Kuroshio current may be responsible for climatic discomfort in Tokyo, scientists find
2021-03-31
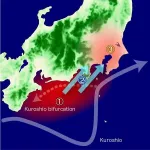
(Press-News.org) Forty million people living in the Kanto region of Japan, which includes Tokyo, may be able to blame a meandering ocean current for increasing hot and humid summers, according to an analysis conducted by an international team of researchers. The Kuroshio Current flows north, bringing warm water from the tropics to Japan's southern coast. Since 2017, however, it has meandered off its traditional path, turning south before continuing north again. Now, scientists have found that the "large meander" is responsible for the uptick in humidity and temperature.
The researchers, from Tohoku University in Japan and the University of Hawaii in the United States, published their results online on Feb. 1 in the Journal of Climate, a journal of the American Meteorological Society.
"In recent years, it has become clear that the ocean influences climate," said first author Shusaku Sugimoto, associate professor of geophysics in the Graduate School of Science at Tohoku University. "Our study shows that the Kuroshio influences the regional climate - especially through the greenhouse effect of water vapor, contributing to significantly warmer temperatures."
The researchers used satellite data from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), as well as data from the Automated Meteorological Data Acquisition System stations operated by the Japan Meteorological Agency, to examine 18 summers since 2003.
The last large meander occurred for a year from 2004 to 2005 before starting again in 2017. Controlling for other climatic events, such as storms, and considering global warming trends, the researchers assessed the differences in summers during typical summers and summers during which Kuroshio's path took a large meander.
"We found that the surface air temperature in the Kanto district increased by about 0.6 degrees Celsius as a result of the Kuroshio large meander," Sugimoto said. "As a mechanism of the warming, we discovered that the Kuroshio large meander increases evaporation and the water vapor flowing into the Kanto region, leading to a hot summer through a local greenhouse effect."
Using Thom's index, a widely used standard of human discomfort based on temperature and humidity, the team found large meander summers resulted in 13.1 days of most people experiencing discomfort. That's a 160% increase over the 8.1 discomfort days of non-large meander summers.
"This is a result that affects the lives of many people," Sugimoto said. "Our analysis showed the Kuroshio path state is responsible for the climatic comfort of living in Tokyo, Japan, and our approach is also applicable in other coastal cities worldwide."
The researchers plan to apply their work to improve both climate and local weather forecasts, according to Sugimoto, so that people may be better prepared to handle higher temperatures and more humidity.
"The results of this research are expected to contribute to the reduction of heatstroke risk and the formulation of climate change adaptation plans," Sugimoto said. "This finding detects the influence of the ocean on regional climate, and we hope that it will contribute to the improvement of weather and seasonal forecasts."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
Osaka, Japan - Streptococcus pyogenes is one of the most important bacterial causes of human skin infections. If S. pyogenes invades deep into the tissue, it can cause life-threatening illnesses, such as sepsis and toxic shock. With its limited supply of carbohydrates, the skin is generally an effective barrier against infection and not a good surface for the survival of S. pyogenes. To survive successfully and invade deep into the tissue, bacteria must be able to find a source of nutrients and also evade the skin's immune defenses.
Now, an international ...
2021-03-31
Scientists from Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with Russian colleagues and researchers from Technical University of Denmark the first time have experimentally proved the existence of a two-dimensional (2D) curved flux of plasmonic quasiparticles, a plasmonic hook. A flat 2D hook is smaller than a 3D hook and possesses new properties, due to them, the researchers consider it as the most promising transmitter in high-speed microoptical circuits. The research findings are published in Applied Physics Letters (IF: 3,597; Q1) academic journal.
Electrons transmit information in existing calculation devices. The scientists suppose if electrons are replaced ...
2021-03-31
New research shows how drinking sugary beverages early in life may lead to impaired memory in adulthood.
The study, published today in Translational Psychiatry, also is the first to show how a specific change to the gut microbiome -- the bacteria and other microorganisms growing in the stomach and intestines -- can alter the function of a particular region of the brain.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, sugar-sweetened beverages are a leading source of added sugars in Americans' diets. Nearly two-thirds of young people in the United States consume at least one sugary drink each day.
Neuroscientist Scott Kanoski, associate professor of biological sciences at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, has studied the link between ...
2021-03-31
LA JOLLA, CA--The faster-spreading B.1.1.7 variant of SARS-CoV-2 first detected in the United Kingdom, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, is quickly on its way to becoming the dominant variant of the virus in the United States, according to a study from scientists at Scripps Research and the COVID-19 test maker Helix.
The findings, which appear today in Cell, suggest that future COVID-19 case numbers and mortality rates in the United States will be higher than would have been otherwise. The analysis suggests that the variant, which has been detectable in an increasing proportion of SARS-CoV-2 samples, is 40-50 percent more transmissible than SARS-CoV-2 lineages that were previously dominant. Other studies have found ...
2021-03-31
Transport Network Companies (TNCs) not only increased road congestion but were also net substitute for public transit reducing PT ridership by almost 9%
The reduction in private vehicle ownership due to TNCs was insignificant
Research findings can provide valuable insights for transportation policy and regulation
Singapore, 31 March 2021 - Transport Network Companies (TNCs) or ridesharing companies have gained widespread popularity across much of the world, with more and more cities adopting the phenomenon. While ridesharing has been credited with being more environmentally friendly than taxis and private vehicles, is that really the case today or do they rather contribute to urban congestion?
Researchers at the Future Urban Mobility ...
2021-03-31
The younger generations are willing to put their money where their mouth is when it comes to sustainable living. In a study questioning both commitment to sustainable behaviors and willingness to trade better pay to work for a more sustainable-minded company, the surveyed young adults in Japan made their preferences clear.
The results were published on Jan. 31 in a special issue of the Journal of Cleaner Production focused on achieving the END ...
2021-03-31
Until now, researchers have believed that dark energy accounted for nearly 70 percent of the ever-accelerating, expanding universe.
For many years, this mechanism has been associated with the so-called cosmological constant, developed by Einstein in 1917, that refers to an unknown repellant cosmic power.
But because the cosmological constant--known as dark energy--cannot be measured directly, numerous researchers, including Einstein, have doubted its existence--without being able to suggest a viable alternative.
Until now. In a new study by researchers at the University of Copenhagen, a model was tested that replaces dark energy with a dark matter in the form of magnetic forces.
"If what we discovered is accurate, it would upend our ...
2021-03-31
Nagoya University researchers have identified a gene that plays a crucial role in regenerating neurons of African clawed frog tadpoles, which has an unusually high capacity for nerve regeneration. Their study, recently published in the journal iScience, showed that introducing the gene into mice with spinal cord injury (SCI) led to a partial recovery of their lost motor functions. These findings could contribute to the development of a new therapy for SCI, which often causes a person to experience permanent and severe physical and neurological disabilities.
Repairing spinal cord injuries in humans and other mammals is difficult, partly because ...
2021-03-31
Cancer patients generally have a higher thrombotic risk than the population at large. This risk is influenced on the one hand by patient-specific factors and the cancer itself and, on the other, by the cancer treatment, that is to say surgery, radiotherapy, or specific chemotherapeutics, which can increase the risk.
In the last few years, immune checkpoint inhibitors have increasingly been used to treat many different types of cancer. By activating the immune system against the tumour, these drugs improve the prognosis for patients with malignant melanoma, ...
2021-03-31
Tropical cyclones -- known as typhoons in the Pacific and as hurricanes in the Atlantic -- are fierce, complex storm systems that cause loss of human life and billions of dollars in damage every year. For decades, scientists have studied each storm, striving to understand the system yet unable to fully measure every intricate variable. Now, the convergence of new observational tools and the launch of an inclusive database may elucidate the innerworkings of tropical cyclones in the Western North Pacific and South China Sea.
Three papers were published in the latest issue of Advances in Atmospheric Science. One paper, led by the Chinese Meteorological Administration (CMA), focuses on a new tropical cyclone database, and the other two, led by The Petrel Meteorological ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Kuroshio current may be responsible for climatic discomfort in Tokyo, scientists find