(Press-News.org) Patients with lupus are more likely to have metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance - both factors linked to heart disease - if they have lower vitamin D levels, a new study reveals.
Researchers believe that boosting vitamin D levels may improve control of these cardiovascular risk factors, as well as improving long-term outcomes for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Given that photosensitivity is a key feature of SLE, the scientists say that a combination of avoiding the sun, using high-factor sunblock and living in more northerly countries may contribute to lower levels of vitamin D in lupus patients. Patients with more severe disease also had lower vitamin D levels.
An international research team, led by experts at the University of Birmingham and University of Manchester, studied vitamin D levels in 1,163 SLE patients across 33 centres in 11 countries (UK, USA, Canada, Spain, The Netherlands, Sweden, Iceland, Switzerland, Turkey, South Korea and Mexico), publishing its findings in Rheumatology.
Report co-author Dr John A Reynolds, Clinical Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology at the University of Birmingham, commented: "Our results suggest that co-existing physiological abnormalities may contribute to long-term cardiovascular risk early on in SLE.
"We found a link between lower levels of vitamin D and metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. Further studies could confirm whether restoring vitamin D levels helps to reduce these cardiovascular risk factors and improve quality of life for patients with lupus."
Lupus is an uncommon incurable immune system illness, more common in women, where the immune system is overactive, causing inflammation anywhere in the body. Untreated, the condition threatens irreversible damage to major organs including kidneys, heart, lungs and brain.
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension), abnormal cholesterol levels, and obesity. People with metabolic syndrome are at greater risk of getting coronary heart disease, stroke and other conditions affecting the blood vessels.
The researchers note that patients with SLE have an excess cardiovascular risk, up to 50 times that seen in people without the condition - this cannot be attributed to traditional cardiovascular risk factors, such as high blood pressure or smoking, alone.
The mechanisms underlying the association between high blood pressure and low vitamin D in SLE are not clear, but researchers believe they may be linked to impact of vitamin D deficiency on the renin-angiotensin hormone system, which regulates blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, as well as systemic vascular resistance.
"This is the largest-ever study examining associations between vitamin D levels and metabolic syndrome in SLE; it also has the advantage of being an international cohort with diverse racial and ethnic backgrounds - generating results that will be applicable across many settings," commented Dr. Reynolds.
INFORMATION:
For further information, interviews or an embargoed copy of the research paper, please contact Tony Moran, International Communications Manager, University of Birmingham on +44 (0)782 783 2312 or t.moran@bham.ac.uk. Out-of-hours +44 (0) 7789 921 165.
Notes for editors
The University of Birmingham is ranked amongst the world's top 100 institutions. Its work brings people from across the world to Birmingham, including researchers, teachers and more than 6,500 international students from over 150 countries.
'Lower vitamin D is associated with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in systemic lupus: data from an international inception cohort' - Christine Chew, John A Reynolds, et al is published by Rheumatology.
Research partners included: University of Manchester; Sandwell and West Birmingham NHS Trust, Birmingham; University of Birmingham; Northwestern University, Chicago; Toronto Western Hospital Centre for Prognosis Studies in the Rheumatic Diseases; Université Laval, Quebec;Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases,Seoul; University of Calgary; McGill University, Montreal; Queen Elizabeth II Health Sciences Centre, Halifax, Canada; University College London; Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Medicas y Nutricion Salvador Zubiran, Mexico; Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation Arthritis and Clinical Immunology Research Program, Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Oklahoma City, OK, USA; Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles; SUNY Downstate Medical Center College of Medicine, Brooklyn, NY; King's College London; Lunds University, Sweden; National University Hospital of Iceland; Allegheny Health Network, Lupus Center of Excellence, Pittsburgh; University of California; University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore; Northwell Health Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Manhasset, NY; Amsterdam University Medical Centres; Kantonsspital Schaffhausen, Switzerland; The University of Alabama at Birmingham; Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta; Hospital Universitario Cruces, Barakaldo, Spain; University of Manitoba, Winnipeg; Columbia University, New York; Medical University of South Carolina; Istanbul University; and Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust;
What The Study Did: Insurance claims were used to assess patterns of telehealth use across surgical specialties before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Grace F.Chao, M.D., M.Sc., of the National Clinician Scholars Program at the University of Michigan and Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor in Michigan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.0979)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
What The Study Did: This article discusses possible pathogenic mechanisms of brain dysfunction in patients with COVID-19.
Authors: Maura Boldrini, M.D., Ph.D., of the New York State Psychiatric Institute, Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.0500)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
Bariatric surgery can significantly reduce the risk of cancer--and especially obesity-related cancers--by as much as half in certain individuals, according to a study by researchers at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School's Center for Liver Diseases and Liver Masses.
The research, published in the journal Gastroenterology, is the first to show bariatric surgery significantly decreases the risk of cancer in individuals with severe obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The risk reduction is even more pronounced in individuals with NAFLD-cirrhosis, the researchers say.
"We knew that obesity leads to certain problems, including cancer, but no one ...
The alarm bells began ringing when dozens of eagles were found dead near an Arkansas lake.
Their deaths--and, later, the deaths of other waterfowl, amphibians and fish--were the result of a neurological disease that caused holes to form in the white matter of their brains. Field and laboratory research over nearly three decades has established the primary clues needed to solve this wildlife mystery: Eagle and waterfowl deaths occur in late fall and winter within reservoirs with excess invasive aquatic weeds, and birds can die within five days after arrival.
But until recently, the toxin that caused the disease, vacuolar myelinopathy, was unknown.
Now, after years spent identifying a new toxic blue-green algal (cyanobacteria) species and isolating ...
PITTSBURGH, March 26, 2021 - As evidence mounts supporting the use of monoclonal antibody treatment to reduce hospitalizations and deaths from COVID-19, UPMC and University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine physician-scientists are sharing the health system's experience administering the life-saving medication.
In a report published today in the scientific journal Open Forum Infectious Diseases, the UPMC/Pitt team shares how it quickly established the largest and most equitable distribution network for COVID-19 monoclonal antibody infusions across Pennsylvania. The team today also reported preliminary results confirming the treatment reduced likelihood of hospitalization ...
EL PASO, Texas - Sreenath Chalil Madathil, Ph.D., assistant professor in industrial manufacturing and systems engineering (IMSE) at The University of Texas at El Paso, is working to streamline the process and ease the patient experience at COVID-19 vaccination clinics in the United States to ensure faster vaccine distribution.
Madathil led a team of UTEP faculty, staff and students who observed several of El Paso's drive-though and walk-in clinics in early 2021. The team identified areas that likely created bottlenecks, which produce delays and other issues. They used the information ...
A University of Florida study of middle-aged and older adults finds those who unknowingly carry methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, or MRSA, on their skin are twice as likely to die within the next decade as people who do not have the bacteria.
"Very few people who carry MRSA know they have it, yet we have found a distinct link between people with undetected MRSA and premature death," said the study's lead author Arch G. Mainous III, Ph.D., a professor in the department of health services research, management and policy at the UF College of Public Health and Health Professions, part of UF Health, the university's academic health center.
The findings suggest that routine screening for undetected ...
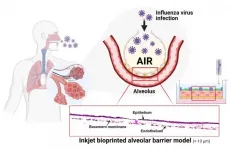
The warmer temperature and blooming flowers signal the arrival of spring. However, worries about respiratory diseases are also on the rise due to fine dust and viruses. The lung, which is vital to breathing, is rather challenging to create artificially for experimental use due to its complex structure and thinness. Recently, a POSTECH research team has succeeded in producing an artificial lung model using 3D printing.
Professor Sungjune Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Professor Joo-Yeon Yoo and Ph.D. candidate Dayoon Kang of the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH have together succeeded in creating ...
Key takeaways
Surgery is an underused treatment for certain pancreatic cancer patients.
Patients with pancreatic cancer who underwent surgery after chemotherapy lived nearly twice as long as those treated with only chemotherapy.
Findings confirms current recommendations for stage II pancreatic cancer: survival improves when patients receive multimodality therapy, chemotherapy before and/or after surgery.
All analyses of the data delivered the same findings.
CHICAGO (March 26, 2021, 9:00 am CDT): Patients with stage II pancreatic cancer who are treated with chemotherapy followed by resection (an operation that removes the cancerous part of the organ, structure or tissue) live nearly twice as long as patients who receive only chemotherapy, according ...
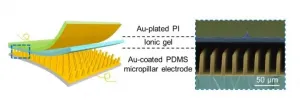
In recent years, with the rapid development of flexible electronic skins, high-performance flexible tactile sensors have received more attention and have been used in many fields such as artificial intelligence, health monitoring, human-computer interaction, and wearable devices. Among various sensors, flexible capacitive tactile sensors have the advantages of high sensitivity, low energy consumption, fast response, and simple structure. Sensitivity is an important parameter of the sensor. A common way to improve sensitivity is to introduce microstructures and use ionic dielectric materials at the interface ...