Small robot swimmers that heal themselves from damage (video)
2021-03-24
(Press-News.org) Living tissue can heal itself from many injuries, but giving similar abilities to artificial systems, such as robots, has been extremely challenging. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Nano Letters have developed small, swimming robots that can magnetically heal themselves on-the-fly after breaking into two or three pieces. The strategy could someday be used to make hardier devices for environmental or industrial clean up, the researchers say. Watch a video of the self-healing swimmers here.
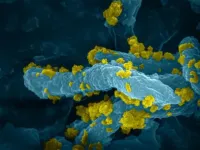
Scientists have developed small robots that can "swim" through fluids and carry out useful functions, such as cleaning up the environment, delivering drugs and performing surgery. Although most experiments have been done in the lab, eventually these tiny machines would be released into harsh environments, where they could become damaged. Swimming robots are often made of brittle polymers or soft hydrogels, which can easily crack or tear. Joseph Wang and colleagues wanted to design swimmers that could heal themselves while in motion, without help from humans or other external triggers.
The researchers made swimmers that were 2 cm long (about the width of a human finger) in the shape of a fish that contained a conductive bottom layer; a rigid, hydrophobic middle layer; and an upper strip of aligned, strongly magnetic microparticles. The team added platinum to the tail, which reacted with hydrogen peroxide fuel to form oxygen bubbles that propelled the robot. When the researchers placed a swimmer in a petri dish filled with a weak hydrogen peroxide solution, it moved around the edge of the dish. Then, they cut the swimmer with a blade, and the tail kept traveling around until it approached the rest of the body, reforming the fish shape through a strong magnetic interaction. The robots could also heal themselves when cut into three pieces, or when the magnetic strip was placed in different configurations. The versatile, fast and simple self-healing strategy could be an important step toward on-the-fly repair for small-scale swimmers and robots, the researchers say.
INFORMATION:
For more of the latest research news, register for our upcoming meeting, ACS Spring 2021. Journalists and public information officers are encouraged to apply for complimentary press registration by emailing us at newsroom@acs.org.
The authors acknowledge funding from the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, the Charles Lee Powell Foundation and UC-MEXUS-CONACYT.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS' mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS' main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-24
Today, Cochrane, a global independent network that gathers and summarizes the best evidence from research to help informed health decision-making, publishes an updated systematic review assessing rapid tests for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). The review shows that rapid antigen tests are better at correctly identifying cases of COVID-19 in people with symptoms than in people without symptoms. There are large differences in the accuracy of different brands of test, with very few meeting the World Health Organization (WHO) minimum acceptable performance standards.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, swift diagnosis of people who are infected with SARS-CoV-2 is important. Then decisions ...
2021-03-24
The more nitrate there is in mothers' drinking water, the smaller the babies they give birth to. But alarmingly, the declining birth weight can also be registered when the women are exposed to nitrate levels below the EU's threshold of 50 milligrams of nitrate per litre.
This is shown by a register-based study of more than 850,000 births in Denmark carried out in a Danish-American partnership led by Professor Torben Sigsgaard from the Department of Public Health at Aarhus University and Professor Leslie Stayner and Dr. Vanessa Coffman from the Division of Epidemiology and Biostatistics at the University of Illinois at Chicago, School of Public Health.
On the ...
2021-03-24
March 24, 2021 - For premature infants who can't breastfeed on their own, "mother's own milk" (MOM) is by far the best nutrition. There's an urgent need for effective ways to increase the relatively low rates of MOM feeding for preterm infants born to Black and Hispanic mothers. But so far, research has offered little or no specific guidance, concludes an evidence-based review in Advances in Neonatal Care, official journal of the National Association of Neonatal Nurses. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Until studies of targeted, culturally appropriate interventions are performed, available evidence points to some promising approaches to overcoming obstacles and facilitating ...
2021-03-24
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Nearly 2,000 active landfills are spread across the U.S., with the majority of garbage discarded by homes and businesses finding its way to a landfill. The resulting chemicals and toxins that build up at these sites can then leach into soil and groundwater, and this "leachate" can present serious hazards to the environment and to the people who live nearby.
To help environmental agencies battle the toxic threats posed by landfills, researchers at the University of Missouri -- in partnership with the USDA Forest Service -- have developed a system ...
2021-03-24
HOUSTON - (Mar 24, 2021) -The mammalian center for learning and memory, hippocampus, has a remarkable capacity to generate new neurons throughout life. Newborn neurons are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs) and they are crucial for forming neural circuits required for learning and memory, and mood control. During aging, the number of NSCs declines, leading to decreased neurogenesis and age-associated cognitive decline, anxiety, and depression. Thus, identifying the core molecular machinery responsible for NSC preservation is of fundamental importance if we are to use neurogenesis to halt or reverse hippocampal age-related pathology.
While there are increasing number of tools available to study NSCs and neurogenesis in mouse models, one of the major ...
2021-03-24
Sickle cell disease is the most prevalent inherited blood disorder in the world, affecting 70,000 to 100,000 Americans. However, it is considered an orphan disease, meaning it impacts less than 200,000 people nationally, and is therefore underrepresented in therapeutic research.
A team led by Abhishek Jain from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Texas A&M University is working to address this disease.
"I'm trying to create these new types of disease models that can impact health care, with the long-term goal of emphasizing on applying these tools ...
2021-03-24
>
CATONSVILLE, MD, March 24, 2021 - COVID-19 has been shown to spread on airplanes by infected passengers, so minimizing the risk of secondary infections aboard aircraft may save lives. New research in the INFORMS journal Service Science uses two models to help solve the airplane seating assignment problem (ASAP). The models can lower the transmission risk of COVID-19 more so than the strategy of blocking the middle seats, given the same number of passengers.
"Blocking the middle seat on an airplane may provide limited benefit in reducing the risk of transmission of COVID-19. Rather, other health protocols are better supported at preventing the transmission ...
2021-03-24
SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, arrived one year ago and turned our lives upside-down.
While worldwide vaccination programs are currently ongoing, we do not yet know for how long the vaccine will provide immune protection against infection, and if the currently approved vaccines can provide protection against the emerging virus variants.
In addition, it appears that vaccines cannot prevent illness for people who have already been infected. In contrast to vaccines, there are currently no effective drugs that act against the virus SARS-CoV-2.
New research by Associate Professor Jasmin Mecinovic and co-workers from the Department of Physics, Chemistry and Pharmacy, University of Southern Denmark, now presents a compound that might provide a basis for the ...
2021-03-24
Decarbonizing the economy and achieving the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energies is one of the most urgent global challenges of the 21st century. Hydrogen can play a key role in this process as a promising climate-neutral energy vehicle. Yet, the so-called green hydrogen economy requires that hydrogen production be based exclusively on renewable energy. In addition, it should ideally not use expensive and rare metal catalysts, whose production has severe environmental consequences. To address this challenge, ITQB NOVA researchers Inês Cardoso Pereira and Mónica Martins are working on an innovative technology to produce hydrogen from light using non-photosynthetic microorganisms.
Hydrogen offers exciting new possibilities as an energy vehicle, ...
2021-03-24
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration, a multinational team of over 300 scientists including two astrophysicists from the University of the Witwatersrand (Wits University), has revealed today a new view of the massive object at the centre of the M87 galaxy: how it looks in polarised light.
This is the first time astronomers have been able to measure polarisation, a signature of magnetic fields, this close to the edge of a black hole. The observations are key to explaining how the M87 galaxy, located 55 million light-years away, is able to launch energetic jets from its core.
"We are now seeing the next crucial piece of evidence to understand how magnetic fields behave around black holes, and how activity in this very compact region of space can drive powerful ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Small robot swimmers that heal themselves from damage (video)