Widespread facemask use is vital to suppress the pandemic as lockdown lifts, say scientists
2021-03-31
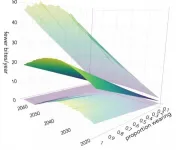
(Press-News.org) A new mathematical model suggests that the easing of lockdown must be accompanied by wider and more effective use of control measures such as facemasks even with vaccination, in order to suppress COVID-19 more quickly and reduce the likelihood of another lockdown.
The model, developed by scientists at the Universities of Cambridge and Liverpool, is published today in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface. It uses mathematical equations to provide general insights about how COVID-19 will spread under different potential control scenarios.
Control measures involving facemasks, handwashing and short-scale (1-2 metre) social distancing can all limit the number of virus particles being spread between people. These are termed 'non spatial' measures to distinguish them from a second category of 'spatial' control measures that include lockdown and travel restrictions, which reduce how far virus particles can spread. The new model compares the efficacy of different combinations of measures in controlling the spread of COVID-19, and shows how non-spatial control needs to be ramped up as lockdown is lifted.
"More effective use of control measures like facemasks and handwashing would help us to stop the pandemic faster, or to get better results in halting transmission through the vaccination programme. This also means we could avoid another potential lockdown," said Dr Yevhen Suprunenko, a Research Associate in the University of Cambridge's Department of Plant Sciences and first author of the paper. The authors stress that their predictions rely on such non-spatial control measures being implemented effectively.
The model also considered the socio-economic impact of both types of measure, and how this changes during the pandemic. The socio-economic consequences of spatial measures such as lockdown have increased over time, while the cost of non-spatial control measures has decreased -for example, facemasks have become more widely available and people have become used to wearing them.
"Measures such as lockdowns that limit how far potentially infected people move can have a stronger impact on controlling the spread of disease, but methods that reduce the risk of transmission whenever people mix provide an inexpensive way to supplement them," said Dr Stephen Cornell at the University of Liverpool, co-author of the paper.
The model arose from a broader research programme to identify control strategies for plant diseases threatening staple crops. By using a mathematical approach rather than a conventional computer simulation model, the authors were able to identify - for a wide range of scenarios - general insights on how to deal with newly emerging infectious diseases of plants and animals.
"Our new model will help us study how different infectious diseases can spread and become endemic. This will enable us to find better control strategies, and stop future epidemics faster and more efficiently," said Professor Chris Gilligan in the University of Cambridge's Department of Plant Sciences, co-author of the paper.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
With shark bites increasing in countries like Australia - scientists say the use of personal electronic deterrents is an effective way to prevent future deaths and injuries which could save the lives of up to 1063 Australians along the coastline over the next 50 years.
The research, published in scientific journal Royal Society Open Science, shows that while shark bites are rare events, strategies to reduce shark-bite risk are also valuable because they can severely affect victims and their support groups - with one third of victims experiencing post-traumatic stress ...
2021-03-31
Heart attacks in young adults are twice as likely to be fatal in those with inflammatory conditions like psoriasis, lupus or rheumatoid arthritis. That's the finding of a study published today in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
At least 2% of people in Europe and worldwide have systemic inflammatory diseases, which often affect multiple organ systems. Many of these systemic inflammatory diseases are driven by autoimmunity, meaning the body's immune system attacks itself. Psoriasis is the most common and causes red, itchy, scaly patches on the skin, and can also cause inflammation in the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis leads to inflammation in joints of the hands and feet and in other organ systems. In systemic ...
2021-03-31
Red algae that grow in Cornwall's Fal Estuary are genetically unique, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists studied the population genetics of Phymatolithon calcareum, a coralline red algal species that forms maerl beds in shallow coastal seas from Portugal to Norway.
Large maerl beds fulfil a similar role to tropical coral reefs, providing habitats and vital shelter for hundreds or even thousands of fish and invertebrates. These algae also play an important role in storing carbon.
The findings reveal genetic differences are "structured geographically", with slight variations between populations sampled from across this large geographic area.
However, maerl ...
2021-03-31
Human disturbance in urban environments makes some squirrels fail, but others perform better in novel problem-solving.
Unlike natural environments, urban areas have artificial buildings, traffics, less greenery and, most prominently, more humans. Despite these seemingly 'harsh' or stressful characteristics, some wildlife like the Eurasian red squirrel have chosen to settle down in urban environments, and they thrive. Urban wildlife often show higher behavioral flexibility and increased ability to solve novel problems, and thus can exploit new resources. However, which characteristics of urban environments influence animals' performance, and their relative importance, have remained ...
2021-03-31
Scientists have discovered a new genetic disease, which causes some children's brains to develop abnormally, resulting in delayed intellectual development and often early onset cataracts.
The majority of patients with the condition, which is so new it doesn't have a name yet, were also microcephalic, a birth defect where a baby's head is smaller than expected when compared to babies of the same sex and age.
Researchers from the universities of Portsmouth and Southampton found that changes in a gene called coat protein complex 1 (COPB1) caused this rare genetic disease.
Now the variant has been identified, it will help clinicians come up with targeted interventions to help patients and their families, also opening the door to screening and prenatal ...
2021-03-31
A new study examining how people with severe and profound intellectual disabilities resist activities while in care recommends that institutions improve training to help carers better understand non-verbal cues, as well as offer greater flexibility to allow individual preferences to take priority over institutional schedules.
The research, published in the journal Sociology of Health and Illness, investigated how people with limited language ability expressed their wishes and preferences, and how their support workers responded. It was carried out at a residential home and a day care centre in the UK.
The study, by Dr Clare Nicholson of St Mary's University, Twickenham, and Dr Mick ...
2021-03-31
In the run up to hibernation, grizzly bears go on a colossal binge, consuming as many calories as possible to get them through the long winter. Yet, little was known about how much energy the massive mammals use as they shamble around their rugged territories. 'Moving across the landscape in search of food can be a huge energetic expense for some animals', Carnahan says. Fortunately, the Washington State University Bear Research, Education and Conservation Center (WSU BREC), where Carnahan is based, is home to 11 bears, including four that formerly lived in Yellowstone National Park, so he and Charles Robbins (also at WSU BREC) decided to measure the animals' metabolic rates as they sauntered on the flat, and up and down gradients to find out how much ...
2021-03-31
New research published in Anaesthesia (a journal of the Association of Anaesthetists) challenges the guidance that special aerosol precautions are only needed when using oxygen therapies for COVID-19 patients, and raises concerns about safety of staff and patients on hospital wards, if they are not protected from infectious aerosols.
The study set out to examine whether oxygen therapies used for patients with severe COVID-19 produce large amounts of small respiratory particles called aerosols, which can transmit virus and can evade routine precautions used on hospital wards. ...
2021-03-31
Rock art of human figures created over thousands of years in Australia's Arnhem Land has been put through a transformative machine learning study to analyse style changes over the years.
The study has tested different styles labelled 'Northern Running figures', 'Dynamic figures', 'Post Dynamic figures' and 'Simple figures with Boomerangs' to understand how these styles relate to one another.
Working with the Mimal and Marrku Traditional Owners of the Wilton River area in Australia's Top End, South Australian researchers led by Flinders University archaeologist Dr Daryl Wesley have taken a closer look at the art of this region.
Flinders researcher Jarrad Kowlessar and the team used machine learning ...
2021-03-31
Highlights
A newly developed tool assesses patients' home dialysis experience.
The 26-item Home Dialysis Care Experience instrument will be a resource for future research use, clinical care, and quality improvement initiatives among home dialysis facilities and organizations.
Washington, DC (March 30, 2021) -- Researchers have developed a new tool to assess patients' opinions and experience concerning home dialysis care. The tool is described in an upcoming issue of CJASN.
Home dialysis, which includes both peritoneal dialysis and home hemodialysis, allows patients to receive their dialysis treatments at home, gives patients independence and flexibility ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Widespread facemask use is vital to suppress the pandemic as lockdown lifts, say scientists