(Press-News.org) 'A transmissible cancer was first discovered in dogs in the middle of the 19th century. It is transmitted sexually from a sick dog to a healthy one, the cancer cells themselves being the infective agent. In the 1990s, a contagious cancer was discovered in the Tasmanian devil. Since the cancer was found in only two species of mammals, scientists used to think that it is quite rare in the nature. However, time has come to reconsider this view. A transmissible cancer appears to be fairly widespread among bivalve molluscs,' says Maria Skazina, a research associate at the Department of Applied Ecology at St Petersburg University and the first author of the publication in Scientific Reports.
Disseminated neoplasia (DN) is a large-scale, fatal cancer disease of bivalve molluscs, which can be compared to leukemia in vertebrates. Diseased mussels have cancer cells, which circulate in the hemolymph, a functional analogue of blood. As neoplasia develops, they infiltrate all tissues and organs, disrupting their work.
The causes of this disease were described for the first time in 2016 in an article published by a group of scientists under the leadership of by Michael Metzger in Nature. The authors showed that disseminated neoplasia was a transmissible cancer lineage. Its cells have their own genotype, different from those of the molluscan hosts. In a way, they are parasites transmitted from sick individuals to healthy ones.
'A study proposing a mechanism of the transfer of cancer cells between individuals was published last year. When the mussel is under stress, the cells of its haemolymph can leave the body, exist for some time in the environment and then invade other mussels. This process has been observed in healthy molluscs. Cancer cells, it would seem, might use this mechanism too,' says Maria Skazina. 'However, this is only a hypothesis. To test it, sophisticated experimental research is necessary'.
Mussels Mytilus are important commercial invertebrates. Two genetic lineages of transmissible cancer are known in them: BTN1 and BTN2 (BTN stands for bivalve transmissible neoplasia). Both of them originated from the Pacific mussel Mytilus trossulus, which is also found in the Far Eastern and Northern seas of Russia.
'So far, BTN1 lineage has been found in a single mussel population at the Pacific coast of North America. BTN2 is much more widespread. Before our research, it had been found in several mussel species in Europe and South America, though not in the parental species Mytilus trossulus,' says Maria Skazina.
In 2019, marine biologists from St Petersburg University, A.V. Zhirmunsky National Research Centre of Marine Biology, and the University of Helsinki joined forces to search for transmissible cancer lineages in the mussels of the Russian seas. To diagnose the disease, they developed an integrated approach, which included cytological and molecular genetic tests, and applied it to the mussels Mytilus trossulus from the Sea of Japan, in which disseminated neoplasia had been previously shown.
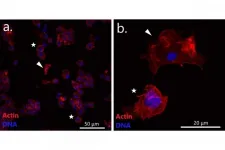
In the haemolymph of molluscs from the Gaydamak Bay near the port city of Nakhodka, flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry methods revealed neoplastic cells. They are large, have polyploid nuclei and an abnormal cytoskeleton resembling the spines of a bristling hedgehog. Genotyping of the haemolymph and other tissues by nuclear and mitochondrial characteristics revealed genetic 'chimerism' of the sick mussels, that is, the presence of more than one individual genotype. Multiple alleles (different forms of the same gene that determine the development of a particular trait) were separated by molecular cloning. All diseased mussels were found to have 'additional' genotypes corresponding to BTN2. This means that the scientists from St Petersburg University and their colleagues proved, for the first time, the presence of BTN2 in Mytilus trossulus as well as the presence of transmittable cancer in mussels from the Sea of Japan and the Northwest Pacific.
At the next stage of the research, the scientists used molecular phylogenetic methods to compare the sequences of the mitochondrial BTN genes obtained by them with all the homologous sequences of the mussels themselves stored in the NCBI genetic bank. It turned out that the mitochondria of BTN2 are most similar to those of Mytilus trossulus from the Russian seas. It was probably there that 'patient zero' lived, the mussel that 'gave birth' to this transmissible cancer.
The Baltic Sea mussels were also shown to have BTN2. In 2014, Polish biologists found an unusual mitochondrial genotype in a Baltic mussel, which they interpreted as the genotype of Mytilus trossulus. It is now clear that this was not a mussel genotype, but a BTN2 genotype. It appears that the transmissible cancer that the scientists were looking for in the Far East could be found much closer to St Petersburg. Whether this disease is common among the molluscs of the Baltic Sea remains to be found out.
'This disease is so virulent for invertebrates because they do not have a developed immune system that can reliably distinguish alien cells from their own. Transmissible cancer of molluscs cannot harm humans in any way. However, the disease can be detrimental for the mussel marine culture. We do not yet know how widespread transmissible cancer is among mussels in Russia,' says Maria Skazina.
The scientists now continue to search for transmissible cancer in mussels in different seas of Russia. Preliminary evidence suggests that it is found not only in mussels in the Sea of Japan and the Baltic Sea and that its diversity is not limited to BTN2 lineage. They are also developing a method for rapid diagnosis of the disease in order to monitor it in natural and commercial populations of molluscs.
'Hopefully, our work might be of help for comparative oncology. I think that mussels, as a research model, can tell a lot about the mechanisms of the spread of cancer in different species, including humans,' notes Maria Skazina.
INFORMATION:
DALLAS - March 30, 2021 - UT Southwestern researchers have identified factors that put patients with childhood-onset lupus at elevated risk for poor outcomes, such as end-stage renal disease or death, as they transition from pediatric to adult health care. The findings, published online in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, emphasize the precarious nature of this period and shine a spotlight on areas prime for intervention to help protect these vulnerable patients.
Patients with chronic diseases that used to be fatal early in life now often survive to live long lives. However, says study senior author END ...
Babies can recognise combinations of words even before they have uttered their first word, a study suggests, challenging ideas of how children learn language.
Assessments in 11-12 month-olds show that infants at the cusp of talking are already processing multiword phrases such as 'clap your hands'.
Researchers say the study is the first to provide evidence that young children can pick up and understand multiword sequences before they can talk or begin producing such combinations themselves.
The findings suggest that babies learn individual words and more complex phrases at the same time, which challenges the perspective that they progress from single words to phrases and sentences, experts say.
It may also explain why adults who learn a new language in later life ...
The first online advertisement was a banner for AT&T that appeared on the HotWired.com website in 1994, when there were just 30 million internet users worldwide. Today, 57% of the world's population has access to the internet and advertising technology has advanced to the point that by 2018 the digital advertising market in Europe alone was worth 55 billion euros. Of this amount, 16.8 billion euros is accounted for by programmatic advertising, which uses artificial intelligence to automate much of the buying and selling of internet advertising.
A new report, published by Open Evidence, a ...
Water quality management in the ocean often targets visible pollution sources such as sewage, rivers or ships. A new global study, led by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, reveals that invisible groundwater discharges may be just as important driving nitrogen into coastal waters.
As we enter the United Nations' Decade of the Oceans, a new research study shed light on an often overlooked source of impact on the coastal ecosystems.
The study, which examined groundwater discharges at more than 200 locations worldwide, showed that groundwater is the major source of nitrogen and phosphorus to the ocean at many locations, including some areas in the Baltic Sea.
"Groundwater is essentially invisible and difficult to investigate. That ...
In order to enable large-scale hydrogen production using solar energy, particulate photocatalysts are being researched as a simple and cost-effective solution to splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen. It is necessary to develop a photocatalyst that can efficiently use visible light, which accounts for a large part of solar energy, in the water decomposition reaction. Barium tantalum oxynitride (BaTaO2N) is an oxynitride semiconductor material that absorbs visible light up to 650 nm and has a band structure capable of decomposing water into hydrogen and oxygen. Until very recently, it had not been possible to load BaTaO2N granules with co-catalyst fine particles, which are reaction ...
Female doctors who suffer domestic abuse can feel unable to get help due to perceptions that it "should not happen to a doctor" and a judgemental culture in medical settings, a new study suggests.
Victim-survivors who work as doctors often do not feel able to talk about abuse confidentially and fear the consequences of reporting it.
Researchers from the University of Southampton interviewed twenty-one female doctors who had previously left an abusive relationship about their experience of domestic abuse, barriers they faced when seeking help, and the impact on their work. The findings have been published in the British Journal of General Practice.
Dr Emily Donovan, who led the study from the University of Southampton's Primary Care Research Centre said: "Domestic ...
Education is considered one of the most critical personal capital investments. But formal educational attainment doesn't necessarily pay off in job satisfaction, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
In fact, there is almost no relationship between the two, according to "Does Educational Attainment Promote Job Satisfaction? The Bittersweet Trade-offs Between Job Resources, Demands and Stress," forthcoming in the Journal of Applied Psychology from Brittany Solomon (Hall), assistant professor of management, and Dean Shepherd, the Ray and Milann Siegfried ...
Researchers at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have developed a new framework for different factors influencing how a child's brain is "wired" to learn to read before kindergarten.
This may help pediatric providers identify risks when the brain is most responsive to experiences and interventions. This "eco-bio-developmental" model of emergent literacy, described in the journal JAMA Pediatrics, reinforces the potential of early screening, prevention, and intervention during pediatric clinic visits in early childhood.
This kind of model is advocated by the American Academy ...
Remote monitoring using airborne devices such as drones or satellites could revolutionise the effectiveness of nature-based solutions (NBS) that protect communities from devastating natural hazards such as floods, storms and landslides, say climate change experts from the University of Surrey.
Grey structural measures (a collective term for engineering projects that use concrete and steel) like floodgates, dams, dikes and sea walls are still the most common methods to guard against natural hazards. However, these 'grey measures' are expensive and lack the long-term flexibility and sustainability needed to help communities manage their growing population and address the planet's ongoing struggle against urbanisation ...
Scientists have discovered that tracking malaria as it develops in humans is a powerful way to detect how the malaria parasite causes a range of infection outcomes in its host.
The study, found some remarkable differences in the way individuals respond to malaria and raises fresh questions in the quest to understand and defeat the deadly disease.
Malaria, caused by the parasite - Plasmodium falciparum - is a huge threat to adults and children in the developing world. Each year, around half a million people die from the disease and another 250 million are infected. Malaria parasites are spread to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes.
The outcomes that follow a malaria infection can vary from no symptoms to life-threatening ...