(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA--The faster-spreading B.1.1.7 variant of SARS-CoV-2 first detected in the United Kingdom, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, is quickly on its way to becoming the dominant variant of the virus in the United States, according to a study from scientists at Scripps Research and the COVID-19 test maker Helix.
The findings, which appear today in Cell, suggest that future COVID-19 case numbers and mortality rates in the United States will be higher than would have been otherwise. The analysis suggests that the variant, which has been detectable in an increasing proportion of SARS-CoV-2 samples, is 40-50 percent more transmissible than SARS-CoV-2 lineages that were previously dominant. Other studies have found evidence that the B.1.1.7 variant may be about 50 percent more likely to cause fatal COVID-19.
"B.1.1.7 rapidly became the dominant SARS-CoV-2 variant in the U.K. and other countries after its emergence late last year, and the U.S. is now on a similar trajectory," says study co-senior author Kristian Andersen, PhD, a professor in the Department of Immunology and Microbiology at Scripps Research and director of Infectious Disease Genomics at the Scripps Research Translational Research Institute. "We need immediate and decisive action to minimize COVID-19 morbidity and mortality."
In addition to Andersen, the other senior author was William Lee, PhD, vice president of science at Helix, which provides PCR-based COVID-19 testing to organizations across the United States. The study was also authored by Nicole Washington, PhD, associate director of research at Helix, and Karthik Gangavarapu of the Andersen Lab.
"B.1.1.7 has a doubling rate of a little over a week and an increased transmission rate of 40-50 percent, which means it could have a meaningful impact on public health," says Lee. "It is critical that we continue to monitor the spread of this and other emerging variants, but our current level of surveillance is inadequate and lags behind that of other countries. We need a more comprehensive national SARS-CoV-2 genomics surveillance program to address this."
The B.1.1.7 variant emerged in southern England last year and has since become the dominant variant in the U.K. In December, Andersen's team at Scripps Research with colleagues at University of California, San Diego confirmed the first evidence of the variant in California.
A pattern of dominance
The B.1.1.7 variant contains several mutations, including several in the gene that encodes the viral spike protein. These mutations increase the spike's ability to bind to the ACE2 receptor on human cells. Although there is no evidence yet that the B.1.1.7 variant can evade COVID-19 vaccines, public health officials fear its relatively high rate of spread will significantly worsen the pandemic before vaccines can end it.
Standard swab tests for the coronavirus check for distinctive genetic sequences at three sites on the viral genome; the B.1.1.7 variant, due to its mutations, shows up as positive for two of those sites, but negative for the third site, which is within the virus's spike gene.
The new analysis of roughly 500,000 Helix test results since July 2020 revealed that this two-of-three pattern, known as S-gene target failure, or SGTF, became consistently evident at a low frequency (0.2 percent) in mid-October. By the third week of February, it had risen to a frequency of 10.6 percent and was detected in patients from 25 different U.S. states and territories.
The SGTF pattern can occur with other SARS-CoV-2 variants that have spike gene mutations, but the researchers found by sequencing every SGTF sample they had from December through February, 662 of the 986 samples (67 percent) contained the B.1.1.7 variant. This suggests that the SGTF pattern on the swab tests can provide a quick albeit rough indication of B.1.1.7 prevalence.
Variant entered the country many times
The analysis also indicated that B.1.1.7 since December has accounted for a rapidly rising proportion of SGTF results--for example, reaching about 95 percent in California by mid-January. In addition to the 659 B.1.1.7 cases they detected via the SGTF method the researchers found three other cases of the B.1.1.7 variant among samples gathered as part of unbiased SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance efforts in California.
The 662 instances of B.1.1.7 sequenced in the study were from samples gathered in 10 U.S. states, although the researchers note that other testing labs covering a total of 33 U.S. states and territories have by now reported to the CDC at least one B.1.1.7 case.
The researchers' family tree-type analysis of the detected B.1.1.7 sequences show the variant has been introduced to the U.S. multiple times since at least late November 2020, especially in California and Florida, and in periods coinciding with increased travel, including Thanksgiving week.
The scientists also found that the variant, on the whole, appears to be spreading 40-50 percent faster than the variants of SARS-CoV-2 that previously dominated. They estimated that by the first week of February 2021, B.1.1.7 made up about 4.3 percent of COVID-19 cases in the U.S., including 4.2 percent of cases in California and about 11.5 percent of cases in Florida.
INFORMATION:
Support for the study was provided by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control (75D30121P10258, 75D30120C09795), the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (3U19AI135995-03S2, U19AI135995, U01AI151812), the National Institutes of Health (UL1TR002550), the Innovative Genomics Institute, and the New Frontiers in Research Fund provided by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Transport Network Companies (TNCs) not only increased road congestion but were also net substitute for public transit reducing PT ridership by almost 9%
The reduction in private vehicle ownership due to TNCs was insignificant
Research findings can provide valuable insights for transportation policy and regulation
Singapore, 31 March 2021 - Transport Network Companies (TNCs) or ridesharing companies have gained widespread popularity across much of the world, with more and more cities adopting the phenomenon. While ridesharing has been credited with being more environmentally friendly than taxis and private vehicles, is that really the case today or do they rather contribute to urban congestion?
Researchers at the Future Urban Mobility ...
The younger generations are willing to put their money where their mouth is when it comes to sustainable living. In a study questioning both commitment to sustainable behaviors and willingness to trade better pay to work for a more sustainable-minded company, the surveyed young adults in Japan made their preferences clear.
The results were published on Jan. 31 in a special issue of the Journal of Cleaner Production focused on achieving the END ...
Until now, researchers have believed that dark energy accounted for nearly 70 percent of the ever-accelerating, expanding universe.
For many years, this mechanism has been associated with the so-called cosmological constant, developed by Einstein in 1917, that refers to an unknown repellant cosmic power.
But because the cosmological constant--known as dark energy--cannot be measured directly, numerous researchers, including Einstein, have doubted its existence--without being able to suggest a viable alternative.
Until now. In a new study by researchers at the University of Copenhagen, a model was tested that replaces dark energy with a dark matter in the form of magnetic forces.
"If what we discovered is accurate, it would upend our ...
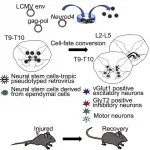
Nagoya University researchers have identified a gene that plays a crucial role in regenerating neurons of African clawed frog tadpoles, which has an unusually high capacity for nerve regeneration. Their study, recently published in the journal iScience, showed that introducing the gene into mice with spinal cord injury (SCI) led to a partial recovery of their lost motor functions. These findings could contribute to the development of a new therapy for SCI, which often causes a person to experience permanent and severe physical and neurological disabilities.
Repairing spinal cord injuries in humans and other mammals is difficult, partly because ...
Cancer patients generally have a higher thrombotic risk than the population at large. This risk is influenced on the one hand by patient-specific factors and the cancer itself and, on the other, by the cancer treatment, that is to say surgery, radiotherapy, or specific chemotherapeutics, which can increase the risk.
In the last few years, immune checkpoint inhibitors have increasingly been used to treat many different types of cancer. By activating the immune system against the tumour, these drugs improve the prognosis for patients with malignant melanoma, ...
Tropical cyclones -- known as typhoons in the Pacific and as hurricanes in the Atlantic -- are fierce, complex storm systems that cause loss of human life and billions of dollars in damage every year. For decades, scientists have studied each storm, striving to understand the system yet unable to fully measure every intricate variable. Now, the convergence of new observational tools and the launch of an inclusive database may elucidate the innerworkings of tropical cyclones in the Western North Pacific and South China Sea.
Three papers were published in the latest issue of Advances in Atmospheric Science. One paper, led by the Chinese Meteorological Administration (CMA), focuses on a new tropical cyclone database, and the other two, led by The Petrel Meteorological ...
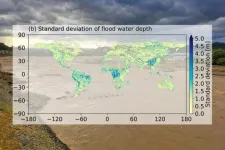
Tokyo, Japan - A research team from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo has conducted a detailed analysis of the uncertainties associated with flood risk modeling at the global scale. They found large uncertainties were mainly associated with runoff data. Flood magnitude is large in wet regions, but uncertainties in flood depth is larger in dry and mountainous regions affected by rare, extreme floods. The results of the study can be used to identify the key areas for improvement in hydrological modeling and improve future predictions of flood risk.
Assessment of the risk of rare and extreme floods is essential ...
A team of Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) researchers has designed a 'smart' device to harvest daylight and relay it to underground spaces, reducing the need to draw on traditional energy sources for lighting.
In Singapore, authorities are looking at the feasibility of digging deeper underground to create new space for infrastructure, storage, and utilities. Demand for round-the-clock underground lighting is therefore expected to rise in the future.
To develop a daylight harvesting device that can sustainably meet this need, the NTU team ...
Japan is a country known for its continuous quality improvement (KAIZEN) in manufacturing. Now doctors are bringing this philosophy to the medical field. In pediatric intensive care units (PICU), quality improvement (QI) is needed to ensure complex medical care is provided to critically ill patients in a timely manner.
A research group led by Associate Professor Etsuko Nakagami-Yamaguchi and Graduate Student Yu Inata of the Department of Medical Quality and Safety Science, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, set out to understand and assess the literature describing quality improvement in PICUs.
"Although ...
Researchers from University of Tübingen (Tübingen, Germany) and Ural Federal University (Ekaterinburg, Russia) have developed and experimentally tested new method to understand how the brain builds associations between previously unrelated words. The findings are published in Journal of Neurolinguistics.
The scientists conducted used electroencephalography to measure how the brain responds to the incongruent sentence endings. So, the brain responses to the last word in the phrase "I like my coffee with cream and sugar" have much smaller magnitude as compared to the phrase "I like my coffee with cream and socks". The brain reacts in a similar way to words ...