(Press-News.org) Use of vouchers and coupons offered by pharmaceutical companies to defray patients' out-of-pocket drug costs is concentrated among a small number of drugs. While these offsets significantly reduce patient costs, they are not targeted to patients who most need the price reduction, according to a study from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers, in what is thought to be the largest study of its kind to date, analyzed tens of millions of pharmacy transactions by more than 600,000 people in the U.S. during 2017-19, in order to get a better sense of how vouchers and other point-of-sale copayment "offsets" are used. These coupons and vouchers come in many forms--some are offered online directly to customers, others by pharmacy chains, some as "drug discount cards," and through smart phone apps.
Their study found that about half of the more than four million offsets included in the analysis were provided by pharmaceutical companies, and half by pharmacies or pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), companies that manage prescription drugs plans for large employers, health insurers and the Medicare program. In each of these categories, offsets were concentrated among a relatively small number of drugs. The researchers found no evidence that offsets differed much depending on the local average income, ethnic/racial makeup, or level of insurance coverage.
The study appears online in JAMA Internal Medicine on March 29.
The disease categories for which offsets for branded drugs were most common included diabetes, lung disease, and cardiovascular disease, and there was a clear concentration among a relatively small number of drugs: 80 percent of manufacturer-sponsored offsets applied to just 164 drugs, out of a total of 2,661 drugs that received at least one manufacturer-sponsored offset. Similarly, 80 percent of pharmacy/PBM-sponsored offsets were for just 156 out of a total of 3,175 drugs receiving pharmacy/PBM offsets.
"The most significant finding was that these offsets are not being targeted to people who likely need them the most--for the pharmaceutical company-sponsored offsets, the goal may be mainly to maintain market share," says study lead author, Aditi Sen, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Health Policy and Management at the Bloomberg School. "Understanding different offset types and which patients use them is important for designing policy."
Coupons, vouchers, and other copay offsets are widely seen as responses to the unusually high prices of prescription drugs in the U.S. Pharmaceutical companies want to make it easier for patients to buy their branded drugs rather than generic competitors, whereas PBMs typically want to steer patients away from the more expensive branded drugs to lower-cost substitutes.
For their study, Sen and her colleagues analyzed retail pharmacy transactions from the IQVIA Formulary Impact Analyzer during the period October 2017 through September 2019. Their analysis covered 631,249 individuals who had at least one use of an offset, and a total of 4,223,114 offsets. Of these offsets, 50.2 percent were from pharmaceutical manufacturers, 47.2 percent were from pharmacy benefit managers or pharmacies, and 2.6 percent were from state assistance programs.
The analysis revealed that manufacturer-provided offsets tended to cover more of a drug's costs--a median of about $51, or about 87.1 percent of the out-of-pocket cost, compared to $16 and 39.3 percent for the pharmacy/PBM offsets. More than a third (35.4 percent) of manufacturer offsets fully covered the patient's out-of-pocket costs, compared to just 0.8 percent for pharmacy/PBM offsets.
The median age of offset users was 48 years, and 57.3 percent were female.
Overall, the analysis showed that offset use did not vary much between lower- and higher-income areas--the study compared use by county--even though lower-income patients are more likely to need and benefit from offsets.
Sen and her colleagues are now following up with further studies, to get a better sense of the factors influencing pharma manufacturers' decision-making when they offer vouchers and coupons, and also to understand how offsets affect patients' health outcomes.
INFORMATION:
"Characteristics of Copayment Offsets for Prescriptions Drugs in the United States" was co-authored by Aditi Sen, So-Yeon Kang, Emaan Rashidi, Devoja Ganguli, Gerard Anderson, and Caleb Alexander.
Funding was provided by Arnold Ventures.
When you bump into someone in the workplace or at your local coffee shop, you might call that an "encounter." That's the scientific term for it, too. As part of urgent efforts to fight COVID-19, a science is rapidly developing for measuring the number of encounters and the different levels of interaction in a group.
At the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), researchers are applying that science to a concept they have created called "encounter metrics." They have developed an encrypted method that can be applied to a device such as your phone to help with the ultimate goal of slowing down or preventing future pandemics. The method is also applicable to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Their research ...
A drop of food coloring slowly spreading in a glass of water is driven by a process known as diffusion. While the mathematics of diffusion have been known for many years, how this process works in living organisms is not as well understood.
Now, a study published in Nature Communications provides new insights on the process of diffusion in complex systems. The result of a collaboration between physicists at Penn, the University of Chile, and Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, this new theoretical framework has broad implications for active surfaces, such as ones found in biofilms, active coatings, and even mechanisms for pathogen clearance.
Diffusion is described ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. - Bullying at boarding schools has a negative impact on students' emotional health, but for male students, having a school staff member to rely on for support may mute the harmful effects of bullying, according to a new University at Buffalo study. Support networks did not have the same effect for female students, the researchers say.
The study, recently published in School Psychology Review, is one of few to examine the impact of bullying at boarding schools, which provide a unique environment where most students live on school grounds, away from their families. It is also one of the first studies to observe the effects ...
Climate labels informing us of a meat product's carbon footprint cause many people to opt for climate-friendlier alternatives. This applies to people who are curious about a product's carbon footprint, as well as to those who actively avoid wanting to know more. The finding is published in a new study from, among others, the University of Copenhagen. As such, climate labeling food products can be a good way of reducing our climate footprint. But according to the researcher behind the study, labels must be obligatory for them to be effective.
Certain situations exist where we humans strategically avoid greater knowledge and more information - a phenomenon known as "active information avoidance". ...
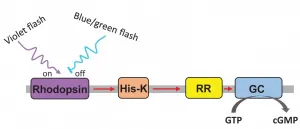
The unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has already given research a massive boost: One of its light sensors, channelrhodopsin-2, founded the success of optogenetics about 20 years ago.
In this technology, the alga's light sensor is incorporated into cells or small living organisms such as threadworms. Afterwards, certain physiological processes can be triggered or stopped by light. This has already led to several new scientific findings, for example on the function of nerve cells.
Now the green alga Chlamydomonas is once again setting an accent. Once again, it is its light sensors, ...
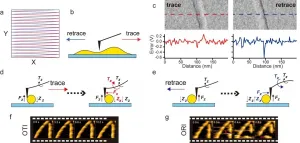
High-speed atomic force microscopy (HS-AFM) is an imaging technique that can be used for visualizing biological processes, for example the activity of proteins. Nowadays, typical HS-AFM frame rates are as high as 12 frames per second. In order to improve the capabilities of the method, so that it can be applied to an ever expanding range of biological samples, better video rates are needed, though. Moreover, faster recording times imply less interaction between the sample and the probe -- a tip scanning the sample's surface -- making the imaging ...
A team of researchers, led by the Instituto de Ciencias del Patrimonio (Incipit-CSIC) and the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), in collaboration with the team from the Arqueological Zone of Caral (Perú) led by Dr. Ruth Shady Solís, has established the relation between the position of the monuments of the Supe Culture (Perú), their orientations, and some astronomical and topographic features, which opens the way to the analysis of the way the inhabitants of this valley conceived space and time 5000 years ago. The results of the study have just been published in the journal Latin American Antiquity.
The valley of the river Supe in Perú contains the first evidence for city building in the Americas. In recent decades in this valley and ...
Next-gen electronics is envisioned to be non-rigid, component-free, flexible, bendable, and easily integrable with different objects.
Direct-write printing techniques provide unique opportunity to enable this vision through use of nanomaterial so-called functional inks, that can be tailored to add desired functionalities on various flexible substrates, such as textiles or plastic.
The technology, known as Printed Electronics (PE), has been known for decades, but has recently gained considerable attention due to innovation in material inks, process technology and design revolution.
To keep the research community abreast with the latest technological advancements in the area of droplet-based PE techniques for next-gen devices, researchers from Aarhus University have now ...
Kanazawa, Japan - Solar cells are excellent renewable energy tools that use sunlight to drive an electrical current for power. They've been used to power homes since the 1980s, and their performance and production cost have improved dramatically since then. The most common solar cells, based on silicon, work well for a long time. They retain more than 80% of their functionality even after 25 years. However, the efficiency--i.e., how much of the incoming sunlight is converted to electrical power--of commercial-scale silicon solar cells is currently only around 20%.
Maximizing solar cells' energy conversion efficiency will improve their competitiveness compared to fossil fuels and help optimize them as a sustainable ...
The B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants of SARS-CoV-2 were first detected in the UK and South Africa respectively, and have since spread to many other countries. Scientists from the Institut Pasteur joined forces with Orléans Regional Hospital, Tours University Hospital, Créteil Intercommunal Hospital, Strasbourg University Hospital and Georges Pompidou European Hospital to study the sensitivity of these two variants to neutralizing antibodies present in the serum samples of people who have been vaccinated or previously infected with SARS-CoV-2. They compared this sensitivity with that of the reference ...