Flood risk uncertainties assessed at the global scale
2021-03-31
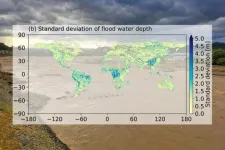
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan - A research team from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo has conducted a detailed analysis of the uncertainties associated with flood risk modeling at the global scale. They found large uncertainties were mainly associated with runoff data. Flood magnitude is large in wet regions, but uncertainties in flood depth is larger in dry and mountainous regions affected by rare, extreme floods. The results of the study can be used to identify the key areas for improvement in hydrological modeling and improve future predictions of flood risk.
Assessment of the risk of rare and extreme floods is essential for disaster management and recovery planning at international, national, and regional levels. However, the accurate assessment of flood risk is limited by the number of observations possible, and relies on hydrological modeling which has limited performance. Theoretical flood hazard maps, which are relied on by governments, regional planners, insurance services, and other stakeholders, are an important part of understanding the potential extent of flood risk. However, they are subject to high levels of uncertainty, especially at the large scale.
"The main problem is that the creation of accurate flood hazard maps relies on excellent flood frequency analysis," explains study co-author Dr. Wenchao Ma, "and the main limitation of that is its reliance on assumptions about the underlying distribution of flood events, which is hugely variable among different regions of the world. There is no single solution that can be applied everywhere."
The research team found that uncertainties in runoff inputs contributed more than 80% of the total uncertainty. Overall uncertainties were highest in Africa, but exposure risk was greatest in Asia. "We found that land susceptible to rare floods - called 1-in-100-year floods - accounts for 9.1% of the global area, excluding Antarctica," says study lead author Dr. Xudong Zhou. "In addition, the numbers show 13.4% of the population may be exposed to such a flood event, with a potential economic impact of up to 14.9 trillion US dollars to global GDP."
More adjustments are needed to flood hazard maps to ensure their accuracy. Further data are needed to take into account the efforts made by flood defenses and dam regulations and to improve inputs for areas with large uncertainties, such as Africa. Such improvements would reduce these uncertainties and improve these resources for use under future climatic conditions.
INFORMATION:
The article, "The uncertainty of flood frequency analyses in hydrodynamic model simulations" was published in Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences at DOI: 10.5194/nhess-21-1071-2021
About Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo
Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo is one of the largest university-attached research institutes in Japan.
More than 120 research laboratories, each headed by a faculty member, comprise IIS, with more than 1,000 members including approximately 300 staff and 700 students actively engaged in education and research. Our activities cover almost all the areas of engineering disciplines. Since its foundation in 1949, IIS has worked to bridge the huge gaps that exist between academic disciplines and realworld applications.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
A team of Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) researchers has designed a 'smart' device to harvest daylight and relay it to underground spaces, reducing the need to draw on traditional energy sources for lighting.
In Singapore, authorities are looking at the feasibility of digging deeper underground to create new space for infrastructure, storage, and utilities. Demand for round-the-clock underground lighting is therefore expected to rise in the future.
To develop a daylight harvesting device that can sustainably meet this need, the NTU team ...
2021-03-31
Japan is a country known for its continuous quality improvement (KAIZEN) in manufacturing. Now doctors are bringing this philosophy to the medical field. In pediatric intensive care units (PICU), quality improvement (QI) is needed to ensure complex medical care is provided to critically ill patients in a timely manner.
A research group led by Associate Professor Etsuko Nakagami-Yamaguchi and Graduate Student Yu Inata of the Department of Medical Quality and Safety Science, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, set out to understand and assess the literature describing quality improvement in PICUs.
"Although ...
2021-03-31
Researchers from University of Tübingen (Tübingen, Germany) and Ural Federal University (Ekaterinburg, Russia) have developed and experimentally tested new method to understand how the brain builds associations between previously unrelated words. The findings are published in Journal of Neurolinguistics.
The scientists conducted used electroencephalography to measure how the brain responds to the incongruent sentence endings. So, the brain responses to the last word in the phrase "I like my coffee with cream and sugar" have much smaller magnitude as compared to the phrase "I like my coffee with cream and socks". The brain reacts in a similar way to words ...
2021-03-31
The protein Asc-1 regulates whether fat-burning beige or fat-storing white adipocytes are formed, which can have an impact on the development of metabolic diseases. This is shown by a current study of the Helmholtz Zentrum München and the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD). The results open up new approaches to prevent the development of metabolic diseases. The study has now been published in Nature Communications.
Not all fat is the same: there is white, brown and beige adipose tissue *. While white fat cells serve as energy stores, excess energy is burned in brown and beige fat tissue. Too much white fat is considered unhealthy. If the white adipose ...
2021-03-31
A thermos bottle has the task of preserving the temperature - but sometimes you want to achieve the opposite: Computer chips generate heat that must be dissipated as quickly as possible so that the chip is not destroyed. This requires special materials with particularly good heat conduction properties.
In collaboration with groups from China and the United States, a research team from TU Wien therefore set out to find the optimal heat conductor. They finally found what they were looking for in a very specific form of tantalum nitride - no other known metallic material has a higher thermal conductivity. In order to be able to identify this record-breaking material, they first had to analyse which processes play a role in heat conduction in such materials at the ...
2021-03-31
Ishikawa, Japan - The focus and ultimate goal of computational research in materials science and condensed matter physics is to solve the Schrödinger equation--the fundamental equation describing how electrons behave inside matter--exactly (without resorting to simplifying approximations). While experiments can certainly provide interesting insights into a material's properties, it is often computations that reveal the underlying physical mechanism. However, computations need not rely on experimental data and can, in fact, be performed independently, an approach known as "ab initio calculations". The density functional theory (DFT) is a popular example of such an approach.
For most material ...
2021-03-31
A new report is highlighting ways we can fight COVID-19 while indoors during cold weather periods.
At the beginning of the COVID-19 crisis, there was a lack of empirical evidence on the virus's airborne transmission. However, an increasing body of evidence - gathered particularly from poorly ventilated environments - has given the scientific community a better understanding of how the disease progresses. Information on the asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic transmission of the virus strongly supports the case for airborne transmission of COVID-19.
In a study published by the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society A, scientists from the University of Surrey, together with other members of the Royal Society's Rapid Action in Modelling ...
2021-03-31
Skyrmions - tiny magnetic vortices - are considered promising candidates for tomorrow's information memory devices which may be able to achieve enormous data storage and processing capacities. A research team led by the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) has developed a method to grow a particular magnetic thin-film material that hosts these magnetic vortices. A central aspect of this new method is the abrupt heating of the material with short, very bright flashes of light, as the international team, consisting of scientists from HZDR, the Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden, TU Dresden (TUD), and Chinese partners, describes in the journal Advanced Functional Materials (DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202009723).
In 2009, a research team had made a remarkable discovery: ...
2021-03-31
New research by the University of Kent has found that using low-cost psychological interventions can reduce vehicle engine idling and in turn improve air quality, especially when there is increased traffic volume at railway level crossings.
A team of psychologists led by Professor Dominic Abrams, Dr Tim Hopthrow and Dr Fanny Lalot at the University's School of Psychology, found that using carefully worded road signage can decrease the number of drivers leaving engines idling during queues at crossing barriers.
The research, which was funded by ...
2021-03-31
Helsinki, Finland -- The EU will be home to 30 million electric cars by 2030 and the European Commission is preparing tough targets for recycling these and other batteries. Yet the impacts of battery recycling, especially for the sizeable lithium-ion batteries of the electric cars soon filling our streets, has been largely unstudied.
In a new study, researchers at Aalto University have investigated the environmental effects of a hydrometallurgical recycling process for electric car batteries. Using simulation-based life-cycle analysis, they considered energy and water consumption, as well as process emissions.
'Battery recycling processes are still developing, so their environmental footprints haven't yet been studied in detail. To be beneficial, recycling must be ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Flood risk uncertainties assessed at the global scale