now, immune checkpoint inhibitors in the metastatic setting are associated with often durable response rates approaching 70% and three-year overall survival of up to 64%.
However, knowledge of predictors of response is lacking. Clinicians require a greater understanding of predictive markers for therapy selection, while researchers require an improved understanding of underlying mechanisms to inform drug development and trial design.
In the present study, the authors build on this prior approach by incorporating multivariable analysis techniques, studying patients over a longer follow-up time period, and by studying a homogeneous MCC population all treated with CPIs.
Additionally, they set out to include a greater number of CPI-treated patients in their work and statistically analyze the correlations of specific single nucleotide variants and copy number variations with response to CPIs.
The Hanna Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Output, "Our study points to several factors for clinicians to consider in the context of other clinical and pathologic findings when making treatment decisions. In particular, patients with ARID2 mutations, NTRK1 mutations, or shorter time to recurrence may be expected to have a higher likelihood of benefit from CPIs. These findings present potential areas for future basic scientific research related to molecular mechanisms. Future clinical study may explore the potential for Trk inhibition in combination or sequence with immunotherapies."
INFORMATION:
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27823
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/27823/text/
Correspondence to - Glenn J. Hanna - glenn_hanna@dfci.harvard.edu
Keywords -
cancer,
genomics,
immunotherapy,
Merkel cell carcinoma,
precision medicine
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a bi-weekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
18009220957x105
Oncotarget published "Cytogenetic and molecular landscape and its potential clinical significance in Hispanic CMML patients from Puerto Rico" which reported that one hundred and eleven Hispanic CMML patients from Puerto Rico were diagnosed in our institute from 2009 to 2018. Karyotypes were available in one hundred and seven patients.
Compared to previously published data, Hispanic CMML patients in this study had significantly lower rates of overall cytogenetic abnormalities and trisomy 8.
Among one hundred and eleven Hispanic CMML patients, 40-gene myeloid molecular profile tests were performed in fifty-six CMML patients.
Previous studies indicated that mutated ASXL1, DNMT3A, NRAS, RUNX1, and SETBP1 may associate with an unfavorable prognosis ...
Oncotarget published "Ibuprofen disrupts a WNK1/GSK3β/SRPK1 protein complex required for expression of tumor-related splicing variant RAC1B in colorectal cells" which reported that although the molecular mechanism behind the antitumor properties of NSAIDs has been largely attributed to inhibition of cyclooxygenases , several studies have shown that the chemopreventive properties of ibuprofen also involve multiple COX-independent effects.
One example is its ability to inhibit the alternative splicing event generating RAC1B, which is overexpressed in a specific subset ...
Aging-US published "Aging and rejuvenation - a modular epigenome model" which reported that the view of aging has evolved in parallel with the advances in biomedical sciences.
Long considered as an irreversible process where interventions were only aimed at slowing down its progression, breakthrough discoveries like animal cloning and cell reprogramming have deeply changed our understanding of postnatal development, giving rise to the emerging view that the epigenome is the driver of aging. The idea was significantly strengthened by the converging discovery that DNA methylation at specific CpG sites could be used as a highly accurate biomarker of age defined by an algorithm known as the Horvath clock (also published in Aging-US here).
It was at this point ...
Having the right tool for the job makes the job a lot easier, less expensive and faster. Chemical engineering researchers have now developed a virtual laboratory that can be used to determine the artificial intelligence (AI) tools best suited for addressing various chemical synthesis challenges in flow chemistry systems.
"Autonomous systems have tremendous potential for accelerating chemical R&D and manufacturing, but they are not in widespread use yet," says Milad Abolhasani, corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of chemical engineering at North Carolina State University. "These systems face two kinds of ...
Scientists from MIPT and ITMO University and their colleagues have studied the formation and growth of crystals from simple organic molecules into large associations. These experiments will help create capsules for targeted drug delivery to specific tissues in the human body. The scientific paper was published in the journal Crystal Growth & Design.
Melamine cyanurate consists of melamine, colourless crystals, and cyanuric acid, whose molecules associate in a similar way to DNA formation. The various studies associated with it could be useful ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - As psychedelics gain ground as a potential therapy for mental health disorders, there remains a pressing concern that patients in clinical trials may have adverse effects to the drugs.
New research identifies personality traits that have been associated with positive and negative experiences on psychedelics in previous studies, information that could help predict how future clinical trial participants will respond to the drugs.
The findings suggest that people more open to new experiences and willing to surrender to the unknown may be best positioned to have a positive experience on psychedelics, and individuals who tend to be preoccupied or apprehensive could be more likely to have a ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - As the COVID-19 pandemic took hold in 2020, the list of things people could not do grew increasingly long.
But while going to the office, attending live events and gathering with large groups of friends became difficult or impossible, other activities grew in popularity - including online learning.
Drawing on records from DataCamp, an online platform tailored toward programming skills, a research team at Cornell University and Arizona State University used U.S. states' staggered adoption of nonessential business closures (NBC) to estimate their effects on the demand for online learning. The gradual closure of businesses across the U.S. gave the researchers a way to make a case for the cause and effect of NBC on increased engagement with the DataCamp ...
Aging-US published "Impact of adiposity on muscle function and clinical events among elders with dynapenia, presarcopenia and sarcopenia: a community-based cross-sectional study" which reported that low muscle function determined unfavorable clinical outcome than low muscle mass; nevertheless, comparison of detrimental parameters among dynapenia, presarcopenia and sarcopenia was sparse.
The authors hypothesized that adiposity is implicated in low muscle function related adverse events.
Associations of different obesity parameters, metabolic syndrome and fall among the groups were analyzed.
Among 765 participants, ...
The COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium (CCC19) published new findings in the Annals of Oncology, showing heightened mortality and racial disparities for patients with cancer diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
After reviewing detailed information from almost 5,000 patients with active or past cancer and laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis, CCC19 study authors found associations among laboratory measures, clinical factors -- including older age, hematological malignancy and recent chemotherapy - and poor clinical outcomes. Of the patients in the study with COVID-19 ...
Aging-US published "Functional analysis of POLD1 p.ser605del variant: the aging phenotype of MDPL syndrome is associated with an impaired DNA repair capacity" which reported that Mandibular hypoplasia, Deafness and Progeroid features with concomitant Lipodystrophy define a rare systemic disorder, named MDPL Syndrome, due to almost always a de novo variant in POLD1 gene, encoding the DNA polymerase δ.
A decline of cell growth, cellular senescence and a blockage of proliferation in G0/G1 phase complete the aged cellular picture.
Moreover, the rate of telomere shortening was greater in pathological ...