(Press-News.org) It can be hard to resist lapsing into an exaggerated, singsong tone when you talk to a cute baby. And that's with good reason. Babies will pay more attention to baby talk than regular speech, regardless of which languages they're used to hearing, according to a study by UCLA's Language Acquisition Lab and 16 other labs around the globe.
The study found that babies who were exposed to two languages had a greater interest in infant-directed speech -- that is, an adult speaking baby talk -- than adult-directed speech. Research has already shown that monolingual babies prefer baby talk.
Some parents worry that teaching two languages could mean an infant won't learn to speak on time, but the new study shows bilingual babies are developmentally right on track. The peer-reviewed study, published today by Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science, found bilingual babies became interested in baby talk at the same age as those learning one language.
"Crucially for parents, we found that development of learning and attention is similar in infants, whether they're learning one or two languages," said Megha Sundara, a UCLA linguistics professor and director of the Language Acquisition Lab. "And, of course, learning a language earlier helps you learn it better, so bilingualism is a win-win."
In the study, which took place at 17 labs on four continents, researchers observed 333 bilingual babies and 384 monolingual babies, ranging in age from 6 to 9 months and 12 to 15 months. UCLA's lab was the only one to provide data on bilingual babies who grew up hearing both English and Spanish. Sundara and Victoria Mateu, a UCLA assistant professor of Spanish and Portuguese, observed babies who were 12 to 15 months old.
Each baby would sit on a parent's lap while recordings of an English-speaking mother, using either infant-directed speech or adult-directed speech, played from speakers on the left or the right. Computer tracking measured how long each baby looked in the direction of each sound.
"The longer they looked, the stronger their preference," Mateu said. "Babies tend to pay more attention to the exaggerated sounds of infant-directed speech."
Infants' interest in English baby talk was very fine-tuned, the study noted. Bilingual parents indicated the percent of time English was spoken at home compared to Spanish. The more English the bilingual babies had been exposed to, the stronger their preference for infant-directed speech compared to adult-directed speech. However, even babies with no exposure to English preferred the English baby talk to the grown-up talk, Mateu said.
Baby talk is found across most languages and cultures, but English has one of the most exaggerated forms, Sundara said.
"Baby talk has a slower rate of speech across all languages, with more variable pitch, and it's more animated and happy," she said. "It varies mainly in how exaggerated it is."
Led by Krista Byers-Heinlein, a psychology professor at Concordia University in Montreal, the study involved labs in the United States, Canada, Europe, Australia and Singapore. The study's global reach strengthened the results, Sundara said.
"When you do language research, you want to know that the results aren't just some quirk of the language you're studying," she said.
According to the study, 6- to 9-month-old babies who had mothers with higher levels of education preferred baby talk more than babies whose mothers had less education.
"We suspect that perhaps the mothers with higher education levels spoke more to the babies and used infant-directed speech more often," Mateu said.
This study is one of the first published by the ManyBabies Consortium, a multi-lab group of researchers. Byers-Heinlein believes the unusual international, multilingual collaboration creates a model for future studies that include a similar breadth of languages and cultures.
"We can really make progress in understanding bilingualism, and especially the variability of bilingualism, thanks to our access to all these different communities," she said.
As the research continues, parents can babble to their babies in one language or two, and rest easy knowing they won't cause any confusion.
INFORMATION:
In Slovakia, in counties subject to two rounds of rapid antigen testing for SARS-CoV-2 where those who tested positive then isolated, the approach helped decrease the prevalence of positive tests by more than 50% in a week - all while primary schools and workplaces remained open. "While it was impossible to disentangle the precise contribution of control measures and mass testing," the authors said, mass testing is likely to have had a substantial effect, their modeling showed. Applying mass testing may provide a valuable tool in future containment of SARS-CoV-2 elsewhere, they say. ...
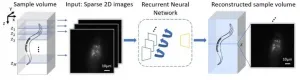
Rapid 3D microscopic imaging of fluorescent samples has gained increasing importance in numerous applications in physical and biomedical sciences. Given the limited axial range that a single 2D image can provide, 3D fluorescence imaging often requires time-consuming mechanical scanning of samples using a dense sampling grid. In addition to being slow and tedious, this approach also introduces additional light exposure on the sample, which might be toxic and cause unwanted damage, such as photo-bleaching.
By devising a new recurrent neural network, UCLA researchers have demonstrated a deep learning-enabled volumetric microscopy framework for 3D imaging of fluorescent samples. This new method only requires a few 2D images of the sample to be ...
NIMS and the Tokyo Institute of Technology have jointly discovered that the chemical compound Ca3SiO is a direct transition semiconductor, making it a potentially promising infrared LED and infrared detector component. This compound--composed of calcium, silicon and oxygen--is cheap to produce and non-toxic. Many of the existing infrared semiconductors contain toxic chemical elements, such as cadmium and tellurium. Ca3SiO may be used to develop less expensive and safer near-infrared semiconductors.
Infrared wavelengths have been used for many purposes, including optical fiber communications, photovoltaic power generation and night vision devices. Existing semiconductors ...
Imperial physicists are part of a team that has announced 'intriguing' results that potentially cannot be explained by our current laws of nature.
The LHCb Collaboration at CERN has found particles not behaving in the way they should according to the guiding theory of particle physics - the Standard Model.
The Standard Model of particle physics predicts that particles called beauty quarks, which are measured in the LHCb experiment, should decay into either muons or electrons in equal measure. However, the new result suggests that this may not be happening, which could point to the existence of new particles or interactions not explained by the Standard Model.
Physicists from Imperial College ...
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, March 23, 2021 - Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) researchers have found that the Pfizer Coronavirus vaccine is moderately less effective against the South African variant, but still neutralizes the British variant and the original SARS-CoV-2 strain.
Their research was just published in the prestigious journal Cell Host and Microbe.
"Our findings show that future variants could necessitate a modified vaccine as the virus mutates to increase its infectivity," says principal investigator Dr. Ran Taube of the Shraga Segal Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Genetics in the Faculty of Health Sciences.
The BGU scientists evaluated the vaccine effectiveness ...
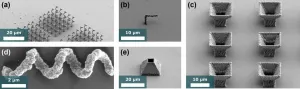
Metallic microstructures are the key components in almost every current or emerging technology. For example, with the next wireless communication standard (6G) being established, the need for advanced components and especially antennas is unbroken. The drive to yet higher frequencies and deeper integration goes hand in hand with miniaturization and fabrication technologies with on-chip capability. Via direct laser writing - an additive manufacturing technology that offers sub-micron precision and feature sizes - highly sophisticated and integrated components come into reach. One big advantage of direct laser writing is that it is not limited to the fabrication of planar structures but enables almost arbitrary 3D microstructures. This ...
A study has found that a new 'care bundle' can reduce the incidence of facial pressure injuries in frontline COVID-19 healthcare workers caused by the prolonged wearing of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences Skin Wounds and Trauma (SWaT) Research Centre, is published in the current edition of the Journal of Wound Care.
The research took place over a two-month period amongst healthcare workers in a large acute hospital in Ireland. In the study, approximately 300 frontline staff were provided with a care ...
Glioma is a fatal neurological disorder that has limited interventional treatment, despite extensive research over the past several decades. A research team led by Dr. Gong Chen, a former professor at Penn State University and now leading a brain repair center at Jinan University in China, has developed a novel gene therapy to reprogram glioma cells into functional neurons, shedding new light on glioma treatment. The work has been published in Cancer Biology & Medicine on March 22, 2021
Glioma is a common malignant cancer growing in the central nervous system. For patients with a type of severe glioma ...
Scientists have developed a pioneering new procedure that will help diagnose a potentially lethal fungal lung disease with greater speed and accuracy, and with less distress to the patient.
A team of international scientists, including Professor Chris Thornton from the University of Exeter, has created a new diagnostic procedure for pulmonary aspergillosis.
Aspergillus is a common mold readily found worldwide in a variety of environments, such as soil and decaying plant material, and can easily be inhaled as air-borne spores in everyday life.
While people with ...
Serious complications due to blood clots, such as heart attacks and strokes, that are experienced by some COVID-19 survivors may be caused by a lingering immune response in the blood vessels after recovery, suggests a study published today in eLife.
The findings may help explain why some COVID-19 survivors, so-called 'long-haulers', report lasting COVID-19 symptoms or why some experience strokes or heart attacks weeks or months after recovery. They may also suggest potential strategies to help prevent these complications.
"During the initial stages of infection, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that ...