(Press-News.org) Heavy caseloads, job stress and biases can strain relations between parole and probation officers and their clients, upping offenders' likelihood of landing back behind bars.
On a more hopeful note, a new University of California, Berkeley, study suggests that nonjudgmental empathy training helps court-appointed supervision officers feel more emotionally connected to their clients and, arguably, better able to deter them from criminal backsliding.
The findings, published March 29 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show, on average, a 13% decrease in recidivism among the clients of parole and probation officers who participated in the UC Berkeley empathy training experiment.
"If an officer received this empathic training, real-world behavioral outcomes changed for the people they supervised, who, in turn, were less likely to go back to jail," said study lead and senior author Jason Okonofua, an assistant professor of psychology at UC Berkeley.
The results are particularly salient in the face of nationwide efforts to reduce prison and jail populations amid a deadly pandemic and other adversities. The U.S. criminal justice system has among the highest rates of recidivism, with approximately two-thirds of incarcerated people rearrested within three years of their release and one-half sent back behind bars.
"The combination of COVID-19 and ongoing criminal justice reforms are diverting more people away from incarceration and toward probation or parole, which is why we need to develop scalable ways to keep pace with this change," said Okonofua, who has led similar interventions for school teachers to check their biases before disciplining students.
At the invitation of a correctional department in a large East Coast city, Okonofua and graduate students in his lab at UC Berkeley sought to find out if a more caring approach on the part of court-appointed supervision officers would reverse trends in recidivism.
Among other duties, parole and probation officers keep track of their clients' whereabouts, make sure they don't miss a drug test or court hearing, or otherwise violate the terms of their release, and provide resources to help them stay out of trouble and out of jail.
For the study, the researchers surveyed more than 200 parole and probation officers who oversee more than 20,000 people convicted of crimes ranging from violent crimes to petty theft. Research protocols bar identifying the agency and its location.
Using their own and other scholars' methodologies, the researchers designed and administered a 30-minute online empathy survey that focused on the officers' job motivation, biases and views on relationships and responsibilities.
To trigger their sense of purpose and values, and tap into their empathy, the UC Berkeley survey asked what parts of the work they found fulfilling. One respondent talked about how, "When I run across those guys, and they're doing well, I'm like, 'Awesome!'" Others reported that being an advocate for people in need was most important to them.
As for addressing biases -- including assumptions that certain people are predisposed to a life of crime -- the survey cited egregious cases in which probation and parole officers abused their power over those under their supervision.
Survey takers were also asked to rate how much responsibility they bear, as individuals and members of a profession, for their peers' transgressions. Most answered that they bore no responsibility.
Ten months after administering the training, researchers found a 13% decrease in recidivism among the offenders whose parole and probation officers had completed the empathy survey.
While the study yielded no specifics on what prevented the parolees and people on probation for reoffending in the period following the officers' empathy training, the results suggest that a change in relationship dynamics played a key role.
"The officer is in a position of power to influence if it's going to be an empathic or punitive relationship in ways that the person on parole or probation is not," Okonofua said.
"As our study shows," he added, "the relationship between probation and parole officers and the people they supervise plays a pivotal role and can lead to positive outcomes, if efforts to be more understanding are taken into consideration."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of the study are Kimia Saadatian, Joseph Ocampo, Michael Ruiz and Perfecta Delgado Oxholm, all at UC Berkeley.
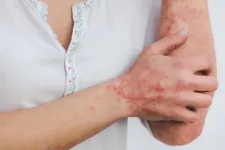
Psoriasis is a chronic disease that causes patients to develop patches of dry, scaly, and itchy skin. It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that it arises from a person's immune system inappropriately targeting that person's own healthy body parts. It is a deeply unpleasant condition, and patients commonly take various medications so that they can live their lives more comfortably.
Professor Min Chen of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Peking Union Medical College has conducted extensive research on psoriasis. "There are many patients with psoriasis who also have cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and coronary heart disease," she notes. The presence of such cardiovascular diseases is an important consideration ...
One of the biggest longitudinal research studies of its kind in the world led by The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) and the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) suggests that positive outcomes for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are more common than previously thought.
ASD refers to a group of neurodevelopmental conditions resulting in challenges related to communication, social understanding and behaviour. One in 100 people may have ASD and although a person can be diagnosed at any time, ASD symptoms generally appear and are diagnosed in the first few years ...
PRINCETON--Slanted media outlets are often blamed for growing polarization, but new research points to another consequence of consuming partisan news: an erosion of trust in the media.
A team of researchers combined computational social science techniques and experimentation to study the long-term effects of online partisan media on political opinions and trust.
Internet users were asked to change their default browser homepages to either the Huffington Post, a left-leaning news site, or Fox News, a more conservative outlet, during the 2018 U.S. midterm elections. As participants went about their daily activities, they allowed the researchers to survey them multiple times ...
LA JOLLA, CA--A team led by scientists at Scripps Research has made a discovery suggesting that experimental antibody therapies for Parkinson's and Alzheimer's have an unintended adverse effect--brain inflammation--that may have to be countered if these treatments are to work as intended.
Experimental antibody treatments for Parkinson's target abnormal clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein, while experimental antibody treatments for Alzheimer's target abnormal clumps of amyloid beta protein. Despite promising results in mice, these potential treatments so far have not seen much success in clinical trials.
"Our findings provide a possible explanation for why antibody treatments have not yet succeeded ...
KANSAS CITY, MO--Since the beginning of the pandemic, a loss of smell has emerged as one of the telltale signs of COVID-19. Though most people regain their sense of smell within a matter of weeks, others can find that familiar odors become distorted. Coffee smells like gasoline; roses smell like cigarettes; fresh bread smells like rancid meat.
This odd phenomenon is not just disconcerting. It also represents the disruption of the ancient olfactory circuitry that has helped to ensure the survival of our species and others by signaling when a reward (caffeine!) or a punishment (food poisoning!) is imminent.
Scientists ...
Dwindling water supplies and a growing population will halve per capita water use in Jordan by the end of this century. Without intervention, few households in the arid nation will have access to even 40 liters (10.5 gallons) of piped water per person per day.
Low-income neighborhoods will be the hardest hit, with 91 percent of households receiving less than 40 liters daily for 11 consecutive months per year by 2100.
Those are among the sobering predictions of a peer-reviewed paper by an international team of 17 researchers published March 29 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Jordan's deepening water crisis offers a glimpse of challenges ...
Materials such as gallium arsenide are extremely important for the production of electronic devices. As supplies of it are limited, or they can present health and environmental hazards, specialists are looking for alternative materials. So-called conjugated polymers are candidates. These organic macromolecules have semi-conductor properties, i.e. they can conduct electricity under certain conditions. One possible way of producing them in the desired two-dimensional - i.e. extremely flat - form is presented by surface chemistry, a field of research established in 2007.
Since then, many reactions have been developed and interesting materials produced for possible applications. ...
When humans look out at a visual landscape like a sunset or a beautiful overlook, we experience something -- we have a conscious awareness of what that scene looks like. This awareness of the visual world around us is central to our everyday existence, but are humans the only species that experiences the world consciously? Or do other non-human animals have the same sort of conscious experience we do?
Scientists and philosophers have asked versions of this question for millennia, yet finding answers -- or even appropriate ways to ask the question -- has proved elusive. But a team of Yale researchers recently devised an ingenious way to try to solve ...
One specific protein may be a master regulator for changing how cancer cells consume nutrients from their environments, preventing cell death and increasing the likelihood the cancer could spread, a study from the University of Notre Dame has shown.
The study, published in Cell Reports, was completed in the laboratory of Zachary Schafer, the Coleman Foundation Associate Professor of Cancer Biology in the Department of Biological Sciences.
Schafer and collaborators found a protein called SGK1, known to be activated in a variety of cancer cell types, signals the ...
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 29, 2021--A first-of-its-kind instrument that samples smoke from megafires and scans humidity will help researchers better understand the scale and long-term impact of fires--specifically how far and high the smoke will travel; when and where it will rain; and whether the wet smoke will warm the climate by absorbing sunlight.
"Smoke containing soot and other toxic particles from megafires can travel thousands of kilometers at high altitudes where winds are fast and air is dry," said Manvendra Dubey, a Los Alamos National Laboratory atmospheric scientist and co-author on a paper published last week in Aerosol Science and Technology. "These smoke-filled clouds can absorb ...