New results challenge leading theory in physics
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) When so-called beauty quarks are produced during the collision of high-energy proton beams in the Large Hadron Collider - the particle accelerator at CERN in Geneva - they decay almost immediately on the spot. Researchers of the Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment (LHCb) reconstruct the properties of the composite particles based on their decay products. According to the established laws of particle physics - the so-called Standard Model - it is expected that beauty quarks decay with the same probability into a final state with electrons and muons, the much heavier siblings of electrons. However, since 2014 measurements at the LHC suggest that this "lepton universality" may be violated in some decays. In these decays, the production ratio of the two types of particles is different from the theoretical prediction of one.
Decay measurements appear inconsistent with particle physics prediction
Members of the group led by Nicola Serra, professor at the Department of Physics at the University of Zurich (UZH), are part of the small research team that worked directly on the measurement. In the newest LHCb analysis, the ratio of decay products containing electrons and muons was determined with much better precision compared to previous measurements, using all the data collected by the LHCb detector so far. The result indicates evidence for a deviation from the ratio of one - and hence a breaking of the "lepton universality" in beauty quark decays with a probability of around 0,1% that the data is compatible with the theoretical prediction. If confirmed, this violation would imply physics beyond the Standard Model such as a new fundamental force in addition to the four fundamental ones: gravity, electromagnetism, weak nuclear interactions responsible for radioactivity and strong nuclear forces that hold matter together.
Too early for a final conclusion, but great potential with upcoming measurements
"The Standard Model has reigned supreme for decades. Our job as experimentalists is to test it more and more precisely and see if it can survive the increased scrutiny", says UZH senior researcher Patrick Owen, who played a leading role in the analysis. In particle physics, observations become true discoveries if the probability of error, taking into account all known errors, is less than one in three million or 0,00003%, which adds caution to researcher's excitement. «So, it is too early to draw a final conclusion. However, this deviation agrees with a pattern of anomalies which have manifested themselves over the last decade», says Nicola Serra. «Fortunately, the LHCb collaboration is well placed to clarify the potential existence of new physics effects in these decays. We just need many more related measurements in the future», he concludes.
The result was presented today for the first time at the Moriond conference on electroweak interactions and unified theories, and at an online seminar at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research in Geneva.
The Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment (LHCb)
The LHCb experiment is one of the four large experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN in Geneva. It is designed to study decays of particles containing a beauty quark, the quark with the highest mass forming bound states. The resulting precision measurements of matter-antimatter differences and rare decays of particles containing a beauty quark allow sensitive tests of the Standard Model of particle physics.
Research groups from the UZH and the EPFL are members of the LHCb collaboration since 1999. They have made important contributions to the design and construction of the LHCb detector and are involved in its upgrades. These will be key to collect the needed statistics to find out whether the anomalies observed in beauty quark decays are indeed real. Since the start of data taking in 2009 the UZH group of Nicola Serra has played a leading role in measurements of decays of particles containing beauty quarks.
INFORMATION:
The UZH team also collaborates closely with two UZH groups working on the theoretical description of these phenomena. Professor Gino Isidori is working on the theoretical interpretation of these decays, dealing with open questions about the nature of basic constituents of matter and their fundamental interactions. Andreas Crivellin, SNSF professor at UZH and based at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) is studying possible implications of these results for other experiments. Together, the UZH research teams fruitfully combine theory and experiment in current research in particle physics.
http://lhcb.web.cern.ch/
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-23
In 2016 the Bank of England introduced plastic (polymer) banknotes, alongside 50 other countries that use polymer banknotes
Counterfeit polymer banknotes on the streets have increased over the last few years, therefore the need to prevent and identify counterfeit banknotes has increased
Using a technique called Polymer Substrate Fingerprinting, researchers from the University of Warwick are able to identify each banknote's own fingerprint, which is unique and unclonable
Since the introduction of plastic (polymer) banknotes in 2016, the number of counterfeit notes on the streets has increased, however, researchers from Department of Computer Science at the University of Warwick have developed a novel technique called Polymer Substrate Fingerprinting, which identifies every ...
2021-03-23
Maps generally indicate elevation in meters above sea level. But sea level is not the same everywhere. A group of experts headed by the Technical University of Munich (TUM), has developed an International Height Reference System (IHRS) that will unify geodetic measurements worldwide.
How high is Mount Everest? 8848 meters? 8844 meters? Or 8850 meters? For years, China and Nepal could not agree. In 2019, Nepal sent a team of geodesists to measure the world's highest mountain. A year later a team from China climbed the peak. Last December the ...
2021-03-23
A gene not previously linked to cancer has been shown to play a key role in the spread of certain cancers to the lungs, new research from scientists at the Wellcome Sanger Institute has shown. The team found that when the gene LRRN4CL was over-expressed in mice, the skin cancer melanoma was more likely to metastasise to the lungs.
The study, published today (23 March 2021) in Communications Biology, also confirmed that over-expression of LRRN4CL was linked to metastasis of colon, breast and bladder cancers to the lung.
Several factors make LRRN4CL an attractive drug target. It encodes a protein found on the surface of cancer cells, making it easier to target with drugs. And because it is expressed at low levels elsewhere in the body, it may ...
2021-03-23
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 22, 2021 - The fear, anxiety and stress associated with the COVID-19 pandemic has taken a toll on mental health. But a new study suggests these symptoms may be alleviated through safe and convenient online mindfulness practices.
The study, which was recently published in the journal Global Advances in Health and Medicine, shows that an online mindfulness intervention may reduce momentary stress, anxiety and COVID-19 concern.
At the onset of the pandemic, Rebecca Erwin Wells, M.D., M.P.H., associate professor of neurology at Wake Forest School of Medicine, part of Wake Forest Baptist Health, and principal investigator ...
2021-03-23
Fatigue, depression, sleep disorders, burnout: the number of cases where employees are unable to work for mental health-related reasons has increased dramatically in recent years. Professor Sascha Alavi, Chair at the Sales Management Department (SMD), has long been keeping a critical eye on this development in society, especially in the corporate world. Together with his former PhD student Dr. Kim Linsenmayer and Professor Johannes Habel from the University of Houston, Alavi has now demonstrated in the Journal of Marketing the negative effects that pressure in the form of performance-based remuneration schemes can have on health. Rubin, the science magazine from RUB, reports on this.
In ...
2021-03-23
Knee osteoarthritis is a painful condition that affects over 14 million U.S. adults, many of whom have extreme obesity, defined by body mass index (BMI) greater than 40kg/m2. Total knee replacement (TKR) is often recommended to treat advanced knee osteoarthritis, but surgeons may be hesitant to operate on patients with extreme obesity due to concerns about the increased risks of tissue infection, poor wound healing and higher risk of implant failure. Using an established, validated and widely published computer simulation called the Osteoarthritis Policy (OAPol) Model, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital, together with collaborators from Yale and Boston University ...
2021-03-23
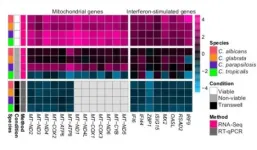
Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by a yeast called Candida. It is a serious global health problem and it can be vaginal, oral or systemic. The latter is the most severe form of infection, as it can lead to death, but vaginal candidiasis infection is the most prevalent, affecting 80% of women at some point in their lives.
Scientists led by Dr. Toni Gabaldón, ICREA researcher and group leader at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC), in collaboration with Dr. Bernhard Hube's group at the Hans Knoell Institute and the University of Jena in Germany, have described the various mechanisms used by the fungus Candida to infect the ...
2021-03-23
LA JOLLA, CA--A discovery involving multiple teams from across Scripps Research has revealed a powerful new approach for treating diabetic foot ulcers, which affect millions of people in the US and often lead to serious complications.
By targeting a gene that controls tissue growth and regeneration, the scientists were able to boost cell division at the site of injury and repair chronic wounds quickly. The new research appears in Nature Chemical Biology.
Given the growing prevalence of diabetes and limited options for treating foot ulcers--which can lead to amputation, in severe cases--it's clear that more effective treatments are needed, says chemist Michael ...
2021-03-23
Metal-insulator transition (MIT) driven by many-body interactions is an important phenomenon in condensed matter physics. Exotic phases always emerge around the metal-insulator transition points where quantum fluctuations arise from a competition among spin, charge, orbital, and lattice degrees of freedom. Two-dimensional (2D) materials are a large class of materials. Their simple structure, low dimensionality, and highly tunable carrier density make them an ideal platform for exploring exotic phases. However, the many-body interactions are normally weak in most 2D materials, hence, the correlation-related phenomena ...
2021-03-23
Call it the evolutionary march of the penguins.
More than 50 million years ago, the lovable tuxedoed birds began leaving their avian relatives at the shoreline by waddling to the water's edge and taking a dive in the pursuit of seafood.
Webbed feet, flipper-like wings and unique feathers all helped penguins adapt to their underwater excursions. But new research from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln has shown that the evolution of diving is also in their blood, which optimized its capture and release of oxygen to ensure that penguins wouldn't waste their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New results challenge leading theory in physics