Why are young adults having less casual sex?
Study finds alcohol, video games and living with parents affects young men's casual sex behavior
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) Casual sex is on the decline for both young men and women, according to a Rutgers University-New Brunswick study that found less alcohol consumption among both genders is a major reason while playing video games and living at home with parents are another--but only for men.
The study, published in the journal Socius, found that between 2007 and 2017, the percentage of 18-to 23-year-old men who had casual sex in the past month dropped from 38 percent to 24 percent. The percentage dropped from 31 percent to 22 percent for young women of the same age.
The most important factor driving the decline among young men is the decrease in drinking, which alone explains more than 33 percent of the drop. The increase in computer video gaming explains about 25 percent of the change in sexual behavior among young men, while the increase in living with parents explains a little more than 10 percent. No other factor explained a significant portion of the decline.
"The recent cohorts of young people adopt adult roles later in their lives and depend on their parents for longer periods," said the study's co-author Lei Lei, an assistant professor of sociology at Rutgers. "The declining engagement in casual sex among this age group could be another sign of delayed transition into adulthood."
For young women, about 25 percent is attributable to a decline in drinking, which was the only factor that explained a significant portion of the decline. Increased internet usage among young women suppressed what would have been a larger 11 percent decline in casual sex. The study said that while both young women and men play computer games more frequently now than in the past, gaming inhibits only young men's casual sexual activity.
Researchers say the odds that young men who live with their parents engage in casual sex are only 63 percent of those who live independently. The odds that young men who play computer games daily have casual sex are less than half the odds for those who never game. And the odds that young men who report drinking daily have casual sex are about 5.5 times the odds for those who don't drink.
"The new generation of young adults became more individualistic and less social in real life, but more involved in social media and online gaming networks," said Lei. "The changes in how young people socialize affect their opportunity to have casual sex, which often serves as a trial or rehearsal for long-term romantic relationships."
Trends in young adults' financial insecurity, including their student debt loan, do not appear to underlie their change in casual sexual activity. Nor does an increase in time spent watching television.
Researchers analyzed survey data from the 2007-2017 Panel Study of Income Dynamics Transition to Adulthood Supplement, which interviewed about 2,000 young adults ages 18 to 23 and focused on sexual activity outside of committed relationships. They examined whether changes in young adults' economic status, living arrangement, technology use and drinking behavior helped explain the decline in casual sex.
INFORMATION:
The study's authors included a researcher from the University of Albany.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-23
The vast reservoir of carbon that is stored in soils probably is more sensitive to destabilization from climate change than has previously been assumed, according to a new study by researchers at WHOI and other institutions.
The study found that the biospheric carbon turnover within river basins is vulnerable to future temperature and precipitation perturbations from a changing climate.
Although many earlier, and fairly localized, studies have hinted at soil organic carbon sensitivity to climate change, the new research sampled 36 rivers from around the ...
2021-03-23
As the pandemic's economic effects drive more people to enroll in Medicaid as safety-net health insurance, a new study suggests that the program's dental coverage can improve their oral health in ways that help them seek a new job or do better at the one they have.
The study focuses on the impact of dental coverage offered through Michigan's Medicaid expansion, called the Healthy Michigan Plan. The researchers, from the University of Michigan, used a survey and interviews to assess the impact of this coverage on the health and lives of low-income people who enrolled.
In all, 60% of the 4,090 enrollees surveyed for the new study had visited a dentist at least once since enrolling ...
2021-03-23
Daily national surveys by Carnegie Mellon University show that while COVID-19 vaccine uptake has increased, the proportion of vaccine-hesitant adults has remained unchanged. The concerns about a side effect remain high, especially among females, Black adults and those with an eligible health condition.
The Delphi Research Group at CMU in partnership with Facebook released its latest survey findings. The analyses show that vaccine hesitancy persists and point to potential tactics to combat it.
"Prior research by the CDC has found that Black and Hispanic adults are the least likely to receive the annual flu vaccine each year," said Alex Reinhart, assistant teaching professor in CMU's Department of Statistics & Data Science and a member of the Delphi ...
2021-03-23
It can be hard to resist lapsing into an exaggerated, singsong tone when you talk to a cute baby. And that's with good reason. Babies will pay more attention to baby talk than regular speech, regardless of which languages they're used to hearing, according to a study by UCLA's Language Acquisition Lab and 16 other labs around the globe.
The study found that babies who were exposed to two languages had a greater interest in infant-directed speech -- that is, an adult speaking baby talk -- than adult-directed speech. Research has already shown that monolingual babies prefer baby talk.
Some parents worry that teaching two languages could mean an infant won't learn to speak on time, but the new study shows bilingual babies are developmentally right ...
2021-03-23
In Slovakia, in counties subject to two rounds of rapid antigen testing for SARS-CoV-2 where those who tested positive then isolated, the approach helped decrease the prevalence of positive tests by more than 50% in a week - all while primary schools and workplaces remained open. "While it was impossible to disentangle the precise contribution of control measures and mass testing," the authors said, mass testing is likely to have had a substantial effect, their modeling showed. Applying mass testing may provide a valuable tool in future containment of SARS-CoV-2 elsewhere, they say. ...
2021-03-23
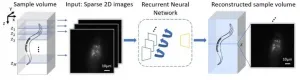
Rapid 3D microscopic imaging of fluorescent samples has gained increasing importance in numerous applications in physical and biomedical sciences. Given the limited axial range that a single 2D image can provide, 3D fluorescence imaging often requires time-consuming mechanical scanning of samples using a dense sampling grid. In addition to being slow and tedious, this approach also introduces additional light exposure on the sample, which might be toxic and cause unwanted damage, such as photo-bleaching.
By devising a new recurrent neural network, UCLA researchers have demonstrated a deep learning-enabled volumetric microscopy framework for 3D imaging of fluorescent samples. This new method only requires a few 2D images of the sample to be ...
2021-03-23
NIMS and the Tokyo Institute of Technology have jointly discovered that the chemical compound Ca3SiO is a direct transition semiconductor, making it a potentially promising infrared LED and infrared detector component. This compound--composed of calcium, silicon and oxygen--is cheap to produce and non-toxic. Many of the existing infrared semiconductors contain toxic chemical elements, such as cadmium and tellurium. Ca3SiO may be used to develop less expensive and safer near-infrared semiconductors.
Infrared wavelengths have been used for many purposes, including optical fiber communications, photovoltaic power generation and night vision devices. Existing semiconductors ...
2021-03-23
Imperial physicists are part of a team that has announced 'intriguing' results that potentially cannot be explained by our current laws of nature.
The LHCb Collaboration at CERN has found particles not behaving in the way they should according to the guiding theory of particle physics - the Standard Model.
The Standard Model of particle physics predicts that particles called beauty quarks, which are measured in the LHCb experiment, should decay into either muons or electrons in equal measure. However, the new result suggests that this may not be happening, which could point to the existence of new particles or interactions not explained by the Standard Model.
Physicists from Imperial College ...
2021-03-23
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, March 23, 2021 - Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) researchers have found that the Pfizer Coronavirus vaccine is moderately less effective against the South African variant, but still neutralizes the British variant and the original SARS-CoV-2 strain.
Their research was just published in the prestigious journal Cell Host and Microbe.
"Our findings show that future variants could necessitate a modified vaccine as the virus mutates to increase its infectivity," says principal investigator Dr. Ran Taube of the Shraga Segal Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Genetics in the Faculty of Health Sciences.
The BGU scientists evaluated the vaccine effectiveness ...
2021-03-23
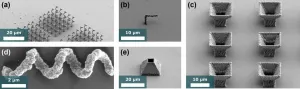
Metallic microstructures are the key components in almost every current or emerging technology. For example, with the next wireless communication standard (6G) being established, the need for advanced components and especially antennas is unbroken. The drive to yet higher frequencies and deeper integration goes hand in hand with miniaturization and fabrication technologies with on-chip capability. Via direct laser writing - an additive manufacturing technology that offers sub-micron precision and feature sizes - highly sophisticated and integrated components come into reach. One big advantage of direct laser writing is that it is not limited to the fabrication of planar structures but enables almost arbitrary 3D microstructures. This ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Why are young adults having less casual sex?
Study finds alcohol, video games and living with parents affects young men's casual sex behavior