High thrombotic risk in cancer patients receiving immunotherapy
Cancer patients generally have a higher thrombotic risk than the population at large
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) Cancer patients generally have a higher thrombotic risk than the population at large. This risk is influenced on the one hand by patient-specific factors and the cancer itself and, on the other, by the cancer treatment, that is to say surgery, radiotherapy, or specific chemotherapeutics, which can increase the risk.
In the last few years, immune checkpoint inhibitors have increasingly been used to treat many different types of cancer. By activating the immune system against the tumour, these drugs improve the prognosis for patients with malignant melanoma, lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma and other types of cancer. "Patients who are treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors have often had previous cancer treatment and, in most cases, have advanced cancers. We might therefore expect a significant risk of thromboembolism but, so far, the large-scale treatment studies conducted for immune checkpoint inhibitors have not reported on it," says Principal Investigator Cihan Ay, who, like Florian Moik, is also associated with the Comprehensive Cancer Center (CCC) of MedUni Vienna and Vienna General Hospital.
In order to close these gaps in knowledge, a cohort study was launched to gather data on venous and arterial thromboembolism in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors at MedUni Vienna/Vienna General Hospital between 2015 and 2018. A total of 672 patients, who had received such treatment for an average of 8.5 months, were included. The result: "The cumulative incidence of venous thromboembolism was 12.9% and of arterial thromboses 1.8%. This risk appears to be independent of the underlying type of cancer and the immune checkpoint inhibitor used, since similar rates of thrombosis were observed in these subgroups," explains Florian Moik. The occurrence of venous thromboembolism was associated with a poorer prognosis and a shorter time before tumour progression. Moreover, they frequently resulted in delays to or even discontinuation of treatment and were associated with a significant risk of recurrent thromboses and haemorrhages during anticoagulation treatment.
"The results underscore the negative impact of venous and arterial thromboembolism on the clinical course of cancer patients," says study author Moik in summary. "This study fails to determine whether the high risk of thromboembolism that has been observed has a causal link with immune-checkpoint-inhibitor therapy or merely reflects the underlying basic risk in this patient group." Irrespective of this, he believes it is important to build awareness of these complications, particularly in the light of the high efficacy of this new cancer treatment. "This paper therefore serves as a basis for future studies with a view to identifying patients who could benefit from thrombosis prophylaxis, especially to prevent venous thromboembolism."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
Tropical cyclones -- known as typhoons in the Pacific and as hurricanes in the Atlantic -- are fierce, complex storm systems that cause loss of human life and billions of dollars in damage every year. For decades, scientists have studied each storm, striving to understand the system yet unable to fully measure every intricate variable. Now, the convergence of new observational tools and the launch of an inclusive database may elucidate the innerworkings of tropical cyclones in the Western North Pacific and South China Sea.
Three papers were published in the latest issue of Advances in Atmospheric Science. One paper, led by the Chinese Meteorological Administration (CMA), focuses on a new tropical cyclone database, and the other two, led by The Petrel Meteorological ...
2021-03-31
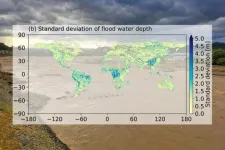
Tokyo, Japan - A research team from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo has conducted a detailed analysis of the uncertainties associated with flood risk modeling at the global scale. They found large uncertainties were mainly associated with runoff data. Flood magnitude is large in wet regions, but uncertainties in flood depth is larger in dry and mountainous regions affected by rare, extreme floods. The results of the study can be used to identify the key areas for improvement in hydrological modeling and improve future predictions of flood risk.
Assessment of the risk of rare and extreme floods is essential ...
2021-03-31
A team of Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) researchers has designed a 'smart' device to harvest daylight and relay it to underground spaces, reducing the need to draw on traditional energy sources for lighting.
In Singapore, authorities are looking at the feasibility of digging deeper underground to create new space for infrastructure, storage, and utilities. Demand for round-the-clock underground lighting is therefore expected to rise in the future.
To develop a daylight harvesting device that can sustainably meet this need, the NTU team ...
2021-03-31
Japan is a country known for its continuous quality improvement (KAIZEN) in manufacturing. Now doctors are bringing this philosophy to the medical field. In pediatric intensive care units (PICU), quality improvement (QI) is needed to ensure complex medical care is provided to critically ill patients in a timely manner.
A research group led by Associate Professor Etsuko Nakagami-Yamaguchi and Graduate Student Yu Inata of the Department of Medical Quality and Safety Science, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, set out to understand and assess the literature describing quality improvement in PICUs.
"Although ...
2021-03-31
Researchers from University of Tübingen (Tübingen, Germany) and Ural Federal University (Ekaterinburg, Russia) have developed and experimentally tested new method to understand how the brain builds associations between previously unrelated words. The findings are published in Journal of Neurolinguistics.
The scientists conducted used electroencephalography to measure how the brain responds to the incongruent sentence endings. So, the brain responses to the last word in the phrase "I like my coffee with cream and sugar" have much smaller magnitude as compared to the phrase "I like my coffee with cream and socks". The brain reacts in a similar way to words ...
2021-03-31
The protein Asc-1 regulates whether fat-burning beige or fat-storing white adipocytes are formed, which can have an impact on the development of metabolic diseases. This is shown by a current study of the Helmholtz Zentrum München and the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD). The results open up new approaches to prevent the development of metabolic diseases. The study has now been published in Nature Communications.
Not all fat is the same: there is white, brown and beige adipose tissue *. While white fat cells serve as energy stores, excess energy is burned in brown and beige fat tissue. Too much white fat is considered unhealthy. If the white adipose ...
2021-03-31
A thermos bottle has the task of preserving the temperature - but sometimes you want to achieve the opposite: Computer chips generate heat that must be dissipated as quickly as possible so that the chip is not destroyed. This requires special materials with particularly good heat conduction properties.
In collaboration with groups from China and the United States, a research team from TU Wien therefore set out to find the optimal heat conductor. They finally found what they were looking for in a very specific form of tantalum nitride - no other known metallic material has a higher thermal conductivity. In order to be able to identify this record-breaking material, they first had to analyse which processes play a role in heat conduction in such materials at the ...
2021-03-31
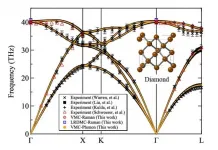
Ishikawa, Japan - The focus and ultimate goal of computational research in materials science and condensed matter physics is to solve the Schrödinger equation--the fundamental equation describing how electrons behave inside matter--exactly (without resorting to simplifying approximations). While experiments can certainly provide interesting insights into a material's properties, it is often computations that reveal the underlying physical mechanism. However, computations need not rely on experimental data and can, in fact, be performed independently, an approach known as "ab initio calculations". The density functional theory (DFT) is a popular example of such an approach.
For most material ...
2021-03-31
A new report is highlighting ways we can fight COVID-19 while indoors during cold weather periods.
At the beginning of the COVID-19 crisis, there was a lack of empirical evidence on the virus's airborne transmission. However, an increasing body of evidence - gathered particularly from poorly ventilated environments - has given the scientific community a better understanding of how the disease progresses. Information on the asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic transmission of the virus strongly supports the case for airborne transmission of COVID-19.
In a study published by the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society A, scientists from the University of Surrey, together with other members of the Royal Society's Rapid Action in Modelling ...
2021-03-31
Skyrmions - tiny magnetic vortices - are considered promising candidates for tomorrow's information memory devices which may be able to achieve enormous data storage and processing capacities. A research team led by the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) has developed a method to grow a particular magnetic thin-film material that hosts these magnetic vortices. A central aspect of this new method is the abrupt heating of the material with short, very bright flashes of light, as the international team, consisting of scientists from HZDR, the Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden, TU Dresden (TUD), and Chinese partners, describes in the journal Advanced Functional Materials (DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202009723).
In 2009, a research team had made a remarkable discovery: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] High thrombotic risk in cancer patients receiving immunotherapy
Cancer patients generally have a higher thrombotic risk than the population at large