(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 22, 2021 - The fear, anxiety and stress associated with the COVID-19 pandemic has taken a toll on mental health. But a new study suggests these symptoms may be alleviated through safe and convenient online mindfulness practices.
The study, which was recently published in the journal Global Advances in Health and Medicine, shows that an online mindfulness intervention may reduce momentary stress, anxiety and COVID-19 concern.
At the onset of the pandemic, Rebecca Erwin Wells, M.D., M.P.H., associate professor of neurology at Wake Forest School of Medicine, part of Wake Forest Baptist Health, and principal investigator for this study, recognized the tremendous impact of this pandemic on emotional health and wanted to evaluate how a safe, online mindfulness meditation strategy might help.
In creating this study, Wells was inspired by Mindfulness for Milan, a program created by co-author Licia Grazzi, M.D., an Italian physician who led free daily mindfulness sessions to help the public manage stress and anxiety during lockdown.
Mindfulness means maintaining a moment-by-moment, non-judgmental awareness of thoughts, feelings, bodily sensations and surrounding environment.
"We are all born with the capacity for mindfulness," said Wells. "It can help reduce stress and anxiety, and mindfulness meditation practice can help enhance this ability."
There were 233 participants from across the world in this non-randomized clinical trial, which included a pre-session survey, a single 15-minute online mindfulness meditation session and a post-session survey. The study ran from March to August 2020. Pre- and post-session surveys evaluated momentary stress, anxiety and COVID-19 concern. Most of the participants (63%) had never practiced mindfulness before, and 89% of participants said the session was helpful, and that the online platform was effective for practicing mindfulness. 76% of participants reported decreased anxiety, 80% reported decreased stress, and 55% had decreased COVID-19 concern. Of note, 21% of participants were retired, suggesting that age did not prevent accessibility.
Participants were also surveyed on how they were helping others during the pandemic. Responses varied with common themes including following public health guidelines, conducting acts of service and connection such as reaching out to elderly neighbors, and self-care activities such as staying positive and calm.
Investigators also assessed online mindfulness resources across time during the pandemic and found a 52% increase in search results of "Mindfulness + COVID" from May to August 2020. "People are searching for ways to help target the stress and anxiety of the pandemic," Wells said. "Mindfulness teachers and programs have expanded offerings, eliminated fees, and converted offerings to online to meet this huge need."
According to Wells, the study shows that a virtual platform can be effective for practicing mindfulness.
"We found that online mindfulness interventions may improve psychological health at a time of uncertainty. We were also encouraged by the survey responses, which showed a sense of connectedness and a desire to help others," Wells said. "Helping others during the pandemic demonstrates the beautiful capacity of the human spirit to find positivity despite the extraordinary negative circumstances."
Wells said that additional research is needed to evaluate the pandemic's effects on post-traumatic growth, the positive psychological change experienced following a challenging life circumstance.
INFORMATION:
Support for the study was provided by the NIH National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (Grant No. K23AT008406).
Fatigue, depression, sleep disorders, burnout: the number of cases where employees are unable to work for mental health-related reasons has increased dramatically in recent years. Professor Sascha Alavi, Chair at the Sales Management Department (SMD), has long been keeping a critical eye on this development in society, especially in the corporate world. Together with his former PhD student Dr. Kim Linsenmayer and Professor Johannes Habel from the University of Houston, Alavi has now demonstrated in the Journal of Marketing the negative effects that pressure in the form of performance-based remuneration schemes can have on health. Rubin, the science magazine from RUB, reports on this.
In ...
Knee osteoarthritis is a painful condition that affects over 14 million U.S. adults, many of whom have extreme obesity, defined by body mass index (BMI) greater than 40kg/m2. Total knee replacement (TKR) is often recommended to treat advanced knee osteoarthritis, but surgeons may be hesitant to operate on patients with extreme obesity due to concerns about the increased risks of tissue infection, poor wound healing and higher risk of implant failure. Using an established, validated and widely published computer simulation called the Osteoarthritis Policy (OAPol) Model, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital, together with collaborators from Yale and Boston University ...
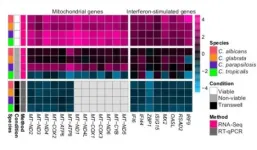
Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by a yeast called Candida. It is a serious global health problem and it can be vaginal, oral or systemic. The latter is the most severe form of infection, as it can lead to death, but vaginal candidiasis infection is the most prevalent, affecting 80% of women at some point in their lives.
Scientists led by Dr. Toni Gabaldón, ICREA researcher and group leader at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC), in collaboration with Dr. Bernhard Hube's group at the Hans Knoell Institute and the University of Jena in Germany, have described the various mechanisms used by the fungus Candida to infect the ...
LA JOLLA, CA--A discovery involving multiple teams from across Scripps Research has revealed a powerful new approach for treating diabetic foot ulcers, which affect millions of people in the US and often lead to serious complications.
By targeting a gene that controls tissue growth and regeneration, the scientists were able to boost cell division at the site of injury and repair chronic wounds quickly. The new research appears in Nature Chemical Biology.
Given the growing prevalence of diabetes and limited options for treating foot ulcers--which can lead to amputation, in severe cases--it's clear that more effective treatments are needed, says chemist Michael ...
Metal-insulator transition (MIT) driven by many-body interactions is an important phenomenon in condensed matter physics. Exotic phases always emerge around the metal-insulator transition points where quantum fluctuations arise from a competition among spin, charge, orbital, and lattice degrees of freedom. Two-dimensional (2D) materials are a large class of materials. Their simple structure, low dimensionality, and highly tunable carrier density make them an ideal platform for exploring exotic phases. However, the many-body interactions are normally weak in most 2D materials, hence, the correlation-related phenomena ...
Call it the evolutionary march of the penguins.
More than 50 million years ago, the lovable tuxedoed birds began leaving their avian relatives at the shoreline by waddling to the water's edge and taking a dive in the pursuit of seafood.
Webbed feet, flipper-like wings and unique feathers all helped penguins adapt to their underwater excursions. But new research from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln has shown that the evolution of diving is also in their blood, which optimized its capture and release of oxygen to ensure that penguins wouldn't waste their ...
LA JOLLA, CA--An analysis of thousands of genomes from people with and without the rare eye disease known as MacTel has turned up more than a dozen gene variants that are likely causing the condition to develop and worsen for a significant share of patients.
The discovery, by a team of scientists from Scripps Research and the Lowy Medical Research Institute, in collaboration with Columbia University in New York and UC San Diego, provides a new avenue to pursue for diagnosis and treatment. It also sheds light on fundamental aspects of metabolism in the retina, a tissue with one of the highest energy demands in the human body. Findings appear today in the journal Nature Metabolism.
"It's exciting to uncover new answers to the ...
The cost of the rechargeable lithium-ion batteries used for phones, laptops, and cars has fallen dramatically over the last three decades, and has been a major driver of the rapid growth of those technologies. But attempting to quantify that cost decline has produced ambiguous and conflicting results that have hampered attempts to project the technology's future or devise useful policies and research priorities.
Now, MIT researchers have carried out an exhaustive analysis of the studies that have looked at the decline in the prices these batteries, which are the dominant rechargeable ...
Stuttgart - A team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) in Germany, from Seoul National University in Korea and from the Harvard University in the US, successfully developed a predictive model and closed-loop controller of a soft robotic fish, designed to actively adjust its undulation amplitude to changing flow conditions and other external disturbances. Their work "Modeling and Control of a Soft Robotic Fish with Integrated Soft Sensing" was published in Wiley's Advanced Intelligent Systems journal, in a special issue on "Energy Storage and Delivery in Robotic Systems".
Each ...
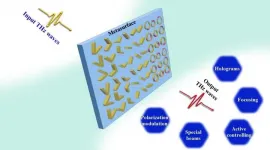
THz waves have a plethora of applications ranging from biomedical and medical examinations, imaging, environment monitoring, to wireless communications, because of the abundant spectral information, low photon energy, strong penetrability, and shorter wavelength. THz waves with technological advances not only determined by the high-efficiency sources and detectors but also decided by a variety of the high-quality THz components/functional devices. However, traditional THz devices should be thick enough to realize the desired wave-manipulating functions, hindering the development of THz integrated systems and applications. Although metamaterials have been ...