2D materials for conducting hole currents from grain boundaries in perovskite solar cells
2021-04-01
(Press-News.org) Grain boundaries (GBs) in PSCs have been found to be detrimental to the photovoltaic performance of the devices. Numerous papers reported that the defects in perovskite GBs should be passivated by suitable materials, such as quaternary ammonium halide, fullerene derivatives and CH3NH3I, to alleviate carrier recombination and consequently improve the device performance.
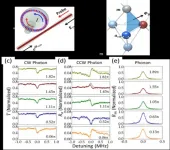
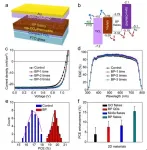
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Professor Feng Yan from Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong, and co-workers have developed a novel method to overcome the drawback of perovskite GBs without defect passivation on them. Several 2-D materials, including black phosphorus (BP), MoS2 and graphene oxide (GO), are specifically modified on the edge of perovskite GBs by a solution process. The 2-D materials have high carrier mobilities, ultrathin thicknesses and smooth surfaces without dangling bonds. The PCEs of the devices are substantially enhanced by the 2-D flakes, in which BP flakes can induce the highest relative enhancement of about 15%. More interestingly, they find that, under certain conditions, GBs modified with the 2-D materials are favorable for the device performance. Therefore, a synergistic effect between the 2-D flakes and perovskite GBs is observed for the first time. Although the nanotechnology of using 2-D materials in PSCs has been reported in some papers, the synergistic effect between the 2-D flakes and perovskite GBs has not been reported until now. To better understand the underlying mechanism of the above effect, device simulation was conducted by using a commercial software. The hole conduction processes from GBs to 2-D flakes in PSCs are clearly demonstrated, showing that the GBs and 2-D flakes all act as hole channels in the devices. The simulation results confirm that the performance enhancement induced by BP is higher than that by other 2-D materials because of the highest hole mobility of BP. In addition, the modification of the 2-D flakes on the perovskite grains away from GBs has little effect on the device performance, indicating that the synergistic effect of 2-D flakes and perovskite GBs is essential to the performance enhancement in our devices.
Although the coverage of the 2-D flakes on the perovskite films is only several percent, most of the flakes are located on perovskite GBs. Due to the high carrier mobilities of the 2-D materials especially BP, hole transfer from GBs is dramatically enhanced in the PSCs, resulting in substantial improvements of the efficiency as well as the stability of the devices. These results also indicate that GBs in PSCs are not detrimental to the device performance if the accumulated holes in the GBs can be conducted out efficiently. Under certain conditions, GBs even can be favorable for the photovoltaic performance of PSCs due to the built-in electric fields around them, which can facilitate photocarrier separation and transfer in the devices. Therefore, perovskite GBs are electrically benign, which is consistent with some theoretical calculations reported before. More importantly, they observed the synergic effect of the 2D flakes on the GBs in PSCs for the first time. Both the carrier mobility and the location of the 2D flakes on the perovskite surface are essential to the performance enhancement. This work provides a guideline of modifying perovskite layers with novel high-mobility 2-D materials to improve the photovoltaic performance as well as the stability of PSCs.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-01
Many slopes in the Campania region are covered with layers of volcanic soil, the result of repeated eruptions over the course of millennia. As the impacts of climate change worsen, including the occurrence of very intense and short rainfall in localized areas, there is a growing need, especially in this and other Italian regions that are vulnerable to landslides, to understand the dynamics that induce such events more precisely and develop models that can predict them. When employed through adequate early warning systems, these tools can support decision-makers in adopting effective and efficient measures to protect people and the areas themselves from landslides.
To ...
2021-04-01
The human body is an incredibly designed machine, and mechanical processes such as those in the lymphatic system play major roles in maintaining healthy tissue and organs.
Donny Hanjaya-Putra is an assistant professor whose work lies at the intersection of engineering and medicine. He studies the lymphatic system -- the part of the immune system that rids the body of toxins and other unwanted materials. He looks at how to restore dysfunctional lymphatic networks, which are associated with a wide range of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, neurological conditions and metabolic syndromes.
Now Hanjaya-Putra and his team -- bioengineering doctoral student Laura Alderfer, along with Elizabeth Russo, a 2019 graduate; ...
2021-04-01
The research team led by Prof. GUO Guangcan and Dr. DONG Chunhua from the University of Science and Technology of China realized synthetic gauge fields in a single optomechanical resonator by controlling geometric phase with the multimode interaction in the micro-resonator.
By engineering a Hamiltonian, uncharged particles or bosonic excitations can acquire a path-dependent phase which realizes a synthetic magnetic field. Such synthetic gauge field can improve the precision of quantum many-body simulation and control over bosons.
Previous works have realized synthetic gauge fields through coupled resonators, while this time the team realized synthetic gauge field in a single optomechanical resonator based on multimode interaction of microcavity. ...
2021-04-01
Close to 60% of working adults who were hospitalized as a result of an injury had returned to their jobs after being discharged, according to a recent study in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery.
However, more than half of the patients in the study's sample were in medical debt, and close to a quarter forwent additional care to save money. Compared to those who were not injured, patients were also more likely to experience food insecurity, physical disability, and difficulty affording and accessing health care.
The research team, which included several Michigan Medicine physicians, ...
2021-04-01
GALVESTON, TEXAS -- A new research study leveraging a database from the largest equal access health system in the US, the Department of Veteran Affairs, offers insight into the outcome of specific treatment patterns for advanced bladder cancer patients. Lead author Dr. Stephen Williams of the University of Texas Medical Branch says it is one of the first comprehensive studies looking at both the outcomes and the costs of treating a potentially lethal and devastating type of bladder cancer.
The study was published today in JAMA Network Open, a ...
2021-04-01
Leesburg, VA, April 1, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting reveals increased rates of emphysema in marijuana smokers, compared to both non-smokers and tobacco-only smokers, as well as greater rates of paraseptal emphysema.
"Marijuana smoking is also associated with airways disease, including bronchial wall thickening, bronchiectasis, and bronchiolar mucoid impaction, in comparison to both the control group and tobacco-only group," wrote first author Luke Murtha of Ottawa Hospital in Canada.
Querying imaging reports on Ottawa Hospital's PACS, Murtha and colleagues identified three ...
2021-04-01
Leesburg, VA, April 1, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting found the COVID-19 "Safer at Home" order resulted in a significant decline in radiology ordering utilization, outpatient consultations, and emergency department (ED) visits.
"There was a disproportionate impact in the outpatient setting, especially on screening and other nonessential imaging," wrote Evan Raff of Olive View-UCLA Medical Center, which "mirrors the impact that the order has had on clinical services, as reflected in outpatient consult volumes, ...
2021-04-01
Osaka, Japan - As the worldwide demand for electronic devices continues to grow, so too does the strain on the finite resources used in their production, such as metals and fossil fuels. In an effort to provide renewable alternatives, researchers from Osaka University have developed a nanocarbon material for electronics applications made from chitin derived from crab shells. Their findings are published in Journal of Materials Chemistry C.
Nanocarbon materials show significant promise for use in electronic devices. In particular, those with porous ...
2021-04-01
A team of researchers has sought to mitigate the mental health impacts of COVID-19 on adolescents by harnessing previous research on youth physical and mental health.
Their review also drew on the psychological stressors of the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami on children. The results were published in the Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine on March 26, 2021.
"We combined past research on the psychological stress on children with present studies on the effects of COVID-19," said Junko Okuyama of the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation at Tohoku University Hospital and lead author of the study. "We found ...
2021-04-01
WASHINGTON--Endocrine-disrupting chemicals may influence hormonal shifts during pregnancy as well as contribute to postpartum depression, according to a small study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Postpartum depression is a serious and common psychiatric disorder that affects up to 1 in 5 childbearing women. The cause of postpartum depression is not well understood, but hormonal changes during pregnancy have been found to be an important factor. Harmful chemicals such as bisphenols and phthalates that are found in plastics and personal care products are known to affect sex hormones.
"We found that phthalate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 2D materials for conducting hole currents from grain boundaries in perovskite solar cells