Thermal power nanogenerator created without solid moving parts
Proposed thermal energy harvester may find applications in waste heat recovery, power supplies within microelectromechanical systems, solar power, space power systems
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, March 31, 2021 -- As environmental and energy crises become increasingly more common occurrences around the world, a thermal energy harvester capable of converting abundant thermal energy -- such as solar radiation, waste heat, combustion of biomass, or geothermal energy -- into mechanical energy appears to be a promising energy strategy to mitigate many crises.
The majority of thermal power generation technologies involve solid moving parts, which can reduce their reliability and lead to frequent maintenance. This inspired researchers in China to develop a thermal power nanogenerator without solid moving parts.
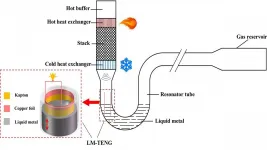
In Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, the researchers propose a thermal power nanogenerator, called a thermoacoustically driven liquid-metal-based triboelectric nanogenerator, or TA-LM-TENG, which converts thermal energy into electrical energy.
"This generator includes two parts: a thermoacoustic engine and a liquid-metal-based triboelectric nanogenerator (LM-TENG)," said Guoyao Yu, a professor at the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
First, the thermoacoustic engine converts thermal energy into acoustic energy via oscillatory thermal expansion and contraction of a gas. Next, the LM-TENG converts acoustic energy into electrical energy via the coupling effect of contact electrification and electrostatic induction.
When heating the heat exchanger of the thermoacoustic engine, "the gas in the engine starts a spontaneous oscillation," Yu said. "The oscillatory motion of the gas pushes a liquid metal column flowing back and forth within a U-shaped tube. This makes the liquid metal periodically immerse and separate with a polyimide film, generating an alternate voltage at the electrodes. This extracts electrical power from the TA-LM-TENG."
A TA-LM-TENG's most desirable feature is the lack of any solid moving parts that can break, which will ensure the nanogenerator is more reliable and help it achieve a long lifespan.
"This generator also promises a theoretically high heat-to-electric conversion efficiency," said Yu. "And we designed and constructed a conceptual prototype to validate the feasibility of our concept. In preliminary experiments, the highest open-circuit voltage amplitude of 15 volts was achieved, which implies that our concept has been well demonstrated."
As long as the proposed thermal power nanogenerator can be reduced in size, it "shows potential for applications, such as waste heat recovery, power supply within (microelectromechanical systems), solar power, and space power systems," said Yu.
INFORMATION:
The article "Thermoacoustically driven liquid-metal-based triboelectric nanogenerator: A thermal power generator without solid moving parts" is authored by Shunmin Zhu, Guoyao Yu, Wei Tang, Jianying Hu, and Ercang Luo. It appears in Applied Physics Letters (DOI 10.1063/5.0041415) and can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0041415.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Letters features rapid reports on significant discoveries in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/apl.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
"SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV are highly similar genetically, generate a homologous repertoire of viral proteins, and use the same receptor to infect human cells. However, despite these similarities, there are also important differences between the two viruses", says Ronald Dijkman from the Institute for Infectious Diseases (IFIK) at the University of Bern. For example, SARS-CoV infection is characterized by severe disease and inflammation in the lower respiratory tract and infected individuals are only contagious after the onset of symptoms, making it easier to identify and interrupt infection chains.
In contrast, SARS-CoV-2 preferentially replicates in the upper airways (nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea) and can be efficiently transmitted ...
2021-03-31
Companies could be hiring that bad boss on purpose. According to new research in the Journal of Business Ethics, the "dark" personality traits - questionable ethical standards, narcissistic tendencies - that make a boss bad also make that person much more likely to go along with manipulating earnings and may be the reason they got the job in the first place.
Co-authors Nick Seybert (University of Maryland's Robert H. Smith School of Business), Ling Harris (University of Nebraska-Lincoln), Scott Jackson (University of South Carolina) and Joel Owens (Portland State University) studied the process of hiring executive ...
2021-03-31
ATLANTA -- Assisted living communities can improve the quality of life for residents with dementia by approaching them as individuals and attempting to include all residents in activities, according to a study led by a Georgia State University gerontology researcher.
The typical "activity programming" at many assisted living residences can leave people with dementia on the sidelines, according to the study, "Meaningful Engagement Among Assisted Living Residents With Dementia: Successful Approaches," published in the Journal of Applied Gerontology.
The study found that the keys to improving ...
2021-03-31
ANN ARBOR--By April last year, up to 28 free-standing alternate care sites ranging in size from 50 to 3,000 beds were underway or finished in the U.S.--the Michigan Medicine Field Hospital among them.
This 500-bed alternate care site was planned and construction underway from March through May to meet the estimated surge in COVID-19 patients, expected to overrun hospitals nationwide and in Michigan. Sue Anne Bell, assistant professor of nursing and a disaster expert, was one of the field hospital's five-member leadership team.
Bell and her ...
2021-03-31
But the study also shows for the first time that performance may be improved by using super recognisers - people who are very skilled at recognising faces. It also reveals that masks do make recognising someone's emotions more difficult.
There are many questions surrounding face masks and the impact that masks will have on face identification. Can we recognise the faces of people who we know well if they are wearing a mask? And, relevant to policing and security scenarios or a supermarket ID check, can an unfamiliar face be recognized across images if it is masked? And how do masks impact our ability to recognize a person's emotions?
Dr Noyes is Senior Lecturer in Cognitive Psychology and conducted the study, published by the Royal ...
2021-03-31
Research conducted in U.S. national parks has focused largely on five iconic parks, with more than a third of academic papers focused on Yellowstone National Park, researchers from North Carolina State University found in a new analysis.
They also found that the number of publications per year increased during the 1990s and 2000s, but has dropped since 2013. The findings, published in the journal Conservation Science and Practice, were drawn from an analysis of nearly 7,000 published, peer-reviewed studies conducted at U.S. designated national parks since 1970.
"Looking at the data was a surprise and perhaps a wake-up call," said the study's lead author Jelena Vukomanovic, assistant professor of ...
2021-03-31
Forty million people living in the Kanto region of Japan, which includes Tokyo, may be able to blame a meandering ocean current for increasing hot and humid summers, according to an analysis conducted by an international team of researchers. The Kuroshio Current flows north, bringing warm water from the tropics to Japan's southern coast. Since 2017, however, it has meandered off its traditional path, turning south before continuing north again. Now, scientists have found that the "large meander" is responsible for the uptick in humidity and temperature.
The researchers, from Tohoku University in Japan and the University of Hawaii in the United States, published ...
2021-03-31
Osaka, Japan - Streptococcus pyogenes is one of the most important bacterial causes of human skin infections. If S. pyogenes invades deep into the tissue, it can cause life-threatening illnesses, such as sepsis and toxic shock. With its limited supply of carbohydrates, the skin is generally an effective barrier against infection and not a good surface for the survival of S. pyogenes. To survive successfully and invade deep into the tissue, bacteria must be able to find a source of nutrients and also evade the skin's immune defenses.
Now, an international ...
2021-03-31
Scientists from Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with Russian colleagues and researchers from Technical University of Denmark the first time have experimentally proved the existence of a two-dimensional (2D) curved flux of plasmonic quasiparticles, a plasmonic hook. A flat 2D hook is smaller than a 3D hook and possesses new properties, due to them, the researchers consider it as the most promising transmitter in high-speed microoptical circuits. The research findings are published in Applied Physics Letters (IF: 3,597; Q1) academic journal.
Electrons transmit information in existing calculation devices. The scientists suppose if electrons are replaced ...
2021-03-31
New research shows how drinking sugary beverages early in life may lead to impaired memory in adulthood.
The study, published today in Translational Psychiatry, also is the first to show how a specific change to the gut microbiome -- the bacteria and other microorganisms growing in the stomach and intestines -- can alter the function of a particular region of the brain.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, sugar-sweetened beverages are a leading source of added sugars in Americans' diets. Nearly two-thirds of young people in the United States consume at least one sugary drink each day.
Neuroscientist Scott Kanoski, associate professor of biological sciences at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, has studied the link between ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Thermal power nanogenerator created without solid moving parts
Proposed thermal energy harvester may find applications in waste heat recovery, power supplies within microelectromechanical systems, solar power, space power systems