Percutaneous image guided thermal ablation safe, effective therapy for metastatic gynecologic cancers
2021-03-29
(Press-News.org) FINDINGS
A new study by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center found using percutaneous image guided needle based thermal ablation -- the precise application of extreme heat or cold to a tumor using sophisticated ultrasound, CT or MRI in a single outpatient session -- is a safe and effective adjunctive therapy for the local control of metastatic gynecologic cancers throughout lungs, liver, soft tissues in the abdomen and pelvis and bones in patients with advanced localized cancers unresponsive to systemic therapy.
Nearly 96% of the patients in the study achieved a complete tumor response over a median follow up period of 10 months. The overall survival rate was 37.5 months and the progression-free survival rate, the length of time their disease is controlled, was 16.5 months. Less than 5% of patients experienced any major side effects.
BACKGROUND
Metastatic gynecological cancers, including ovarian, endometrial or uterine and cervical, are often aggressive tumors with low survival rates. Patients diagnosed with these cancers often undergo extensive and multiple surgeries as part of standard treatment. However, surgery can be invasive and is not always feasible for patients with advanced cancers with localized nonresponsive tumors or patients who are not traditional surgical or radiation candidates.
One alternative option being studied is thermal ablation, which is an image-guided minimally-invasive needle-based approach that delivers highly accurate and precise localized treatment only to cancer cells while minimizing the effects to surrounding tissue. Thermal ablation was pioneered for liver, lung and kidney cancer, but it is currently being looked at to use in the care of other cancers, including prostate and gynecological cancers. Other benefits of thermal ablation are that it is an outpatient procedure, done with minimal sedation with lower risk and lower cost, in combination with systemic therapies, compared to traditional surgery or radiation.
METHOD
For the study, Steven Raman, MD, professor of radiology, urology and surgery and a member of the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, led a multidisciplinary team of expert physicians to demonstrate the high safety and efficacy of percutaneous thermal ablation in targeting localized metastatic gynecologic malignancies. The study group included 42 women, ranging from 25 to 78 years old, with metastatic gynecologic tumors (119 metastatic tumors) treated with radiofrequency (47 tumors), microwave (47 tumors) or cryogenic (30 tumors) ablation from over 2,800 ablations performed from January 2001 to January 2019.
IMPACT
This is the first and largest study to show that image guided needle based thermal ablation is a safe and effective approach for patients with localized metastatic gynecologic cancers throughout the body, especially for those who cannot undergo additional surgery because of a declining health status or in areas previously radiated.
INFORMATION:
AUTHORS
The senior author of the study is Dr. Raman. The lead author is Dr. Frank Yuan, a graduate of the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, and now at Johns Hopkins University. Other expert authors, all of UCLA, include: Dr. Gottfried Konecny, Dr. Sanaz Memarzadeh, Dr. Sindy Wei, Dr. Robert Suh, Dr. James Sayre and Dr. David Lu.
JOURNAL
The study was published online in the Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology.
FUNDING
The research was supported by funding from the UCLA Radiology Integrated Diagnostics Program.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-29
BOSTON - In the last 20 years, Black adults living in rural areas of the United States have experienced high mortality rates due to diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease and stroke compared to white adults. In a research letter written by colleagues at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and published in the END ...
2021-03-29
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), which leads to a loss of central vision, is the most frequent cause of blindness in adults 50 years of age or older, affecting an estimated 196 million people worldwide. There is no cure, though treatment can slow the onset and preserve some vision.
Recently, however, researchers at the University of Rochester have made an important breakthrough in the quest for an AMD cure. Their first three-dimensional (3D) lab model mimics the part of the human retina affected in macular degeneration.
Their model combines stem cell-derived ...
2021-03-29
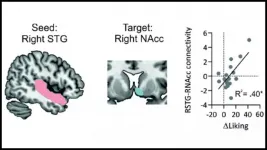
Communication between the brain's auditory and reward circuits is the reason why humans find music rewarding, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Despite no obvious biological benefits, humans love music. Neuroimaging studies highlight similarities between how the brain's reward circuits process music and other rewards like food, money, and alcohol. Yet neuroimaging studies are correlational by nature. In a new study, Mas-Herrero et al. sought to nail down the causal role of this circuitry by using non-invasive brain stimulation.
A group of pop music fans listened ...
2021-03-29
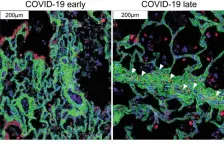
A team led by investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian has used advanced technology and analytics to map, at single-cell resolution, the cellular landscape of diseased lung tissue in severe COVID-19 and other infectious lung diseases.
In the study, published online March 29 in Nature, the researchers imaged autopsied lung tissue in a way that simultaneously highlighted dozens of molecular markers on cells. Analyzing these data using novel analytical tools revealed new insights into the causes of damage in these lung illnesses and a rich data resource for further research.
"COVID-19 is a complex disease, and we still don't understand exactly what it does to a lot of organs, but with this study we were able to develop ...
2021-03-29
Researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, have developed a novel far red light-emitting luciferin-luciferase system that is more efficient than those available commercially. An article on the subject is published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
The study was supported by São Paulo Research Foundation - FAPESP via the Thematic Project "Arthropod bioluminescence: biological diversity in Brazilian biomes, biochemical origin, structural/functional evolution of luciferases, molecular differentiation of lanterns, biotechnological, environmental and educational applications", for which the principal ...
2021-03-29
ANN ARBOR--In a two-year study that could help guide educators developing the post-pandemic new normal, student groups at the University of Michigan assigned to make video presentations showed more creativity and risk-taking than groups making conventional in-person presentations.
"Given the importance of project-based learning, our study provides a way to turn virtual limitations into an advantage," said Fei Wen, U-M associate professor of chemical engineering. "We can enhance the student experience and learning outcomes."
Higher education, along with society at large, anticipates a shift in the balance between ...
2021-03-29
More physicians and pharmacists are advocating for patients to be made aware of animal byproducts contained in common medications, according to new research in the Journal of Osteopathic Medicine. Common medications, including widely used blood thinners and hormones, are often derived from animal byproducts and prescribed without consulting the patient about their beliefs.
"Patients deserve to know what their medications are made of, yet this information is rarely shared," said Sara Reed, student doctor at Lincoln Memorial University (LMU) DeBusk ...
2021-03-29
Climate change is altering the world we share with all living things. But it's surprisingly difficult to single out climate change as an extinction threat for any one particular species protected under the Endangered Species Act.
To date, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has only formally considered impacts from climate change in listing actions for four animal species and one alpine tree.
But the effects of climate change extend to temperate climates as well. A new analysis of population data published in the journal Ecosphere shows that climate change represents a specific extinction threat for an endangered coastal lupine plant.
Biologists including Eleanor Pardini at Washington University in St. Louis have tracked all of the known stands ...
2021-03-29
HOUSTON - (March 29, 2021) - This could be where the rubber truly hits the road.
Rice University scientists have optimized a process to convert waste from rubber tires into graphene that can, in turn, be used to strengthen concrete.
The environmental benefits of adding graphene to concrete are clear, chemist James Tour said.
"Concrete is the most-produced material in the world, and simply making it produces as much as 9% of the world's carbon dioxide emissions," Tour said. "If we can use less concrete in our roads, buildings and bridges, we can eliminate some of the emissions at the very start."
Recycled tire waste is already used as a component of Portland cement, but graphene has been proven to strengthen cementitious materials, ...
2021-03-29
SUVA, Fiji (March 29, 2021) - A new study published in the journal Environmental Science and Policy addresses the impacts of COVID-19 and Cyclone Harold on Indo-Fijians engaged in small scale fisheries.
The paper says that countries, including Fiji, need to address ethical and social justice considerations and the politics of recovery efforts by putting vulnerable and marginalized groups front and center in the aftermath of pandemics and natural disasters.
What countries cannot afford is for economic recovery efforts to put additional burdens and risk on those invested in the SSF sector, and cause further widening of inequities, and increase ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Percutaneous image guided thermal ablation safe, effective therapy for metastatic gynecologic cancers