Cervical cancer testing tech could replace pap smears, save lives
Emerging techniques could help detect the virus leading to cervical cancer low-income and developing nations
2021-03-30
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, March 30, 2021 -- Emerging technologies can screen for cervical cancer better than Pap smears and, if widely used, could save lives both in developing nations and parts of countries, like the United States, where access to health care may be limited.
In Biophysics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, scientists at Massachusetts General Hospital write advances in nanotechnology and computer learning are among the technologies helping develop HPV screening that take the guesswork out of the precancer tests. That could mean better screening in places that lack highly trained doctors and advanced laboratories.
Cervical cancer is the world's fourth-most common cancer, with more than 500,000 cases diagnosed every year. Almost all cases of cervical cancer are caused by HPV, or human papillomavirus. Detecting precancer changes in the body gives doctors a chance to cure what could otherwise become a deadly cancer.
Pap smears, which were introduced in the 1940s, are subjective and not always reliable. The tests, which can detect about 80% of developing cervical cancer if given regularly, require high-quality laboratories, properly trained clinical doctors, and repeated screenings. These test conditions are not widely available in many countries or even in low-income and remote parts of wealthier nations.
"The Pap smear has done wonders in terms of reducing mortality from a cancer that is very treatable when caught early and almost invariably fatal when it is caught late," said author Cesar Castro, an oncologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School. "And it is not even a great test. Part of its imperfection is that there is subjectivity to it. The trained eye is the limiting step in the process. The untrained eye, or relatively untrained eye, can miss cancers."
The subjectivity of the test has led to a much higher death rate from cervical cancer in lower-income countries. The authors highlight a list of existing and emerging technologies that can be used to close the testing gap in those areas. They range from existing DNA testing and other Pap smear alternatives to next-generation technologies that use recent advances in nanotechnology and artificial intelligence.
One technique involves screening with tiny beads made of biological material that form a diamond shape when they contact HPV. Those shapes can be detected with powerful microscopes. When those microscopes are not available, a mobile phone app, built through machine learning, can be used to read them.
"Similar to COVID-19 testing, we have great technology in places like the United States that does not work well enough in other countries," said author Hyungsoon Im, a biomedical engineer at Massachusetts General Hospital and assistant professor at Harvard Medical School. "This is why there is great motivation to find next-generation, affordable technology to address this problem."
INFORMATION:
The article "Addressing cervical cancer screening disparities through advances in artificial intelligence and nanotechnologies for cellular profiling" is authored by Zhenzhong Yang, Jack Francisco, Alexandra S. Reese, David R. Spriggs, Hyungsoon Im, and Cesar M. Castro. The article will appear in Biophysics Reviews on March 30, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0043089). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0043089.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Biophysics Reviews publishes research studies and comprehensive review articles of new and emerging areas of interest to the biophysics community. The journal's focus includes experimental and theoretical research of fundamental issues in biophysics in addition to the application of biophysics in other branches of science, medicine, and engineering. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/bpr.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-30
WASHINGTON, March 30, 2021 -- As ethanol, biodiesel, and other biofuels continue to present challenges, such as competing with food security or lacking the technology for more efficient and low-cost production, microalgae are gaining momentum as a biofuel energy crop.
In their paper, published in the Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, Yangzhou University researchers in China show how a combination of monochromatic red and blue LED illumination on one type of microalga can enhance its growth and increase the biosynthesis of critical components, such ...
2021-03-30
New observations with the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope (ESO's VLT) indicate that the rogue comet 2I/Borisov, which is only the second and most recently detected interstellar visitor to our Solar System, is one of the most pristine ever observed. Astronomers suspect that the comet most likely never passed close to a star, making it an undisturbed relic of the cloud of gas and dust it formed from.
2I/Borisov was discovered by amateur astronomer Gennady Borisov in August 2019 and was confirmed to have come from beyond the Solar System a few weeks ...
2021-03-30
WASHINGTON, March 30, 2021 -- Scientists are developing tools to observe the biological machinery in in vivo animal models to be able to understand and better treat severe brain diseases like Alzheimer's disease and many other conditions. Holographic endoscopes attracted researchers' interest because of their potential to conduct minimally invasive observations inside the human body.
These tools can shed light on the biological processes occurring at the macromolecular and subcellular levels, which usually remain hidden from sight as most tissue is opaque to visible radiation. In APL Photonics, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the Leibniz Institute of Photonic Technology in Germany created a particularly narrow ...
2021-03-30
It makes evolutionary sense for long-lived animals to have complex social relationships - such as friends and enemies - researchers say.
Some species and individuals focus their energy on reproduction (live fast, die young), while "slow-living" animals prioritise survival and tend to live longer lives.
In the new paper, University of Exeter scientists argue that natural selection favours complex social structures among slow-living animals - meaning that knowing their friends and enemies is easier for animals with longer lifespans, and helps them live even longer.
Meanwhile, fast-lived species should only bother with such social relationships if it increases ...
2021-03-30
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated COVID-19 vaccine intentions among racially and ethnically diverse samples of health workers and the general population in the San Francisco Bay area.
Authors: Kevin Grumbach, M.D., of the San Francisco General Hospital and University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.1445)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
2021-03-30
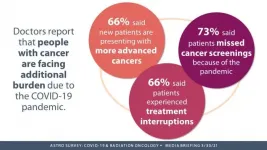
ARLINGTON, Va., March 30, 2021 -- Doctors who oversee cancer clinics say that new patients are arriving for treatment with more advanced disease than before the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new survey from the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO). The national survey of radiation therapy practice leaders fielded this winter also indicates that treatment postponements and deferrals that were common a year ago have largely subsided and that clinics continue to use a variety of enhanced safety measures to protect their patients and staff.
"One year into the COVID-19 pandemic, we already see the consequences of pandemic-driven drops in cancer screening and diagnostics," said Thomas J. Eichler, MD, FASTRO, ...
2021-03-30
Boston - For decades, the power of the placebo effect was thought to lie in patients' belief that they were -- or at least, could be -- receiving a pharmacologically active treatment. A new study by physician-researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) suggests that patients don't need to be deceived to receive benefit from treatment with placebo.
In a randomized clinical trial published in the journal PAIN, researchers found participants with moderate to severe irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) who were knowingly treated with a pharmacologically inactive pill -- referred to as an honest or open-label placebo -- reported clinically meaningful improvements in their IBS symptoms. People who received the open-label placebo experienced improvements ...
2021-03-30
LAWRENCE -- Recent incidents of racial discrimination and violence against Asians and Asian-Americans in the United States have prompted critical discussions about how to talk about such biases with younger age groups. New research from the University of Kansas shows using critical race media literacy, or examining how race and gender are addressed in popular culture, can be an effective way to discuss those topics and engage students.
KU researchers published a study in which they observed an American teacher using critical race media literacy to discuss racism and sexism in superhero movies in English as a foreign language classes in a South Korean high school. They argued that successful implementation ...
2021-03-30
Through his role on the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, UVA Health's Li Li, MD, PhD, MPH, has helped develop new lung cancer screening guidelines that expand screenings to more high-risk patients.
The new guidelines are focused on Americans at higher risk because of their history of smoking, which is the leading cause of lung cancer. There are two significant changes in the new guidelines. For those who are still smoking or quit less than 15 years ago, a yearly screening using a low-dose computed tomography (CT) scan is now recommended:
beginning at age 50, instead of age 55.
for anyone who has smoked 20 pack-years in their lifetime, instead of 30 pack-years. A pack-year equals smoking a pack of cigarettes a day for a year.
The ...
2021-03-30
Physicists from the University of Sussex have developed an extremely thin, large-area semiconductor surface source of terahertz, composed of just a few atomic layers and compatible with existing electronic platforms.
Terahertz sources emit brief light pulses oscillating at 'trillion of times per second'. At this scale, they are too fast to be handled by standard electronics, and, until recently, too slow to be handled by optical technologies. This has great significance for the evolution of ultra-fast communication devices above the 300GHz limit - such as that required for 6G mobile phone technology - something that is still fundamentally beyond the limit of current electronics.
Researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cervical cancer testing tech could replace pap smears, save lives
Emerging techniques could help detect the virus leading to cervical cancer low-income and developing nations