(Press-News.org) Lithium-ion batteries have made possible the lightweight electronic devices whose portability we now take for granted, as well as the rapid expansion of electric vehicle production. But researchers around the world are continuing to push limits to achieve ever-greater energy densities -- the amount of energy that can be stored in a given mass of material -- in order to improve the performance of existing devices and potentially enable new applications such as long-range drones and robots.
One promising approach is the use of metal electrodes in place of the conventional graphite, with a higher charging voltage in the cathode. Those efforts have been hampered, however, by a variety of unwanted chemical reactions that take place with the electrolyte that separates the electrodes. Now, a team of researchers at MIT and elsewhere has found a novel electrolyte that overcomes these problems and could enable a significant leap in the power-per-weight of next-generation batteries, without sacrificing the cycle life.
The research is reported in the journal Nature Energy in a paper by MIT professors Ju Li, Yang Shao-Horn, and Jeremiah Johnson, postdoc Weijiang Xue, and 19 others at MIT, two national laboratories, and elsewhere. The researchers say the finding could make it possible for lithium-ion batteries, which now typically can store about 260 watt-hours per kilogram, to store about 420 watt-hours per kilogram. That would translate into longer ranges for electric cars and longer-lasting changes on portable devices.
The basic raw materials for this electrolyte are inexpensive (though one of the intermediate compounds is still costly because it's in limited use), and the process to make it is simple. So, this advance could be implemented relatively quickly, the researchers say.
The electrolyte itself is not new, explains Johnson, a professor of chemistry. It was developed a few years ago by some members of this research team, but for a different application. It was part of an effort to develop lithium-air batteries, which are seen as the ultimate long-term solution for maximizing battery energy density. But there are many obstacles still facing the development of such batteries, and that technology may still be years away. In the meantime, applying that electrolyte to lithium-ion batteries with metal electrodes turns out to be something that can be achieved much more quickly.
The new application of this electrode material was found "somewhat serendipitously," after it had initially been developed a few years ago by Shao-Horn, Johnson, and others, in a collaborative venture aimed at lithium-air battery development.
"There's still really nothing that allows a good rechargeable lithium-air battery," Johnson says. However, "we designed these organic molecules that we hoped might confer stability, compared to the existing liquid electrolytes that are used." They developed three different sulfonamide-based formulations, which they found were quite resistant to oxidation and other degradation effects. Then, working with Li's group, postdoc Xue decided to try this material with more standard cathodes instead.
The type of battery electrode they have now used with this electrolyte, a nickel oxide containing some cobalt and manganese, "is the workhorse of today's electric vehicle industry," says Li, who is a professor of nuclear science and engineering and materials science and engineering.
Because the electrode material expands and contracts anisotropically as it gets charged and discharged, this can lead to cracking and a breakdown in performance when used with conventional electrolytes. But in experiments in collaboration with Brookhaven National Laboratory, the researchers found that using the new electrolyte drastically reduced these stress-corrosion cracking degradations.
The problem was that the metal atoms in the alloy tended to dissolve into the liquid electrolyte, losing mass and leading to cracking of the metal. By contrast, the new electrolyte is extremely resistant to such dissolution. Looking at the data from the Brookhaven tests, Li says, it was "sort of shocking to see that, if you just change the electrolyte, then all these cracks are gone." They found that the morphology of the electrolyte material is much more robust, and the transition metals "just don't have as much solubility" in these new electrolytes.
That was a surprising combination, he says, because the material still readily allows lithium ions to pass through -- the essential mechanism by which batteries get charged and discharged -- while blocking the other cations, known as transition metals, from entering. The accumulation of unwanted compounds on the electrode surface after many charging-discharging cycles was reduced more than tenfold compared to the standard electrolyte.
"The electrolyte is chemically resistant against oxidation of high-energy nickel-rich materials, preventing particle fracture and stabilizing the positive electrode during cycling," says Shao-Horn, a professor of mechanical engineering and materials science and engineering. "The electrolyte also enables stable and reversible stripping and plating of lithium metal, an important step toward enabling rechargeable lithium-metal batteries with energy two times that of the state-the-art lithium-ion batteries. This finding will catalyze further electrolyte search and designs of liquid electrolytes for lithium-metal batteries rivaling those with solid state electrolytes."
The next step is to scale the production to make it affordable. "We make it in one very easy reaction from readily available commercial starting materials," Johnson says. Right now, the precursor compound used to synthesize the electrolyte is expensive, but he says, "I think if we can show the world that this is a great electrolyte for consumer electronics, the motivation to further scale up will help to drive the price down."
Because this is essentially a "drop in" replacement for an existing electrolyte and doesn't require redesign of the entire battery system, Li says, it could be implemented quickly and could be commercialized within a couple of years. "There's no expensive elements, it's just carbon and fluorine. So it's not limited by resources, it's just the process," he says.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation, and made use of facilities at Brookhaven National Laboratory and Argonne National Laboratory.
Written by David L. Chandler, MIT News Office
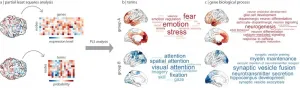
Many psychiatric disorders have genetic causes, but the exact mechanism of how genes influence higher brain function remains a mystery. A new study provides a map linking the genetic signature of functions across the human brain, a tool that may provide new targets for future treatments.
Led by Bratislav Misic, a researcher at The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute-Hospital) of McGill University, a group of scientists performed machine learning analysis of two Open Science datasets: the gene expression atlas from the Allen Human Brain Atlas and the functional ...
DURHAM, N.C. - Engineers at Duke University have developed an electronics-free, entirely soft robot shaped like a dragonfly that can skim across water and react to environmental conditions such as pH, temperature or the presence of oil. The proof-of-principle demonstration could be the precursor to more advanced, autonomous, long-range environmental sentinels for monitoring a wide range of potential telltale signs of problems.
The soft robot is described online March 25 in the journal Advanced Intelligent Systems.
Soft robots are a growing trend in the industry due to their versatility. Soft parts can handle delicate objects such as biological tissues that metal or ceramic components would damage. Soft bodies can help robots float or squeeze into tight spaces where rigid ...
Lincoln, Neb., March 25, 2021 -- Palm oil, the most important source of vegetable oil in the world, is derived from the fruit of perennial palm trees, which are farmed year-round in mostly tropical areas. The palm fruit is harvested manually every 10 days to two weeks, then transported to a mill for processing, and ultimately exported and made into a dizzying array of products from food to toiletries to biodiesel.
"You probably ate palm oil for breakfast," said Patricio Grassini, an associate professor of agronomy at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. "There is probably palm oil in your ...
Precision genome editing enables the precise modification of DNA in living cells, thus enabling a breadth of opportunities for plant breeding. Prime editors, developed by Prof. David R. Liu and his colleagues, permit the installation of desired edits in a programmable target site. They are comprised of an engineered Cas9 nickase (H840A)-reverse transcriptase (RT) fusion protein and a prime editing guide RNA (pegRNA).
Prime editors were previously developed and optimized as an extremely versatile editing strategy for generating programmable point mutations, insertions and deletions in rice and wheat by Prof. GAO Caixia of the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology (IGDB) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences ...
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have discovered specific regions within the DNA of neurons that accumulate a certain type of damage (called single-strand breaks or SSBs). This accumulation of SSBs appears to be unique to neurons, and it challenges what is generally understood about the cause of DNA damage and its potential implications in neurodegenerative diseases.
Because neurons require considerable amounts of oxygen to function properly, they are exposed to high levels of free radicals--toxic compounds that can damage DNA within cells. ...
Fossil remains of the human pelvis are rare because the pelvic bones do not preserve very well. Therefore, it has remained unclear when human sex differences in the pelvis evolved: jointly with upright walking, or later, together with the large human brains. "We have discovered that the pattern of sex differences in the human pelvis is probably much older than previously thought", says evolutionary biologist Barbara Fischer.
A team of biologists from the University of Vienna, the KLI for Evolution and Cognition Research, and the University of Calgary compared pelvic sex differences in humans with those in chimpanzees, the most closely-related living species to modern ...
Power converters are the little-known systems that make electricity so magical. They are what allow us to plug in our computers, lamps and televisions and turn them on in a snap. Converters transform the alternating current (AC) that comes out of wall sockets into the exact level of direct current (DC) that our electronics need. But they also tend to lose, in average, up to 20% of their energy in the process.
Power converters work by using power transistors - tiny semiconductor components designed to switch on and off and withstand high voltages. Designing novel power transistors to improve the converters' efficiency is the aim of the team of EPFL engineers. With their entirely new transistor design, based on the counterintuitive application ...
University of Texas at Dallas researchers have discovered that a novel surface they developed to harvest water from the air encourages tiny water droplets to move spontaneously into larger droplets.
When researchers placed microdroplets of water on their liquid-lubricant surface, the microdroplets propelled themselves to climb, without external force, into larger droplets along an oily, ramp-shaped meniscus that forms from the lubricant around the larger droplets. The "coarsening droplet phenomenon" formed droplets large enough for harvesting.
"This meniscus-mediated climbing effect enabled rapid coalescence on hydrophilic ...
The evolving science of wisdom rests on the idea that wisdom's defined traits correspond to distinct regions of the brain, and that greater wisdom translates into greater happiness and life satisfaction while being less wise results in opposite, negative consequences.
Scientists have found in multiple studies that persons deemed to be wiser are less prone to feel lonely while those who are lonelier also tend to be less wise. In a new study, published in the March 25, 2021 issue of the journal Frontiers in Psychiatry, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine take the connection between wisdom, loneliness ...
An analysis of adult human brain tissue reveals over 900 proteins tied to epilepsy. The brain disorder, estimated to afflict more than 3 million Americans, is mostly known for symptoms of hallucinations, dreamlike states, and uncontrolled, often disabling bodily seizures.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study examined molecular differences among the brains of 14 epilepsy patients and another group of 14 adults of similar age and gender who did not have the disease.
Study results showed that altered levels of brain proteins predominated in the hippocampus, a structure located deep inside ...