INFORMATION:
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the American Heart Association's Cardiovascular Disease in Older Populations Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology and Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; the Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; and the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health.
Co-authors are Adam D. Gepner, M.D., vice chair; Mary A. Dolansky, Ph.D., R.N.; Daniel E. Forman, M.D., FAHA; Linda G. Park, Ph.D., M.S., F.N.P.-B.C., FAHA; Kristina S. Petersen, Ph.D., A.P.D., FAHA; Carolyn H. Still, Ph.D., M.S.M., A.G.P.C.N.P.-B.C., C.C.R.P.; Tracy Y. Wang, M.D., M.H.S., M.Sc.; Nanette K. Wenger, M.D., FAHA. Author disclosures are in the manuscript.
Additional Resources:
Available multimedia is on right column of release link - https://newsroom.heart.org/news/screen-time-for-older-adults-mobile-health-tech-can-support-seniors-with-heart-disease?preview=aac6d20df5bc79514728ddf15a507cd0
After April 1, view the manuscript online.
What is Cardiovascular Disease?
Current Science on Consumer Use of Mobile Health for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention
Phone app gets more adults to take their blood pressure medication
Follow AHA/ASA news on Twitter @HeartNews
The Association receives funding primarily from individuals. Foundations and corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations and fund specific Association programs and events. The Association has strict policies to prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers and health insurance providers are available here, and the Association's overall financial information is available here.
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public's health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for nearly a century. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, Twitter or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
Screen time for older adults: Mobile health tech can support seniors with heart disease
American Heart Association scientific statement
2021-04-01
(Press-News.org) Statement Highlights:
Two-thirds of people with heart disease are ages 60 and older.
People who have had a heart attack or stroke are 20 times more likely to have additional cardiac events compared to people without heart disease.
Lifestyle modifications and medication adherence are key strategies to address heart disease.
Mobile health technology, which incorporates apps, devices, texting and phone calls, can inform and monitor older adults to support lifestyle modifications.
DALLAS, April 1, 2021 -- Mobile health technology can be beneficial in encouraging lifestyle behavior changes and medication adherence among adults ages 60 and older with existing heart disease, yet more research is needed to determine what methods are the most effective, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association published today in the American Heart Association journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Mobile health technology--the use of mobile and wireless technologies to support the achievement of health objectives--can include voice and short messaging services (text messaging), global positioning systems (GPS) and/or Bluetooth technology, as well as wearable devices that can monitor and inform the user about specific health measures or behaviors to improve health.
"Over the last decade, mobile health technology, especially the wearable technology and mobile health application markets, has grown substantially," said the chair of the statement writing committee Erica N. Schorr, Ph.D., B.S.B.A, R.N., FAHA, an associate professor in the Adult and Gerontological Health Cooperative at the University of Minnesota School of Nursing. "There is, however, a common misperception that mobile health technology use is lower among older adults, when in fact most Americans aged 60 years and older own a cell phone and spend a significant amount of leisure time in front of a screen. This statement highlights the potential benefits that mobile health interventions can provide for monitoring, prompting, encouraging and educating older adults with cardiovascular disease."
An estimated two-thirds of all people with heart disease are 60 years old and over, and the prevalence of physical activity declines with aging, particularly in people who have heart disease. People who have experienced a major cardiac event, such as a heart attack or stroke, are at 20 times the risk for future cardiac events compared to people without heart disease, therefore more research is needed to identify strategies to slow the progression of heart disease - secondary prevention strategies - in this population.
The scientific statement highlights research from 26 studies from the past 11 years that examined mobile health technology for secondary heart disease prevention in adults ages 60 and older with existing heart disease.
Studies that incorporated text messaging and website resource information showed improvements in people's physical activity and other lifestyle behavioral changes after three months of enrollment and led to an increase in medication adherence among study participants. Significant improvements in medication adherence have also been noted in some trials when study participants used a mobile app or received a text messaging reminder. A large systematic review showed that successful mobile health interventions include frequent, personalized, two-way messaging.
"We know that controlling blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol are essential secondary prevention strategies and often require medication management," added Schorr. "Reducing sedentary time, increasing physical activity, maintaining an optimal body weight and adopting a healthy diet are other significant lifestyle strategies to optimize the health of individuals with cardiovascular disease. Wearable devices and mobile devices and applications play an important role because they can assist individuals in monitoring and tracking health behaviors and heart disease risk factors, referred to as the AHA's Life's Simple 7, to reduce their risk of a cardiac event and achieve ideal cardiovascular health."
In the 60 and older age group, the research indicates that the ease of using a program or app is a significant factor in this group's willingness to use a device, service or program. In the studies where participants reviewed apps, over half of the users reported they were easy to operate. However, the statement authors point out that many of the studies enrolled a small number of people, and the apps were geared to a very specific use, thus limiting external validity.
There were some other limitations in the research reviewed. Although the results for studies with a text messaging component were positive, it did not focus solely on older adults, making it hard to determine the impact of text messaging specific to older adults with heart disease. Additionally, differences among groups based upon race, ethnicity, sex or age were not measured. Few of the identified studies made a comparison between behavioral interventions with mobile health technology versus behavioral interventions with no technology, so the results relative to traditional interventions are unknown.
The statement writing committee notes there are challenges and barriers to mobile health use among older adults. People in underrepresented racial and ethnic groups are less likely to use technology, and some older adults have concerns over security, costs and privacy issues. There may also be cognitive, physical, visual and hearing limitations that could impact an older adult's ability to use technology. Some older adults prefer in-person visits with health care professionals, as technology may be considered isolating. Yet, research has shown adults who engage in technology can actually become more connected to others and make small, yet meaningful lifestyle and behavior changes that can help improve their health.
Schorr added there are still important questions to answer about which mobile health interventions and technology would be most effective and accepted, and how best to use them to see clinically meaningful changes in secondary cardiovascular prevention in older adults. "Answering these questions is critical to identify and implement effective, widely accepted, cost-effective and time-efficient mobile interventions that improve health outcomes for older adults," she said.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Where we live can affect male reproductive health, finds new study
2021-04-01
New research, led by scientists at the University of Nottingham, suggests that the environment in which men live may affect their reproductive health.
The research, published in Scientific Reports, looked at the effects of geographical location on polluting chemicals found in dog testes, some of which are known to affect reproductive health. The unique research focused on dogs because, as a popular pet, they share the same environment as people and are effectively exposed to the same household chemicals as their owners.
The team also looked for signs of abnormalities ...
Melting ice sheets caused sea levels to rise up to 18 metres
2021-04-01
It is well known that climate-induced sea level rise is a major threat. New research has found that previous ice loss events could have caused sea-level rise at rates of around 3.6 metres per century, offering vital clues as to what lies ahead should climate change continue unabated.
A team of scientists, led by researchers from Durham University, used geological records of past sea levels to shed light on the ice sheets responsible for a rapid pulse of sea-level rise in Earth's recent past.
Geological records tell us that, at the end of the last ice age around 14,600 years ago, sea levels rose at ten times the current rate due to Meltwater Pulse 1A (MWP-1A); a 500 year, ~18 metre sea-level rise event.
Until now, the scientific community has not ...
Genome sequencing shows coronavirus variation drives pandemic surges
2021-04-01
Genome sequencing of thousands of SARS-CoV-2 samples shows that surges of COVID-19 cases are driven by the appearance of new coronavirus variants, according to new research from the School of Veterinary Medicine at the University of California, Davis published April 1 in Scientific Reports.
"As variants emerge, you're going to get new outbreaks," said Bart Weimer, professor of population health and reproduction at the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine. The merger of classical epidemiology with genomics provides a tool public health authorities could use to predict the course of pandemics, whether of coronavirus, influenza or some new pathogen.
Although it has just 15 genes, SARS-CoV-2 is constantly mutating. Most of these changes make very little ...
Possible trigger for Crohn's disease identified
2021-04-01
Hamilton, ON (April 1, 2021) - People living with the often-debilitating effects of Crohn's disease may finally gain some relief, thanks to ground-breaking research led by McMaster University.
McMaster investigator Brian Coombes said his team identified a strain of adherent-invasive E-coli (AIEC) that is strongly implicated in the condition and is often found in the intestines of people with Crohn's disease.
"If you examine the gut lining of patients with Crohn's disease, you will find that around 70 to 80 per cent of them test positive for AIEC bacteria, but one of the things we don't understand is why," said Coombes, professor and chair of the Department of Biochemistry and ...
A statistical solution to processing very large datasets efficiently with memory limit
2021-04-01
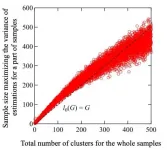
Ishikawa, Japan - Any high-performance computing should be able to handle a vast amount of data in a short amount of time -- an important aspect on which entire fields (data science, Big Data) are based. Usually, the first step to managing a large amount of data is to either classify it based on well-defined attributes or--as is typical in machine learning--"cluster" them into groups such that data points in the same group are more similar to one another than to those in another group. However, for an extremely large dataset, which can have trillions of sample points, it is tedious to even group data points into a single cluster without huge memory requirements.
"The problem can be formulated as follows: Suppose we have a clustering tool that ...
Unique macro-vertebrate at risk from blood sport and climate change
2021-04-01
The kangaskhan, Australia's only species of endemic Pokemon in Pokemon Go, is commonly poached within its natural habitat by Pokemon trainers for use in fighting contests
Researchers used several species distribution modeling algorithms to predict how climate change, on top of the already existing human-induced pressures, would impact the distribution of the kangaskhan in the future
In addition to this, they found a way to measure how biased commonly used species distribution models are, and found that some models are so biased that their results weren't influenced by the data at all
The ...
Weight loss changes people's responsiveness to food marketing: study
2021-04-01
Obesity rates have increased dramatically in developed countries over the past 40 years -- and many people have assumed that food marketing is at least in part to blame. But are people with obesity really more susceptible to food marketing? And if they are, is that a permanent predisposition, or can it change over time?
According to a new study by UBC Sauder School of Business Assistant Professor Dr. Yann Cornil (he/him/his) and French researchers, people with obesity do tend to be more responsive to food marketing -- but when their weight drops significantly, so does their responsiveness to marketing.
For the study, which was published in the Journal of Consumer Psychology, the researchers followed three groups: patients with severe ...
SLAS Discovery special issue "Advances in Protein Degradation" available now
2021-04-01
Oak Brook, IL - The April edition of SLAS Discovery is a special issue on advances in protein degradation curated by guest editors M. Paola Castaldi, Ph.D., and Stewart L. Fisher, Ph.D.
Targeted protein degradation has generated interest within the drug discovery arena due to the inhibition of one particular function of a protein not often delivering the successful results that comes from whole-protein depletion. The pharmacology of PROTACs present challenges, however, namely for the development of orally bioavailable drugs. In the article "Target Validation Using PROTACs: Applying the Four Pillars Framework" authors Rados?aw P. Nowak, Ph.D., and Lyn H. Jones, Ph.D., describe the application of a translational pharmacology framework (the four pillars) ...
SLAS Technology April issue dives into reactive oxygen species
2021-04-01
Oak Brook, IL - The April edition of SLAS Technology features the cover article "Therapeutic Potential of Reactive Oxygen Species: State of the Art and Recent Advances" by Valeria Graceffa, Ph.D. (Institute of Technology Sligo, Sligo, Ireland).
The cover article explores the therapeutic potential of reactive oxygen species (ROS) including applications ranging from wound healing and hair growth enhancement, to cancer treatment, stem cell differentiation and tissue engineering. At low concentrations, ROS can be utilized as inexpensive and convenient inducers of tissue regeneration, triggering stem cell differentiation and enhancing collagen synthesis. Recent cancer studies have represented ROS as the 'Achilles Heels' of cancers given their high basal levels, leaving ...
UTSA criminology professor studies impact of COVID-19on gender-based violence
2021-04-01
(APRIL 1, 2021) -The pandemic has exacerbated risk factors for gender-based violence, such as unemployment and financial strain, substance use, isolation, depression anxiety, and general stress, according to the American Psychological Association. That's inspired The University of Texas at San Antonio criminology and criminal justice professor Kellie Lynch, along with professor TK Logan from the University of Kentucky, to work with the National Coalition Against Domestic Violence on a national survey to investigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the dynamics of gender-based violence and the experiences of those serving victims of gender-based violence.
"The consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic are far-reaching and we still have much to learn about ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
National poll finds gaps in community preparedness for teen cardiac emergencies
One strategy to block both drug-resistant bacteria and influenza: new broad-spectrum infection prevention approach validated
Survey: 3 in 4 skip physical therapy homework, stunting progress
College students who spend hours on social media are more likely to be lonely – national US study
Evidence behind intermittent fasting for weight loss fails to match hype
How AI tools like DeepSeek are transforming emotional and mental health care of Chinese youth
Study finds link between sugary drinks and anxiety in young people
Scientists show how to predict world’s deadly scorpion hotspots
ASU researchers to lead AAAS panel on water insecurity in the United States
ASU professor Anne Stone to present at AAAS Conference in Phoenix on ancient origins of modern disease
Proposals for exploring viruses and skin as the next experimental quantum frontiers share US$30,000 science award
ASU researchers showcase scalable tech solutions for older adults living alone with cognitive decline at AAAS 2026
Scientists identify smooth regional trends in fruit fly survival strategies
Antipathy toward snakes? Your parents likely talked you into that at an early age
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for Feb. 2026
Online exposure to medical misinformation concentrated among older adults
Telehealth improves access to genetic services for adult survivors of childhood cancers
Outdated mortality benchmarks risk missing early signs of famine and delay recognizing mass starvation
Newly discovered bacterium converts carbon dioxide into chemicals using electricity
Flipping and reversing mini-proteins could improve disease treatment
Scientists reveal major hidden source of atmospheric nitrogen pollution in fragile lake basin
Biochar emerges as a powerful tool for soil carbon neutrality and climate mitigation
Tiny cell messengers show big promise for safer protein and gene delivery
AMS releases statement regarding the decision to rescind EPA’s 2009 Endangerment Finding
Parents’ alcohol and drug use influences their children’s consumption, research shows
Modular assembly of chiral nitrogen-bridged rings achieved by palladium-catalyzed diastereoselective and enantioselective cascade cyclization reactions
Promoting civic engagement
AMS Science Preview: Hurricane slowdown, school snow days
Deforestation in the Amazon raises the surface temperature by 3 °C during the dry season
Model more accurately maps the impact of frost on corn crops
[Press-News.org] Screen time for older adults: Mobile health tech can support seniors with heart diseaseAmerican Heart Association scientific statement