New study finds false memories can be reversed
Rich false memories of autobiographical events can be planted - and then reversed, a new paper has found.
2021-03-24
(Press-News.org) Rich false memories of autobiographical events can be planted - and then reversed, a new paper has found.
The study highlights - for the first time - techniques that can correct false recollections without damaging true memories. It is published by researchers from the University of Portsmouth, UK, and the Universities of Hagen and Mainz, Germany.
There is plenty of psychological research which shows that memories are often reconstructed and therefore fallible and malleable. However, this is the first time research has shown that false memories of autobiographical events can be undone.
Studying how memories are created, identified and reversed could be a game changer in police and legal settings, where false memories given as evidence in a courtroom can lead to wrongful convictions.
According to Dr Hartmut Blank, co-author of the research from the University of Portsmouth's Department of Psychology, "believing, or even remembering something that never happened may have severe consequences. In police interrogations or legal proceedings, for instance, it may lead to false confessions or false allegations, and it would be highly desirable, therefore, to reduce the risk of false memories in such settings.
"In this study, we made an important step in this direction by identifying interview techniques that can empower people to retract their false memories."
The researchers recruited 52 participants for a study on 'childhood memories' and with the help of parents, they implanted two false negative memories that definitely didn't happen, but were plausible. For example getting lost, running away or being involved in a car accident.
Along with two true events, which had actually happened, participants were persuaded by their parents that all four events were part of their autobiographical memory.
The participants were then asked to recall each event in multiple interview sessions. By the third session, most believed the false events had happened and - similar to previous research - about 40 per cent had developed actual false memories of them.
The researchers then attempted to undo the false memories by using two strategies.
The first involved reminding participants that memories may not always be based on people's own experience, but also on other sources such as a photograph or a family member's narrative. They were then asked about the source of each of the four events.
The second strategy involved explaining to them that being asked to repeatedly recall something can elicit false memories. They were asked to revisit their event memories with this in mind.
The result, according to Dr Blank, was that "by raising participants' awareness of the possibility of false memories, urging them to critically reflect on their recollections and strengthening their trust in their own perspective, we were able to significantly reduce their false memories. Moreover, and importantly, this did not affect their ability to remember true events.
"We designed our techniques so that they can principally be applied in real-world situations. By empowering people to stay closer to their own truth, rather than rely on other sources, we showed we could help them realise what might be false or misremembered - something that could be very beneficial in forensic settings."
INFORMATION:
The paper is published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
ENDS
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-24
Infants prefer baby talk in any language, but particularly when it's in a language they're hearing at home.
A unique study of hundreds of babies involving 17 labs on four continents showed that all babies respond more to infant-directed speech -- baby talk -- than they do to adult-directed speech. It also revealed that babies as young as six months can pick up on differences in language around them.
"We were able to compare babies from bilingual backgrounds to babies from monolingual backgrounds, and what seemed to matter the most was the match between the language they ...
2021-03-24
A new study is the first to identify how human brains grow much larger, with three times as many neurons, compared with chimpanzee and gorilla brains. The study, led by researchers at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, UK, identified a key molecular switch that can make ape brain organoids grow more like human organoids, and vice versa.
The study, published in the journal END ...
2021-03-24
Scientists have genetically engineered immune cells, called myeloid cells, to precisely deliver an anticancer signal to organs where cancer may spread. In a study of mice, treatment with the engineered cells shrank tumors and prevented the cancer from spreading to other parts of the body. The study, led by scientists at the National Cancer Institute's (NCI) Center for Cancer Research, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), was published March 24, 2021, in Cell.
"This is a novel approach to immunotherapy that appears to have promise as a potential treatment for metastatic cancer," said the study's leader, Rosandra Kaplan, M.D., of NCI's Center for Cancer Research.
Metastatic cancer--cancer that has spread from its original location to other parts of the body--is notoriously ...
2021-03-24
What The Study Did: Researchers evaluated the association between a recent diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment or dementia and the risk of attempting suicide among older adults.
Authors: Amy L Byers, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.0150)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding and support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
2021-03-24
What The Study Did: This comparative effectiveness research study that included a high proportion of non-White individuals assesses whether remdesivir administered alone or with corticosteroids is associated with time to clinical improvement or time to death in patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19.
Authors: Brian T. Garibaldi, M.D,. M.E.H.P., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3071)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. ...
2021-03-24
What The Study Did: This survey study investigated the frequency and nature of sexist and racial/ethnic microaggressions against female and racial/ethnic-minority surgeons and anesthesiologists and the association with physician burnout.
Authors: Neha T. Sudol, M.D., of the Southern California Permanente Medical Group in Irvine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.0265)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
2021-03-24
Female adult sockeye from the Fraser River are dying at significantly higher rates than their male counterparts on the journey back to their spawning grounds, finds new UBC research. For every male salmon that doesn't make it to their natal stream, at least two, sometimes three female salmon die.
"This is causing skewed sex ratios in their spawning grounds, something that has been observed in recent years," says lead researcher Dr. Scott Hinch, a professor in the faculty of forestry and head of the Pacific Salmon Ecology and Conservation Laboratory at UBC. "The implications on the health of Fraser River stocks are concerning, particularly as Pacific ...
2021-03-24
Three-dimensional or "volumetric" images are widely used in medical imaging. These images faithfully represent the 3D spatial relationships present in the body. Yet 3D images are typically displayed on a two-dimensional monitor, which creates a dimensionality mismatch that must be resolved in a clinical setting where practitioners must search a 2D or a 3D image to find a particular trait or target of interest.
To learn more about this problem, Craig K. Abbey, Miguel A. Lago, and Miguel P. Eckstein, of the Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences at University of California Santa Barbara, used techniques from the field of vision science to examine how the observers use information in images to perform a given task. Their research, published in the Journal of ...
2021-03-24
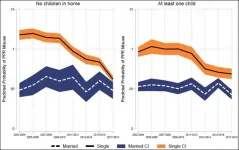
Syracuse, N.Y. - As opioid use disorders and overdoses continue to skyrocket in the United States, a study by researchers from Syracuse University and Pennsylvania State University shows that unmarried young adults who do not have children are mostly likely to misuse opioids.
The growing number of these "disconnected" young adults may also result in continued rises in substance use disorders and overdoses, the researchers say. The study, "Opioid misuse and family structure: Changes and continuities in the role of marriage and children over two decades," was published ...
2021-03-24
Living tissue can heal itself from many injuries, but giving similar abilities to artificial systems, such as robots, has been extremely challenging. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Nano Letters have developed small, swimming robots that can magnetically heal themselves on-the-fly after breaking into two or three pieces. The strategy could someday be used to make hardier devices for environmental or industrial clean up, the researchers say. Watch a video of the self-healing swimmers here.
Scientists have developed small robots that can "swim" through fluids ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study finds false memories can be reversed
Rich false memories of autobiographical events can be planted - and then reversed, a new paper has found.