(Press-News.org) Water quality management in the ocean often targets visible pollution sources such as sewage, rivers or ships. A new global study, led by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, reveals that invisible groundwater discharges may be just as important driving nitrogen into coastal waters.
As we enter the United Nations' Decade of the Oceans, a new research study shed light on an often overlooked source of impact on the coastal ecosystems.
The study, which examined groundwater discharges at more than 200 locations worldwide, showed that groundwater is the major source of nitrogen and phosphorus to the ocean at many locations, including some areas in the Baltic Sea.
"Groundwater is essentially invisible and difficult to investigate. That is why coastal water quality managers often overlook groundwater discharges to the oceans," says Isaac Santos, professor in marine chemistry at the University of Gothenburg, who led the study in collaboration with thirteen worldwide universities.
"Nitrogen pollution is a major threat to marine biodiversity and a worldwide concern. Surprisingly, our global analysis revealed that groundwater nitrogen discharge exceeds river nitrogen discharge at 60 percent of the sites where both sources have been quantified."
Groundwater accumulates nitrogen from fertilisers used on crops, and may take decades to release this nitrogen to the ocean. When the nitrogen reaches the ocean, it increases algal biomass and decreases marine biodiversity and eventually fisheries.
Many lakes and rivers are connected to groundwater aquifers, geological formations that store groundwater. This high connectivity has prompted legislation to protect those groundwater-dependent ecosystems at the national and European level.
"However, this study shows that the coastal ocean is also highly connected to aquifers, so we need to consider groundwater aquifers as well when managing coastal water quality. For example, the Baltic Sea and many other coastal areas have suffered from nitrogen pollution for decades," says Stefano Bonaglia, a marine chemist at the University of Gothenburg who also participated in the study
They both emphasise that the management of groundwater discharges to the coastal ocean is challenging and may require decades of work. At the University of Gothenburg marine researchers will continue to investigate submarine groundwater discharge with a number of international research projects.
"Climate change, sea level rise and land use change will modify the chemistry of coastal aquifers, and we are now trying to understand how this will have long term impacts on submarine groundwater discharge", says Isaac Santos.
INFORMATION:
Contact:
Isaac Santos, professor in marine chemistry at the University of Gothenburg, Department of Marine Sciences
Telephone: +46 76 618 3146
E-mail: isaac.santos@gu.se
About the research
Title: Submarine groundwater discharge impacts on coastal nutrient biogeochemistry
Scientific journal: Nature Reviews Earth & Environment
Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s43017-021-00152-0
In order to enable large-scale hydrogen production using solar energy, particulate photocatalysts are being researched as a simple and cost-effective solution to splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen. It is necessary to develop a photocatalyst that can efficiently use visible light, which accounts for a large part of solar energy, in the water decomposition reaction. Barium tantalum oxynitride (BaTaO2N) is an oxynitride semiconductor material that absorbs visible light up to 650 nm and has a band structure capable of decomposing water into hydrogen and oxygen. Until very recently, it had not been possible to load BaTaO2N granules with co-catalyst fine particles, which are reaction ...
Female doctors who suffer domestic abuse can feel unable to get help due to perceptions that it "should not happen to a doctor" and a judgemental culture in medical settings, a new study suggests.
Victim-survivors who work as doctors often do not feel able to talk about abuse confidentially and fear the consequences of reporting it.
Researchers from the University of Southampton interviewed twenty-one female doctors who had previously left an abusive relationship about their experience of domestic abuse, barriers they faced when seeking help, and the impact on their work. The findings have been published in the British Journal of General Practice.
Dr Emily Donovan, who led the study from the University of Southampton's Primary Care Research Centre said: "Domestic ...
Education is considered one of the most critical personal capital investments. But formal educational attainment doesn't necessarily pay off in job satisfaction, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
In fact, there is almost no relationship between the two, according to "Does Educational Attainment Promote Job Satisfaction? The Bittersweet Trade-offs Between Job Resources, Demands and Stress," forthcoming in the Journal of Applied Psychology from Brittany Solomon (Hall), assistant professor of management, and Dean Shepherd, the Ray and Milann Siegfried ...
Researchers at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have developed a new framework for different factors influencing how a child's brain is "wired" to learn to read before kindergarten.
This may help pediatric providers identify risks when the brain is most responsive to experiences and interventions. This "eco-bio-developmental" model of emergent literacy, described in the journal JAMA Pediatrics, reinforces the potential of early screening, prevention, and intervention during pediatric clinic visits in early childhood.
This kind of model is advocated by the American Academy ...
Remote monitoring using airborne devices such as drones or satellites could revolutionise the effectiveness of nature-based solutions (NBS) that protect communities from devastating natural hazards such as floods, storms and landslides, say climate change experts from the University of Surrey.
Grey structural measures (a collective term for engineering projects that use concrete and steel) like floodgates, dams, dikes and sea walls are still the most common methods to guard against natural hazards. However, these 'grey measures' are expensive and lack the long-term flexibility and sustainability needed to help communities manage their growing population and address the planet's ongoing struggle against urbanisation ...
Scientists have discovered that tracking malaria as it develops in humans is a powerful way to detect how the malaria parasite causes a range of infection outcomes in its host.
The study, found some remarkable differences in the way individuals respond to malaria and raises fresh questions in the quest to understand and defeat the deadly disease.
Malaria, caused by the parasite - Plasmodium falciparum - is a huge threat to adults and children in the developing world. Each year, around half a million people die from the disease and another 250 million are infected. Malaria parasites are spread to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes.
The outcomes that follow a malaria infection can vary from no symptoms to life-threatening ...
A team of scientists has been using DESY's X-ray source PETRA III to analyse the structural changes that take place in an egg when you cook it. The work reveals how the proteins in the white of a chicken egg unfold and cross-link with each other to form a solid structure when heated. Their innovative method can be of interest to the food industry as well as to the broad field of research surrounding protein analysis. The cooperation of two groups, headed by Frank Schreiber from the University of Tübingen and Christian Gutt from the University of Siegen, with scientists at DESY and European XFEL reports the research in two articles in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Eggs are among the most versatile food ingredients. They can take the form of a gel or ...
Adding the nutrient selenium to diets protects against obesity and provides metabolic benefits to mice, according to a study published today in eLife.
The results could lead to interventions that reproduce many of the anti-aging effects associated with dietary restriction while also allowing people to eat as normal.
Several types of diet have been shown to increase healthspan - that is, the period of healthy lifespan. One of the proven methods of increasing healthspan in many organisms, including non-human mammals, is to restrict dietary intake of an amino acid ...
Humans are creating or exacerbating the environmental conditions that could lead to further pandemics, new University of Sydney research finds.
Modelling from the Sydney School of Veterinary Science suggests pressure on ecosystems, climate change and economic development are key factors associated with the diversification of pathogens (disease-causing agents, like viruses and bacteria). This has potential to lead to disease outbreaks.
The research, by Dr Balbir B Singh, Professor Michael Ward, and Associate Professor Navneet Dhand, is published in the international journal, Transboundary and Emerging Diseases.
They found a greater diversity ...
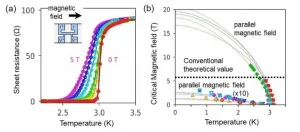
Superconductivity is known to be easily destroyed by strong magnetic fields. NIMS, Osaka University and Hokkaido University have jointly discovered that a superconductor with atomic-scale thickness can retain its superconductivity even when a strong magnetic field is applied to it. The team has also identified a new mechanism behind this phenomenon. These results may facilitate the development of superconducting materials resistant to magnetic fields and topological superconductors composed of superconducting and magnetic materials.
Superconductivity has been used in various technologies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ...