Effective Field Theories and the nature of the universe
Effective Field Theories were introduced to simplify the mathematics involved in unifying interactions into the Standard Model of particle physics. An article in EPJ H presents Steven Weinberg's recent lecture on the development of these theories.
2021-03-24
(Press-News.org) What is the world made of? This question, which goes back millennia, was revisited by theoretical physicist Steven Weinberg from the University of Texas in Austin, TX, USA in the first of an international seminar series, 'All Things EFT'. Weinberg's seminar has now been published as an article in the journal EPJ H.
And Weinberg is well placed to discuss both Effective Field Theories (EFTs) and the nature of the Universe, as he shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Physics for developing a theory to unify the weak and electromagnetic interactions between elementary particles. This fed into the development of the widely used Standard Model of particle physics that unifies these two forces with the strong interaction.
The introduction to the article describes Weinberg as the 'pioneer' of EFTs. In his wide-ranging talk, Weinberg sets out the early history of EFTs from a personal perspective and describes some implications for future research.
Briefly, an EFT is a type of theory or approximation that describes a physical phenomenon at given length or energy scales, while averaging over shorter length or higher energy scales. Weinberg describes how the unifying Standard Model came to be seen as a valid approximation to a more fundamental theory that will likely take over at the highest energies, such as string theory.
He remembers how physicists of 1950s and 1960s had difficulty linking quantum field theory to the strong interaction. Eventually, he and others produced a standardised methodology that could fit observed data at least as well as the rather cumbersome mathematics that was being used. These ideas can be generalised; eventually, he states, 'all [physicists'] theories will survive as approximations to a future theory'.
As Weinberg explains, the techniques of EFTs apply to diverse areas including hadronic physics and superconductivity. Weinberg clearly enjoys and values teaching, and his introduction to this key concept of particle physics in this first lecture is both engaging and enlightening.
INFORMATION:
Reference
S. Weinberg, On the development of Effective Field Theory, European Physical Journal H 46, 6 (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1140/epjh/s13129-021-00004-x
Weinberg's lecture is also freely available online at https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC1_KF6kdJFoDEcLgpcegwCQ
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-24
Ruptures of the carotid artery (cervical artery dissection) are the most common cause of stroke in people under 50 years of age, with an annual incidence of 2-3 cases per 100,000 persons. Salicylic-acid preparations (acetylsalicylic acid: aspirin, Aspegic) and blood-thinning medication (anticoagulants) are used for treatment. The multicenter therapy study "Biomarkers and Antithrombotic Treatment in Cervical Artery Dissection (TREAT-CAD, NCT02046460)" investigated whether dissections - tears in the wall of vessels supplying blood to the brain - can be treated with aspirin or whether more complex blood thinning (anticoagulation) ...
2021-03-24
Copepods are tiny crustaceans about the size of a grain of rice, but they are one of the most important parts of the Earth's aquatic ecosystems. Their behavior and interaction with the environment, however, remains a relative mystery. Now, a recent paper published in the Journal of Experimental Biology sheds new light on how these miniature marvels move and cluster in the ocean.
Researchers from Bigelow Laboratory of Ocean Sciences and the Georgia Institute of Technology found that the copepods gather around small vortexes in the ocean, a finding which could have significant implications for the food web.
"We're getting at a mechanism that helps us understand how the ecosystem ...
2021-03-24
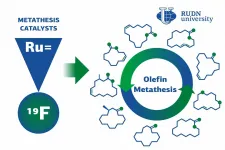
Chemists from RUDN University found out that fluorine and fluoroalkyl groups increase the efficiency of catalysts in metathesis reactions that are used in the pharmaceutical industry and polymer chemistry. The team also identified fluorine-containing compounds that can simplify the purification of the catalyst from the reaction product, making it reusable. The results of the study were published in the Russian Chemical Reviews journal.
Many medicinal drugs and polymers are based on olefins, organic compounds with a double bond between carbon atoms. To obtain useful substances from them, scientists used the metathesis reaction. In the course of metathesis, ...
2021-03-24
New research from the University of Kent and Leeds Beckett University has found that feelings of shame and stigmatisation at the idea of contracting Covid-19 are linked to lower compliance of social distancing and the likelihood of reporting infection to authorities and potential contacts in Italy, South Korea and the USA.
In contrast, the study found that individuals who trust their Government's response to the Covid-19 pandemic and feel a mutual solidarity are more likely to report Covid-19 contraction to authorities and acquaintances.
In Italy and South Korea, individuals are also more likely to follow social distancing regulations if they trust their Government's response to the pandemic, while in the USA, trust does not lead to social distancing compliance. This could ...
2021-03-24
The invisibility of dads who lose access to their children because of concerns about child neglect or their ability to provide safe care comes under the spotlight in new research.
A research partnership between the University of East Anglia and Lancaster University provides new evidence ('Up Against It': Understanding Fathers' Repeat Appearance in Local Authority Care Proceedings) about fathers' involvement in care and recurrent care proceedings in England.
A national conference today (Wednesday 24th March), co-hosted online by the two universities, will share key insights from this study, funded by the Nuffield ...
2021-03-24
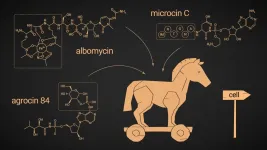
Skoltech researchers examined the antibiotic compounds that employ a 'Trojan horse' strategy to get into a bacterial cell unrecognized and prevent the synthesis of proteins, ultimately killing the cell. They were able to identify new gene clusters that look like those of known 'Trojan horses' - these likely guide the biosynthesis of new antimicrobials that require further investigation. The review paper was published in the journal RSC Chemical Biology.
When it comes to antimicrobial attacks, the most difficult thing is breaching the formidable outer defenses: getting inside a target cell to deploy the deadly weapon can be tricky. A number of antimicrobial compounds employ the well-known 'Trojan horse' strategy: they present themselves to a cell ...
2021-03-24
During this unique study researchers from the University of Surrey and European Food Information Council (EUFIC) reviewed over 100 scientific papers to examine if different criteria exist in developing classification systems for processed foods and, if so, what distinguishes them.
Classification systems that categorise foods according to their "level of processing" have been used to predict diet quality and health outcomes, inform guidelines and in product development.
Researchers found that most classification system's criteria are not aligned with existing scientific evidence on nutrition and food processing. It is thought that this may stem from different perspectives and intentions behind the development of some classification systems. Researchers also noted a failure ...
2021-03-24
A new study from the University of Kent's School of Anthropology and Conservation has found that Oldowan and Acheulean stone tool technologies are likely to be tens of thousands of years older than current evidence suggests.
They are currently the two oldest, well-documented stone tool technologies known to archaeologists.
These findings, published by the Journal of Human Evolution, provide a new chronological foundation from which to understand the production of stone tool technologies by our early ancestors. They also widen the time frame within which to discuss the evolution of human technological capabilities and associated dietary and behavioural shifts.
For the study, a team led by Kent's Dr Alastair Key and Dr David Roberts, alongside Dr Ivan Jaric from the Biology ...
2021-03-24
BEER-SHEVA, Israel...March 24, 2021 - Surprisingly, exposure to a high background radiation might actually lead to clear beneficial health effects in humans, according to Ben-Gurion University of the Negev and Nuclear Research Center Negev (NRCN) scientists. This is the first large-scale study which examines the two major sources of background radiation (terrestrial radiation and cosmic radiation), covering the entire U.S. population.
The study's findings were recently published in Biogerontology.
Background radiation is an ionizing radiation that exists ...
2021-03-24
Ahead of the first U.S. emergency use authorization for a COVID-19 vaccine, only half of Americans said they were likely to get vaccinated as soon as possible, according to an in-depth study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers conducted an online survey of 2,525 Americans in a two-week period from late November to early December, asking them about their intentions regarding COVID-19 vaccination as well as other values and beliefs. About 50 percent responded that they intended to get vaccinated as soon as possible. About 10 percent said they intended not to be vaccinated at all. The remaining 40 percent replied that they probably wouldn't be vaccinated, or probably would be but not as soon as possible.
The findings ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Effective Field Theories and the nature of the universe
Effective Field Theories were introduced to simplify the mathematics involved in unifying interactions into the Standard Model of particle physics. An article in EPJ H presents Steven Weinberg's recent lecture on the development of these theories.