Heat conduction record with tantalum nitride
How can we remove heat from computer chips as fast as possible? At TU Wien, a metal compound has now been identified that is particularly well suited for this purpose.
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) A thermos bottle has the task of preserving the temperature - but sometimes you want to achieve the opposite: Computer chips generate heat that must be dissipated as quickly as possible so that the chip is not destroyed. This requires special materials with particularly good heat conduction properties.
In collaboration with groups from China and the United States, a research team from TU Wien therefore set out to find the optimal heat conductor. They finally found what they were looking for in a very specific form of tantalum nitride - no other known metallic material has a higher thermal conductivity. In order to be able to identify this record-breaking material, they first had to analyse which processes play a role in heat conduction in such materials at the atomic level. The results have now been published in the scientific journal Physical Review Letters.
Electrons and lattice vibrations
"Basically, there are two mechanisms by which heat propagates in a material," explains Prof. Georg Madsen from the Institute of Materials Chemistry at TU Wien. "Firstly, through the electrons that travel through the material, taking energy with them. This is the main mechanism in good electrical conductors. And secondly through the phonons, which are collective lattice vibrations in the material." The atoms move, causing other atoms to wobble. At higher temperatures, heat conduction through propagation of these vibrations is usually the decisive effect.
But neither the electrons nor the lattice vibrations can propagate completely unhindered through the material. There are various processes that slow down this propagation of thermal energy. Electrons and lattice vibrations can interact with each other, they can scatter, they can be stopped by irregularities in the material.
In some cases, heat conduction can even be dramatically limited by the fact that different isotopes of an element are built into the material - i.e. similar atoms with different numbers of neutrons. In that case, the atoms do not have exactly the same mass, and this affects the collective vibrational behaviour of the atoms in the material.
"Some of these effects can be suppressed - but usually not all at the same time," says Georg Madsen. "It's like playing Whack-A-Mole: You solve one problem, and at the same time a new one arises somewhere else."
Tantalum nitride, the all-rounder
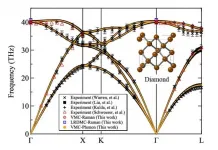
Despite our everyday experience of burning our hands on a hot metal plate, metals typically have a mediocre thermal conductivity. The metal with the highest known thermal conductivity is silver - with only a fraction of the conductivity of the record holding material diamond. But diamonds are expensive and very difficult to process.
With elaborate theoretical analyses and computer simulations, the team finally succeeded in identifying a suitable material: The hexagonal θ-phase of tantalum nitride. Tantalum is particularly favourable because there are hardly any different isotopes. Almost 99.99% of the naturally occurring tantalum is the isotope tantalum 181, other variants hardly occur.
"The combination with nitrogen and the special atomic scale geometry make the phase metallic, and it suppresses interactions of the heat carrying vibrations with other vibrations and with the conducting electrons. It is exactly those interactions that inhibit heat conduction in other materials," says Georg Madsen. "These interactions are not possible in this material because they would violate the law of energy conservation."
Therefore, this form of tantalum nitride combines several important advantages, making it a record-breaking material with a thermal conductivity several times higher than silver and comparable to diamond.
"For the chip industry, tantalum nitride is a highly promising material," Madsen is convinced. "Chips are getting smaller and more powerful, so conducting heat is becoming a bigger and bigger problem. No other material solves this problem better than the θ-phase tantalum nitride."
INFORMATION:
Contact
Prof. Georg Madsen
Institut für Materialchemie
Technische Universität Wien
+43 1 58801 165306
georg.madsen@tuwien.ac.at
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
Ishikawa, Japan - The focus and ultimate goal of computational research in materials science and condensed matter physics is to solve the Schrödinger equation--the fundamental equation describing how electrons behave inside matter--exactly (without resorting to simplifying approximations). While experiments can certainly provide interesting insights into a material's properties, it is often computations that reveal the underlying physical mechanism. However, computations need not rely on experimental data and can, in fact, be performed independently, an approach known as "ab initio calculations". The density functional theory (DFT) is a popular example of such an approach.
For most material ...
2021-03-31
A new report is highlighting ways we can fight COVID-19 while indoors during cold weather periods.
At the beginning of the COVID-19 crisis, there was a lack of empirical evidence on the virus's airborne transmission. However, an increasing body of evidence - gathered particularly from poorly ventilated environments - has given the scientific community a better understanding of how the disease progresses. Information on the asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic transmission of the virus strongly supports the case for airborne transmission of COVID-19.
In a study published by the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society A, scientists from the University of Surrey, together with other members of the Royal Society's Rapid Action in Modelling ...
2021-03-31
Skyrmions - tiny magnetic vortices - are considered promising candidates for tomorrow's information memory devices which may be able to achieve enormous data storage and processing capacities. A research team led by the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) has developed a method to grow a particular magnetic thin-film material that hosts these magnetic vortices. A central aspect of this new method is the abrupt heating of the material with short, very bright flashes of light, as the international team, consisting of scientists from HZDR, the Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden, TU Dresden (TUD), and Chinese partners, describes in the journal Advanced Functional Materials (DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202009723).
In 2009, a research team had made a remarkable discovery: ...
2021-03-31
New research by the University of Kent has found that using low-cost psychological interventions can reduce vehicle engine idling and in turn improve air quality, especially when there is increased traffic volume at railway level crossings.
A team of psychologists led by Professor Dominic Abrams, Dr Tim Hopthrow and Dr Fanny Lalot at the University's School of Psychology, found that using carefully worded road signage can decrease the number of drivers leaving engines idling during queues at crossing barriers.
The research, which was funded by ...
2021-03-31
Helsinki, Finland -- The EU will be home to 30 million electric cars by 2030 and the European Commission is preparing tough targets for recycling these and other batteries. Yet the impacts of battery recycling, especially for the sizeable lithium-ion batteries of the electric cars soon filling our streets, has been largely unstudied.
In a new study, researchers at Aalto University have investigated the environmental effects of a hydrometallurgical recycling process for electric car batteries. Using simulation-based life-cycle analysis, they considered energy and water consumption, as well as process emissions.
'Battery recycling processes are still developing, so their environmental footprints haven't yet been studied in detail. To be beneficial, recycling must be ...
2021-03-31
The nucleus is the headquarters of a cell and molecules constantly move across the nuclear membrane through pores. The transport of these molecules is both selective and fast; some 1,000 molecules per second can move in or out. Scientists from the University of Groningen and Delft University of Technology, both in the Netherlands, and a colleague from the Swedish Chalmers University of Technology, have developed an artificial model of these pores using simple design rules, which enabled them to study how this feat is accomplished. Their results were published on 31 March in Nature Communications.
Nuclear pores are extremely complicated structures. The pore itself is a big protein complex and the opening of the pore is filled with a dense network of ...
2021-03-31
First study in bereaved relatives' experience during Covid-19 pandemic lockdown published today
The study makes important recommendations for health and social care professionals providing end-of-life-care
Bereaved families highlighted their need for practical and emotional support when a family member was at end of life
The study found families have increased communication needs when a family member was at end of life, encompassing holistic as well as clinical connections
Phone calls between patients and their relatives should be prioritised during the pandemic to allow loved ones to say goodbye, a new study providing recommendations to healthcare professionals has suggested.
The ...
2021-03-31
Gustavo Aguirre and William Beltran, veterinary ophthalmologists and vision scientists at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine, have studied a wide range of different retinal blinding disorders. But the one caused by mutations in the NPHP5 gene, leading to a form of Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), is one of the most severe.
"Children with this disorder are not visual," says Aguirre. "They have a wandering, searching look on their faces and are usually diagnosed at a young age."
A nearly identical disease naturally occurs in dogs. In a new paper in the journal Molecular Therapy, Aguirre, Beltran, and colleagues at Penn and other institutions have demonstrated that a canine gene therapy can restore both normal structure and function to the retina's ...
2021-03-31
University of California, Irvine, biologists have discovered that plants influence how their bacterial and fungal neighbors react to climate change. This finding contributes crucial new information to a hot topic in environmental science: in what manner will climate change alter the diversity of both plants and microbiomes on the landscape? The paper appears in Elementa: Sciences of the Anthropocene.
The research took place at the Loma Ridge Global Change Experiment, a decade-long study in which scientists simulate the impacts of climate change on neighboring grasslands and coastal scrublands in Southern California. Experimental treatments there include nitrogen addition, a common result of local fossil fuel burning, ...
2021-03-31
The human brain regions responsible for speech and communication keep our world running by allowing us to do things like talk with friends, shout for help in an emergency and present information in meetings.
However, scientific understanding of just how these parts of the brain work is limited. Consequently, knowledge of how to improve challenges such as speech impediments or language acquisition is limited as well.
Using an ultra-lightweight, wireless implant, a University of Arizona team is researching songbirds - one of the few species that share humans' ability to learn new vocalizations - to improve scientific ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Heat conduction record with tantalum nitride
How can we remove heat from computer chips as fast as possible? At TU Wien, a metal compound has now been identified that is particularly well suited for this purpose.