Research reveals why redheads may have different pain thresholds
Study in red-haired mice uncovers mechanisms involved and suggests new treatment strategies for pain
2021-04-02
(Press-News.org) BOSTON - New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) provides insights on why people with red hair exhibit altered sensitivity to certain kinds of pain. The findings are published in Science Advances.
In people with red hair (as in numerous other species of animals with red fur), the pigment-producing cells of the skin--called melanocytes--contain a variant form of the melanocortin 1 receptor. This receptor sits on the cell surface, and if it becomes activated by circulating hormones called melanocortins, it causes the melanocyte to switch from generating yellow/red melanin pigment to producing brown/black melanin pigment. Earlier work by David E. Fisher, MD, PhD, director of the Mass General Cancer Center's Melanoma Program and director of MGH's Cutaneous Biology Research Center, demonstrated that the inability of red-haired individuals to tan or darken their skin pigment is traced to inactive variants of this receptor.
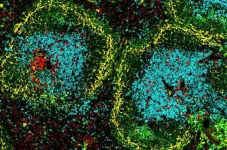
To investigate the mechanisms behind different pain thresholds in red-haired individuals, Fisher and his colleagues studied a strain of red-haired mice that (as in humans) contains a variant that lacks melanocortin 1 receptor function and also exhibits higher pain thresholds.
The team found that loss of melanocortin 1 receptor function in the red-haired mice caused the animals' melanocytes to secrete lower levels of a molecule called POMC (proopiomelanocortin) that is subsequently cut into different hormones including one that sensitizes to pain and one that blocks pain. The presence of these hormones maintains a balance between opioid receptors that inhibit pain and melanocortin 4 receptors that enhance perception of pain.
In red-haired mice (and therefore, possibly humans), having both hormones at low levels would seemingly cancel each other out. However, the body also produces additional, non-melanocyte-related factors that activate opioid receptors involved in blocking pain. Therefore, the net effect of lower levels of the melanocyte-related hormones is more opioid signals, which elevates the threshold for pain.
"These findings describe the mechanistic basis behind earlier evidence suggesting varied pain thresholds in different pigmentation backgrounds," says Fisher. "Understanding this mechanism provides validation of this earlier evidence and a valuable recognition for medical personnel when caring for patients whose pain sensitivities may vary."
Fisher adds that the results suggest new ways to manipulate the body's natural processes that control pain perception--for example, by designing new medications that inhibit melanocortin 4 receptors involved in sensing pain.
"Our ongoing work is focused on elucidating how additional skin-derived signals regulate pain and opioid signaling," adds co-lead author Lajos V. Kemény, MD, PhD, a research fellow in Dermatology at MGH. "Understanding these pathways in depth may lead to the identification of novel pain-modulating strategies."
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Melanoma Research Alliance, the U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation, and the Dr. Miriam and Sheldon G. Adelson Medical Research Foundation.
About the Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The Mass General Research Institute conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the nation, with annual research operations of more than $1 billion and comprises more than 9,500 researchers working across more than 30 institutes, centers and departments. In August 2020, Mass General was named #6 in the U.S. News & World Report list of "America's Best Hospitals."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-02
PHILADELPHIA - A team led by scientists in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has identified nine potential new COVID-19 treatments, including three that are already approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating other diseases.
The team, whose findings were published in Cell Reports, screened thousands of existing drugs and drug-like molecules for their ability to inhibit the replication of the COVID-19-causing coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2. In contrast to many prior studies, the screens tested the molecules for anti-coronaviral activity in a variety of cell types, including human airway-lining cells that are similar to the ones principally affected in COVID-19.
Of ...
2021-04-02
A new Veterans Affairs study finds that combat experience is associated with a higher risk of alcohol use to cope with PTSD symptoms. But the connection is weaker when accounting for the severity of the PTSD.
The findings appeared online in the Journal of Dual Diagnosis in March 2021.
In an observational study of more than 11,000 men with at least one traumatic experience, the researchers found that those with combat experience were much more likely than those without to report drinking alcohol to cope with PTSD. The diversity of traumatic experiences, the severity of PTSD, and diagnoses ...
2021-04-02
Aquaculture--the farming of fish, shellfish, and other aquatic animals for food--has reached unprecedented levels of growth in recent years, but largely without consideration of its impact on individual animals, finds a new analysis by a team of researchers.
"The scale of modern aquaculture is immense and still growing," says Becca Franks, a research scientist at New York University's Department of Environmental Studies and the lead author of the paper, which appears in the journal Science Advances. "Yet we know so little about the animals that we are putting into mass production, ...
2021-04-02
ANN ARBOR--We are made of stardust, the saying goes, and a pair of studies including University of Michigan research finds that may be more true than we previously thought.
The first study, led by U-M researcher END ...
2021-04-02
WEHI researchers have discovered a key differentiation process that provides an essential immune function in helping to control cancer and infectious diseases.
The research, published in Science Immunology, is the first to show a new factor - DC-SCRIPT - is required for the function a particular type of dendritic cell - called cDC1 - that is essential in controlling the immune response to infection.
Led by WEHI Professor Stephen Nutt, Dr Michael Chopin and Mr Shengbo Zhang, it defines the role for a new regulatory protein - DC-SCRIPT - in producing dendritic cells.
At a glance
WEHI researchers have uncovered a key step in the formation of a particular type of dendritic cell - called cDC1 - in controlling ...
2021-04-02
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- If you walk with your spouse or partner on a regular basis, you might want to speed up. Or tell them to.
A new study by Purdue University nursing, health and kinesiology, and human development and family studies researchers shows that couples often decreased their speed when walking together. Speed further decreased if they were holding hands.
The study looked at walking times and gait speeds of 141 individuals from 72 couples. The participants ranged from age 25-79 and were in numerous settings, including clear or obstacle-filled pathways, walking together, walking together holding hands and walking individually.
"In our study, we focused on couples because partners in committed relationships often provide essential support ...
2021-04-02
Wearing a face mask can protect yourself and others from Covid-19, but the type of material and how many fabric layers used can significantly affect exposure risk, finds a study from the Georgia Institute of Technology.
The study measured the filtration efficiency of submicron particles passing through a variety of different materials. For comparison, a human hair is about 50 microns in diameter while 1 millimeter is 1,000 microns in size.
"A submicron particle can stay in the air for hours and days, depending on the ventilation, so if you have a room that is not ventilated or poorly ventilated then these small particles can stay there for a very long period of time," said Nga Lee (Sally) Ng, associate professor and Tanner Faculty Fellow in the School of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering ...
2021-04-02
New research led by investigators from Boston Medical Center and Grady Memorial Hospital demonstrates the significant decline in hospitalizations for neurological emergencies during the COVID-19 pandemic. The rate of Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) - bleeding in the space between the brain and the tissue covering the brain - hospitalizations declined 22.5 percent during the study period, which is consistent with the other reported decreases in emergencies such as stroke or heart attacks.
Published in Stroke & Vascular Neurology, the study compares subarachnoid hemorrhage hospital admissions for the months following throughout the initial COVID surge, in hospitals that bore ...
2021-04-02
In a new study, researchers identify three clinical COVID-19 phenotypes, reflecting patient populations with different comorbidities, complications and clinical outcomes. The three phenotypes are described in a paper published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE 1st authors Elizabeth Lusczek and Nicholas Ingraham of University of Minnesota Medical School, US, and colleagues.
COVID-19 has infected more than 18 million people and led to more than 700,000 deaths around the world. Emergency department presentation varies widely, suggesting that distinct clinical phenotypes exist and, importantly, that these distinct phenotypic presentations may respond differently ...
2021-04-02
HOUSTON - (April 2, 2021) - Understanding what drives food choices can help high-volume food service operations like universities reduce waste, according to a new study.
Researchers have concluded that food waste in places like university cafeterias is driven by how much people put on their plates, how familiar they are with what's on the menu and how much they like - or don't like - what they're served.
Food waste has been studied often in households, but not so often in institutional settings like university dining commons. What drives food choices in these "all-you-care-to-eat" facilities is different because diners don't perceive personal financial penalty if they leave food on their plates.
Published in the journal Foods, "Food Choice and Waste in University Dining Commons ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research reveals why redheads may have different pain thresholds
Study in red-haired mice uncovers mechanisms involved and suggests new treatment strategies for pain