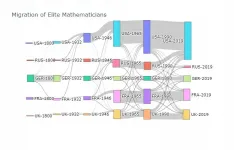
(Press-News.org) Math's top prize, the Fields Medal, has succeeded in making mathematics more inclusive but still rewards elitism, according to a Dartmouth study.
Published in Nature's END
Big data tells story of diversity, migration of math's elite
Analysis of nearly 250,000 mathematicians gives a picture of the world of math
2021-03-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers develop new method for identifying mutational signatures in cancer
2021-03-30
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center used machine learning techniques to detect mutational signatures in cancer patients. Their algorithm outperformed the current standard of analysis and revealed new mutational signatures associated with obesity, which is believed by cancer prevention experts to be becoming the most significant lifestyle factor contributing to cancer in the U.S. and most of the Western world.
The study was published in the Jan. 25 issue of the journal eLife.
"Mutational signatures are important in current cancer research as they enable you to see the signs left by underlying factors, such as aging, smoking, alcohol use, UV exposure, and BRCA inherited mutations that contribute to the development ...
New COVID-19 research: How to make people follow restrictions without appealing to fear
2021-03-30
Making people fear the coronavirus may motivate us to wash our hands, keep our distance and wear a face mask. But fear also takes a heavy toll on our mental health and is fertile ground for discrimination and prejudice. New research shows a different path.
When the coronavirus pandemic hit the world in the spring of 2020, feelings of being capable or efficacious against the virus were a key factor in driving compliance with the authorities' guidelines. This is the result of a new study based on large surveys across eight Western democracies, published in British Journal of Health Psychology.
The extent to which we personally felt informed and capable of acting clearly affected the extent of our behaviour to prevent infection, e.g. by keeping our distance ...
New early warning system for self-driving cars
2021-03-30
A team of researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has developed a new early warning system for vehicles that uses artificial intelligence to learn from thousands of real traffic situations. A study of the system was carried out in cooperation with the BMW Group. The results show that, if used in today's self-driving vehicles, it can warn seven seconds in advance against potentially critical situations that the cars cannot handle alone - with over 85% accuracy.
To make self-driving cars safe in the future, development efforts often rely on sophisticated models aimed at giving cars the ability to analyze the behavior of all traffic participants. But what happens if the models are not yet capable of handling some complex ...
Changes in mouth bacteria after drinking beetroot juice may promote healthy ageing
2021-03-30
Drinking beetroot juice promotes a mix of mouth bacteria associated with healthier blood vessels and brain function, according to a new study of people aged 70-80.
Beetroot - and other foods including lettuce, spinach and celery - are rich in inorganic nitrate, and many oral bacteria play a role in turning nitrate to nitric oxide, which helps to regulate blood vessels and neurotransmission (chemical messages in the brain).
Older people tend to have lower nitric oxide production, and this is associated with poorer vascular (blood vessel) and cognitive (brain) health.
In the new study, by the University of Exeter, 26 healthy older people took part in two ten-day supplementation periods: one with nitrate-rich ...
Growing appetite for meat alternatives in Brussels
2021-03-30
Increasing numbers of people in Belgium are turning away from meat in favour of plant-based alternatives, according to new research from psychologists at the University of Bath, in collaboration with Belgian animal welfare organisation GAIA.
New analysis finds that in 2020, over half of Belgians (51%) were 'satisfied' with meat alternatives - a figure that has increased from 44% since 2019.
The results of the research which gauged responses from a representative sample of 1,000 people in Belgium over two years (in 2019 and 2020) highlights concerns around animal agriculture and the environment that are impacting individuals' dietary choices.
Additional findings from ...
The early death of nerve cells is crucial to form healthy brains
2021-03-30
Computer scientists at the University of Surrey have created a ground-breaking model that could improve our understanding of developmental disorders such as autism.
Scientists have long tried to better understand how the cerebral cortex and its layers develop, with pathologies such as autism, schizophrenia and epilepsy linked to this process.
In a paper published by the journal Cerebral Cortex, scientists from Surrey, Newcastle University, and Nottingham University detail how they developed and used a computational model to simulate cell division, cell migration and apoptosis (cell death) in the hope of understanding how these processes affect the development of the brain.
With the help of their computer model, the ...
Gender discrimination threatens crop yield among smallholder farmers in Africa, researchers say
2021-03-30
A study examining bean productivity among smallholder farmers in Tanzania, has found that on average, yields are 6% lower among female than male farmers. Women are often 'invisible' in agriculture, researchers say, due to social structural barriers and national agricultural policies, which do not address discriminatory land rights; education and agricultural information and decision making, which must be tackled to reverse this trend.
The paper 'What Does Gender Yield Gap Tell Us about Smallholder Farming in Developing Countries?' published in the open access scientific journal Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing (MDPI), analyzed data from southern region in Tanzania since 2016 and also drew on research ...
Russian biologists discover a transmissible cancer lineage in the Far Eastern mussels
2021-03-30
'A transmissible cancer was first discovered in dogs in the middle of the 19th century. It is transmitted sexually from a sick dog to a healthy one, the cancer cells themselves being the infective agent. In the 1990s, a contagious cancer was discovered in the Tasmanian devil. Since the cancer was found in only two species of mammals, scientists used to think that it is quite rare in the nature. However, time has come to reconsider this view. A transmissible cancer appears to be fairly widespread among bivalve molluscs,' says Maria Skazina, a research associate at the ...
Helping childhood-onset lupus patients stay healthy as adults
2021-03-30
DALLAS - March 30, 2021 - UT Southwestern researchers have identified factors that put patients with childhood-onset lupus at elevated risk for poor outcomes, such as end-stage renal disease or death, as they transition from pediatric to adult health care. The findings, published online in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, emphasize the precarious nature of this period and shine a spotlight on areas prime for intervention to help protect these vulnerable patients.
Patients with chronic diseases that used to be fatal early in life now often survive to live long lives. However, says study senior author END ...
Infants' language skills more advanced than first words suggest
2021-03-30
Babies can recognise combinations of words even before they have uttered their first word, a study suggests, challenging ideas of how children learn language.
Assessments in 11-12 month-olds show that infants at the cusp of talking are already processing multiword phrases such as 'clap your hands'.
Researchers say the study is the first to provide evidence that young children can pick up and understand multiword sequences before they can talk or begin producing such combinations themselves.
The findings suggest that babies learn individual words and more complex phrases at the same time, which challenges the perspective that they progress from single words to phrases and sentences, experts say.
It may also explain why adults who learn a new language in later life ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
[Press-News.org] Big data tells story of diversity, migration of math's eliteAnalysis of nearly 250,000 mathematicians gives a picture of the world of math