(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR--We are made of stardust, the saying goes, and a pair of studies including University of Michigan research finds that may be more true than we previously thought.
The first study, led by U-M researcher END
From stardust to pale blue dot: Carbon's interstellar journey to Earth
2021-04-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
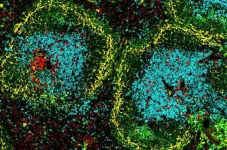
Unravelling the secret of a critical immune cell for cancer immunity
2021-04-02
WEHI researchers have discovered a key differentiation process that provides an essential immune function in helping to control cancer and infectious diseases.
The research, published in Science Immunology, is the first to show a new factor - DC-SCRIPT - is required for the function a particular type of dendritic cell - called cDC1 - that is essential in controlling the immune response to infection.
Led by WEHI Professor Stephen Nutt, Dr Michael Chopin and Mr Shengbo Zhang, it defines the role for a new regulatory protein - DC-SCRIPT - in producing dendritic cells.
At a glance
WEHI researchers have uncovered a key step in the formation of a particular type of dendritic cell - called cDC1 - in controlling ...
Keep pace: Walking with a partner is great but might slow you down
2021-04-02
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- If you walk with your spouse or partner on a regular basis, you might want to speed up. Or tell them to.
A new study by Purdue University nursing, health and kinesiology, and human development and family studies researchers shows that couples often decreased their speed when walking together. Speed further decreased if they were holding hands.
The study looked at walking times and gait speeds of 141 individuals from 72 couples. The participants ranged from age 25-79 and were in numerous settings, including clear or obstacle-filled pathways, walking together, walking together holding hands and walking individually.
"In our study, we focused on couples because partners in committed relationships often provide essential support ...
Covid-19 mask study finds layering, material choice matter
2021-04-02
Wearing a face mask can protect yourself and others from Covid-19, but the type of material and how many fabric layers used can significantly affect exposure risk, finds a study from the Georgia Institute of Technology.
The study measured the filtration efficiency of submicron particles passing through a variety of different materials. For comparison, a human hair is about 50 microns in diameter while 1 millimeter is 1,000 microns in size.
"A submicron particle can stay in the air for hours and days, depending on the ventilation, so if you have a room that is not ventilated or poorly ventilated then these small particles can stay there for a very long period of time," said Nga Lee (Sally) Ng, associate professor and Tanner Faculty Fellow in the School of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering ...
Significant decline in subarachnoid hemorrhage hospitalizations due to COVID-19
2021-04-02
New research led by investigators from Boston Medical Center and Grady Memorial Hospital demonstrates the significant decline in hospitalizations for neurological emergencies during the COVID-19 pandemic. The rate of Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) - bleeding in the space between the brain and the tissue covering the brain - hospitalizations declined 22.5 percent during the study period, which is consistent with the other reported decreases in emergencies such as stroke or heart attacks.
Published in Stroke & Vascular Neurology, the study compares subarachnoid hemorrhage hospital admissions for the months following throughout the initial COVID surge, in hospitals that bore ...
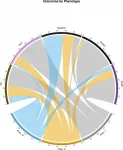
COVID-19 patients can be categorized into three groups
2021-04-02
In a new study, researchers identify three clinical COVID-19 phenotypes, reflecting patient populations with different comorbidities, complications and clinical outcomes. The three phenotypes are described in a paper published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE 1st authors Elizabeth Lusczek and Nicholas Ingraham of University of Minnesota Medical School, US, and colleagues.
COVID-19 has infected more than 18 million people and led to more than 700,000 deaths around the world. Emergency department presentation varies widely, suggesting that distinct clinical phenotypes exist and, importantly, that these distinct phenotypic presentations may respond differently ...
Serving size, satisfaction influence food waste on campus
2021-04-02
HOUSTON - (April 2, 2021) - Understanding what drives food choices can help high-volume food service operations like universities reduce waste, according to a new study.
Researchers have concluded that food waste in places like university cafeterias is driven by how much people put on their plates, how familiar they are with what's on the menu and how much they like - or don't like - what they're served.
Food waste has been studied often in households, but not so often in institutional settings like university dining commons. What drives food choices in these "all-you-care-to-eat" facilities is different because diners don't perceive personal financial penalty if they leave food on their plates.
Published in the journal Foods, "Food Choice and Waste in University Dining Commons ...
Novel cancer vaccine targets oncogenes known to evade immunity in melanoma and neuroblastoma models
2021-04-02
A personalized tumor cell vaccine strategy targeting Myc oncogenes combined with checkpoint therapy creates an effective immune response that bypasses antigen selection and immune privilege, according to a pre-clinical study for neuroblastoma and melanoma. The neuroblastoma model showed a 75% cure with long-term survival, researchers at Children's National Hospital found.
Myc is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that help manage cell growth and differentiation in the body. When Myc mutates to an oncogene, it can promote cancer cell growth. The Myc oncogenes are ...
Experimental therapy for parasitic heart disease may also help stop COVID-19
2021-04-02
James McKerrow, MD, PhD, dean of the Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at University of California San Diego, has long studied neglected tropical diseases -- chronic and disabling parasitic infections that primarily affect poor and underserved communities in developing nations. They're called "neglected" because there is little financial incentive for pharmaceutical companies to develop therapies for them.
One of these neglected diseases is Chagas disease, the leading cause of heart failure in Latin America, which is spread by "kissing bugs" carrying the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. These parasites produce an enzyme called cruzain that helps ...
Unusual mechanism in rare mutation associated with Alzheimer's uncovered
2021-04-02
A novel mechanism has been identified that might explain why a rare mutation is associated with familial Alzheimer's disease in a new study by investigators at the University of Chicago. The paper, published on April 2 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, characterizes a mutation located in a genetic region that was not previously thought be pathogenic, upending assumptions about what kinds of mutations can be associated with Alzheimer's Disease.
Alzheimer's, a neurodegenerative disease that currently affects more than 6 million Americans, has ...
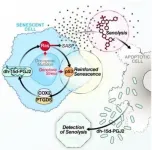
The first non-invasive biomarker to track and verify efficacy of senolytic drugs
2021-04-02
Buck Institute researchers have discovered and are developing a novel, non-invasive biomarker test that can be used to measure and track performance of senolytics: a class of drugs that selectively eliminate senescent cells. The discovery is expected to play a major role in efforts to develop treatments that would battle a myriad of chronic age-related conditions that range from arthritis to lung disease to Alzheimer's disease and glaucoma. This biomarker is a unique signaling lipid metabolite, normally exclusively intracellular, but is released when senescent cells are forced to die. This metabolite is detectible in blood and urine, making non-invasive ...