Breakthrough in developing new diagnostic procedure for pulmonary aspergillosis
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) Scientists have developed a pioneering new procedure that will help diagnose a potentially lethal fungal lung disease with greater speed and accuracy, and with less distress to the patient.
A team of international scientists, including Professor Chris Thornton from the University of Exeter, has created a new diagnostic procedure for pulmonary aspergillosis.
Aspergillus is a common mold readily found worldwide in a variety of environments, such as soil and decaying plant material, and can easily be inhaled as air-borne spores in everyday life.
While people with healthy immune systems are able to combat these spores when inhaled, those who have a weakened immune system from illness or medications have fewer infection-fighting cells. This allows Aspergillus to take hold, invading the lungs and, in the most serious cases, other parts of the body.
For COVID-19 patients admitted in intensive care units in particular, the infection has become a significant problem - an estimated 30 percent of them develop COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis.
The diagnosis of the infection is extremely difficult, and current diagnostic procedures are unpleasant for the already weakened patients. Medical professionals rely on highly invasive techniques such as lung biopsies or broncho-alveolar lavages - where fluid is injected directly into the lungs through the nose or mouth.
Now, the team of researchers have conducted a study, using a mouse model of infection, and utilizing a patent-pending Aspergillus-specific monoclonal antibody, JF5, developed by ground-breaking University of Exeter spin-out company, ISCA Diagnostics.
The research shows that the humanised JF5 antibody can specifically and rapidly recognize the infection in the lungs of infected animals without the need for the invasive procedures.
Using a radiotracer injected only intravenously, advanced molecular imaging techniques developed at the University of Tübingen were able to provide a rapid and specific diagnosis of the disease while allowing for precise monitoring of therapy.
The imaging results were then be complemented by 3D microscopy performed at the University of Duisburg-Essen, which underlined the accuracy of the developed imaging method with a precise (quantitative) evaluation of the infection.
This innovative dual approach proved that all sites of infection could be accurately uncovered, a crucial step to not only provide an estimate of the severity of the infection, but also as a first step in monitoring the success of its treatment.
The researchers demonstrated the potential of therapy monitoring using molecular imaging during administration of the front-line antifungal drug Voriconazole.
Professor Thornton, an expert in Fungal Immunology at the University of Exeter and co-author of the published work said: "This highly innovative and ground-breaking diagnostic technology is a step-change in the way we diagnose this devastating disease of immunocompromised patients, eliminating our current reliance on unpleasant invasive procedures."
"We strongly expect," says Dr. Nicolas Beziere of the Department of Preclinical Imaging and Radiopharmacy at Tübingen University Hospital and senior author of the study, "that the performance of the newly developed radiotracer will be similar in humans and hope that future clinical trials will show a highly positive impact on survivability with a far lower risk and higher comfort for the patient."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-23
Serious complications due to blood clots, such as heart attacks and strokes, that are experienced by some COVID-19 survivors may be caused by a lingering immune response in the blood vessels after recovery, suggests a study published today in eLife.
The findings may help explain why some COVID-19 survivors, so-called 'long-haulers', report lasting COVID-19 symptoms or why some experience strokes or heart attacks weeks or months after recovery. They may also suggest potential strategies to help prevent these complications.
"During the initial stages of infection, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that ...
2021-03-23
The last glacial period, which lasted about 100,000 years, reached its peak about 20,000 to 25,000 years ago: Huge ice sheets covered large parts of northern Europe, North America and northern Asia, some of them kilometres thick, and the sea level was about 125 metres below today's level. The Earth looked very different during this so-called Last Glacial Maximum than it does today. This relatively recent period of the last maximum ice extent has long been of interest to researchers and subject to intensive research. What actually led to this extreme glacier growth, however, ...
2021-03-23
A study of young men with COVID-19 has revealed a genetic variant linked to disease severity.
The discovery, published recently in eLife, means that men with severe disease could be genetically screened to identify who has the variant and may benefit from interferon treatment.
For most people, COVID-19, the disease caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2, causes only mild or no symptoms. However, severe cases can rapidly progress towards respiratory distress syndrome.
"Although older age and the presence of long-term conditions such as cardiovascular disease or diabetes are known risk factors, they alone do not fully explain differences in severity," explains first author ...
2021-03-23
New research from Copenhagen Business School finds sexual harassment in the workplace severely hurts company value.
"Sexual harassment has serious consequences for the victim. But it is also something managers and investors should be interested in for purely financial reasons, as it can wipe off enormous amounts of market value in a matter of days," says Associate Professor Ulf Nielsson from the Department of Finance at Copenhagen Business School.
The research found that the stock market value of a listed company drops by 1.5% following sexual ...
2021-03-23
When so-called beauty quarks are produced during the collision of high-energy proton beams in the Large Hadron Collider - the particle accelerator at CERN in Geneva - they decay almost immediately on the spot. Researchers of the Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment (LHCb) reconstruct the properties of the composite particles based on their decay products. According to the established laws of particle physics - the so-called Standard Model - it is expected that beauty quarks decay with the same probability into a final state with electrons and muons, the ...
2021-03-23
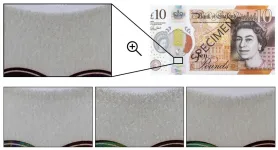
In 2016 the Bank of England introduced plastic (polymer) banknotes, alongside 50 other countries that use polymer banknotes
Counterfeit polymer banknotes on the streets have increased over the last few years, therefore the need to prevent and identify counterfeit banknotes has increased
Using a technique called Polymer Substrate Fingerprinting, researchers from the University of Warwick are able to identify each banknote's own fingerprint, which is unique and unclonable
Since the introduction of plastic (polymer) banknotes in 2016, the number of counterfeit notes on the streets has increased, however, researchers from Department of Computer Science at the University of Warwick have developed a novel technique called Polymer Substrate Fingerprinting, which identifies every ...
2021-03-23
Maps generally indicate elevation in meters above sea level. But sea level is not the same everywhere. A group of experts headed by the Technical University of Munich (TUM), has developed an International Height Reference System (IHRS) that will unify geodetic measurements worldwide.
How high is Mount Everest? 8848 meters? 8844 meters? Or 8850 meters? For years, China and Nepal could not agree. In 2019, Nepal sent a team of geodesists to measure the world's highest mountain. A year later a team from China climbed the peak. Last December the ...
2021-03-23
A gene not previously linked to cancer has been shown to play a key role in the spread of certain cancers to the lungs, new research from scientists at the Wellcome Sanger Institute has shown. The team found that when the gene LRRN4CL was over-expressed in mice, the skin cancer melanoma was more likely to metastasise to the lungs.
The study, published today (23 March 2021) in Communications Biology, also confirmed that over-expression of LRRN4CL was linked to metastasis of colon, breast and bladder cancers to the lung.
Several factors make LRRN4CL an attractive drug target. It encodes a protein found on the surface of cancer cells, making it easier to target with drugs. And because it is expressed at low levels elsewhere in the body, it may ...
2021-03-23
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 22, 2021 - The fear, anxiety and stress associated with the COVID-19 pandemic has taken a toll on mental health. But a new study suggests these symptoms may be alleviated through safe and convenient online mindfulness practices.
The study, which was recently published in the journal Global Advances in Health and Medicine, shows that an online mindfulness intervention may reduce momentary stress, anxiety and COVID-19 concern.
At the onset of the pandemic, Rebecca Erwin Wells, M.D., M.P.H., associate professor of neurology at Wake Forest School of Medicine, part of Wake Forest Baptist Health, and principal investigator ...
2021-03-23
Fatigue, depression, sleep disorders, burnout: the number of cases where employees are unable to work for mental health-related reasons has increased dramatically in recent years. Professor Sascha Alavi, Chair at the Sales Management Department (SMD), has long been keeping a critical eye on this development in society, especially in the corporate world. Together with his former PhD student Dr. Kim Linsenmayer and Professor Johannes Habel from the University of Houston, Alavi has now demonstrated in the Journal of Marketing the negative effects that pressure in the form of performance-based remuneration schemes can have on health. Rubin, the science magazine from RUB, reports on this.
In ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Breakthrough in developing new diagnostic procedure for pulmonary aspergillosis