New paper shows benefits of Louisiana coastal restoration to soil carbon sequestration
2021-04-05
(Press-News.org) BATON ROUGE, La. (March 2021) - Without restoration efforts in coastal Louisiana, marshes in the state could lose half of their current ability to store carbon in the soil over a period of 50 years, according to a new paper published in American Geophysical Union Journal of Geophysical Research Biogeosciences.
"This reduction in capacity could significantly alter the global carbon budget, given that Louisiana's marsh soils account for between 5 and 21 percent of the global soil carbon storage in tidally influenced wetlands," said Melissa Baustian, lead author and coastal ecologist at The Water Institute of the Gulf.
The article, "Long-term carbon sinks in marsh soils of coastal Louisiana are at risk to wetland loss" examined 24 south Louisiana sites located within four marsh habitats defined by the amount of saltwater influence - fresh, intermediate, brackish, and saline. Carbon sink is a reservoir that stores more carbon than it releases.
By working with colleagues from U.S. Geological Survey, Vernadero Group, Abt Associates, and Tulane University the team used marsh habitat maps from 1949 to 2013, deep soil cores, soil carbon accumulation rates, and maps of future marsh area, to confirm the importance of considering historical habitats when evaluating a coastal areas' long-term ability to store carbon in the soil. Due to the evolving nature of coastal wetland habitats, simply looking at current conditions might not reflect how much carbon was buried historically or how much carbon can be buried in the future, especially in Louisiana where land loss is a continuing concern.
"Protection and restoration of these marshes is vital to help protect the pool of buried carbon in the soils, and to prevent release of carbon to the atmosphere from soil oxidation," Baustian said.
As Louisiana continues to build projects contained with its 50-year Coastal Master Plan, Gov. John Bel Edwards announced in August that the Institute, led by Baustian, will be working with the state to quantify the carbon sink potential of coastal Louisiana with and without restoration projects in the state's 2017 Coastal Master Plan to examine how these potential coastal carbon sinks could help reach the Governor's greenhouse gas emissions goals of 2025, 2030, and 2050.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-05
A new study shows a correlation between the end of solar cycles and a switch from El Nino to La Nina conditions in the Pacific Ocean, suggesting that solar variability can drive seasonal weather variability on Earth.
If the connection outlined in the journal Earth and Space Science holds up, it could significantly improve the predictability of the largest El Nino and La Nina events, which have a number of seasonal climate effects over land. For example, the southern United States tends to be warmer and drier during a La Nina, while the northern U.S. tends to be colder ...
2021-04-05
PULLMAN, Wash. - The ability to control your own behavior, known as executive function, might not exist all in your head. A new theory proposes that it develops with many influences from outside the mind.
The theory, detailed in Perspectives on Psychological Science, draws on dynamic systems theory which originated in mathematics and physics and has been used to describe complex organizing phenomena like cloud formation and flying patterns of birds. Now, a research team led by Washington State University human development assistant professor Sammy Perone is applying ...
2021-04-03
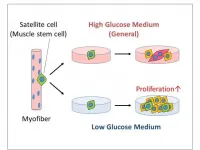
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have shown that skeletal muscle satellite cells, key players in muscle repair, proliferate better in low glucose environments. This is contrary to conventional wisdom that says mammalian cells fare better when there is more sugar to fuel their activities. Because ultra-low glucose environments do not allow other cell types to proliferate, the team could produce pure cultures of satellite cells, potentially a significant boost for biomedical research.
Healthy muscles are an important part of a healthy life. With the wear and tear of everyday use, our muscles continuously repair themselves to keep them in top condition. In recent years, scientists have begun to understand how muscle repair ...
2021-04-03
The neurons in our nervous system "talk" to each other by sending and receiving chemical messages called neurotransmitters. This communication is facilitated by cell membrane proteins called receptors, which pick up neurotransmitters and relay them across cells. In a recent study published in Nature Communications, scientists from Japan report their findings on the dynamics of receptors, which can enable understanding of the processes of memory formation and learning.
The regulation of receptor movement and localization within the neuron is important for synaptic plasticity, an important process in the central nervous system. A specific type of ...
2021-04-03
DEPRIVATION among society at large is 'driving' Covid-19 disparities among minority ethnic groups - predominantly South Asian and Black African or Caribbean populations - and could be considered the main cause of disproportionate infection rates, hospitalisation and deaths experienced by these populations, according to new analysis from the University of Leicester.
The study, supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Leicester Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) comes a day after a government-commissioned review concluded race and racism have become less important factors in explaining social disparities in the UK.
Researchers at the University of Leicester used UK Biobank data of 407,830 South Asian, Black ...
2021-04-03
Waiting for your turn can be frustrating, especially when it comes to COVID-19 vaccinations. But prioritizing who receives the limited supply of vaccines available saves lives and reduces spread of infection, according to a study published today in the journal PNAS from the University of California, Davis.
While there is mostly universal agreement that older people should be prioritized, debates are currently underway about prioritizing a variety of other groups. Still others argue against targeting at all.
"Prioritization has benefits because people differ in at least two key ways -- their risk of infection and the likelihood of serious consequences from infection," said senior author ...
2021-04-02
Within southeast Michigan's Middle Eastern and North African community, those who worry about deportation or believe they've been treated unfairly are likely to face more adverse conditions associated with poor health, including food insecurity and financial distress.
The MENA people who face several of these barriers are also more likely to report chronic illness and mental health issues as well as worse overall health.
That's according to a new study by the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center, the University of Michigan School of Public Health, and the Arab Community Center for ...
2021-04-02
Washington, April 2, 2021--The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) will release a new PISA report on student growth mindset on Thursday, April 8 at 5:00 a.m. ET, followed by a press conference held in collaboration with the American Educational Research Association (AERA) and the Yidan Prize Foundation at 10:30 a.m. ET.
The new report "Sky's the limit: Growth mindset, students, and schools in PISA" provides analyses on student growth mindset, a concept much discussed in the current field of psychology. Growth mindset is the belief that someone's ability and intelligence can be developed over time. PISA collected international ...
2021-04-02
BOSTON - New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) provides insights on why people with red hair exhibit altered sensitivity to certain kinds of pain. The findings are published in Science Advances.
In people with red hair (as in numerous other species of animals with red fur), the pigment-producing cells of the skin--called melanocytes--contain a variant form of the melanocortin 1 receptor. This receptor sits on the cell surface, and if it becomes activated by circulating hormones called melanocortins, it causes the melanocyte to switch from generating yellow/red melanin pigment to producing brown/black melanin pigment. Earlier work by David E. Fisher, MD, PhD, director of the Mass General Cancer Center's ...
2021-04-02
PHILADELPHIA - A team led by scientists in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has identified nine potential new COVID-19 treatments, including three that are already approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating other diseases.
The team, whose findings were published in Cell Reports, screened thousands of existing drugs and drug-like molecules for their ability to inhibit the replication of the COVID-19-causing coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2. In contrast to many prior studies, the screens tested the molecules for anti-coronaviral activity in a variety of cell types, including human airway-lining cells that are similar to the ones principally affected in COVID-19.
Of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New paper shows benefits of Louisiana coastal restoration to soil carbon sequestration