People with HIV at high risk for intimate partner violence
Intimate partner violence found to be associated with riskier behaviors associated with elevated transmission of HIV, increased depression and anxiety, and poor adherence to HIV treatment, scientists report in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine
2021-04-06
(Press-News.org) Ann Arbor, April 6, 2021 - New data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that one in four adults with HIV in the United States has experienced intimate partner violence (IPV), which disproportionately affects women and LGBT populations. Further, people with HIV who experienced IPV in the past 12 months were more likely to engage in behaviors associated with elevated HIV transmission risk, were less likely to be engaged in routine HIV care and more likely to seek emergency care services and have poor HIV clinical outcomes. The findings are reported in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier.
Lead Investigator Ansley B. Lemons-Lyn, MPH, and colleagues from the CDC's National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention and the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control in Atlanta, GA, USA, used data from the Medical Monitoring Project, an annual survey used to produce national estimates of sociodemographic, behavioral, and clinical characteristics of adults diagnosed with HIV. Analysts estimated the prevalence of respondents who had ever experienced IPV and those who experienced IPV within the last 12 months and compared that with sociodemographic information, behavioral characteristics, clinical outcomes, and the use of emergency or inpatient medical services in the past year.
Among individuals with HIV, 26.3 percent had at least one experience of IPV. Significant differences were found by race/ethnicity and age; 35.6 percent of women, 28.9 percent of transgender people, and 23.2 percent of men had experienced IPV. There were also significant differences based on gender and sexual identity. Although women overall experienced the highest prevalence of IPV, bisexual women experienced the highest proportion (51.5 percent) compared with all gender and sexual identity groups.
Overall, 4.4 percent of people with HIV had experienced IPV in the last 12 months. Statistically significant differences were found by sociodemographic characteristics, such as age and gender/sexual identify but not by race/ethnicity or gender identity. The study found that compared with individuals with HIV who did not experience IPV in the last 12 months, those who did engaged in riskier behavior such as binge drinking, use of injection drugs, and transactional sex. They were more likely to report not receiving additional needed services.
These findings suggest that screening people with HIV for IPV and linking them to services, not only during HIV testing but also during routine HIV care, is important. A higher proportion of individuals reporting IPV in the last 12 months were not receiving HIV medical care, were not taking antiretroviral therapy, and were more likely to miss HIV-related medical appointments. They were also more likely to have more than one emergency room visit or hospital admission in the past 12 months.
The study suggests that when IPV is identified, the safety and health of people with HIV can be improved with supportive services. IPV is preventable, especially when efforts begin early. The investigators note that most IPV and protection programs are tailored for heterosexual women. Given the extent to which the study found risk to other gender/sexual identity groups and racial/ethnic minorities, investigators suggest that programming should be tailored for marginalized groups.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
At a cost of $38 billion a year, an estimated 5.3 million people are living with a permanent disability related to traumatic brain injury in the United States today, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The physical, mental and financial toll of a TBI can be enormous, but new research from the University of Georgia provides promise.
In a new study, researchers at UGA's Regenerative Biosciences Center have demonstrated the long-term benefits of a hydrogel, which they call "brain glue," for the treatment of traumatic brain injury. The new study provides evidence that not only does the gel protect against loss of brain tissue after ...
2021-04-06
Bethesda, MD (April 6, 2021) -- Obesity is a global pandemic, affecting about 40% of adults in the United States. There is an enormous unmet need for an effective weight-loss solution. After a detailed review of available literature, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has released new clinical guidelines recommending the use of intragastric balloons (IGB) for patients with obesity who have not been able to lose weight with traditional weight-loss strategies. This treatment is most successful with accompanying therapy, such as lifestyle modifications and pharmacological agents, ...
2021-04-06
Researchers have uncovered pathways involved in the body's response to glucocorticoid treatments and identified a novel biomarker that could be used to monitor how these drugs work in patients, according to a clinical study published today in eLife.
A more reliable indicator of an individual's response to glucocorticoid drugs could be used to develop a clinically applicable test that could help tailor treatments and potentially minimise side-effects.
Glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, are a type of hormone with key roles in the body's response to stress. Glucocorticoid ...
2021-04-06
Researchers from Skoltech and their collaborators have designed, synthesized and evaluated new compounds that can serve as catholytes and anolytes for organic redox flow batteries, bringing this promising technology closer to large-scale implementation. The two papers were published in the END ...
2021-04-06
A new U.S. Geological Survey study provides an updated, statewide estimate of high levels of naturally occurring arsenic and uranium in private well water across Connecticut. This research builds on a USGS report published in 2017, with the new study including additional groundwater samples and focusing on previously underrepresented areas.
The research, undertaken in cooperation with the Connecticut Department of Public Health, projects that approximately 3.9% of private wells across Connecticut contain water with arsenic at concentrations higher than the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's maximum contaminant level for ...
2021-04-06
Sea urchins receive a lot of attention in California. Red urchins support a thriving fishery, while their purple cousins are often blamed for mowing down kelp forests to create urchin barrens. Yet for all the notice we pay them, we know surprisingly little about the microbiomes that support these spiny species.
Researchers at UC Santa Barbara led by geneticist Paige Miller sought to uncover the diversity within the guts of these important kelp forest inhabitants. Their results reveal significant differences between the microbiota of the two species, as well as between individuals living ...
2021-04-06
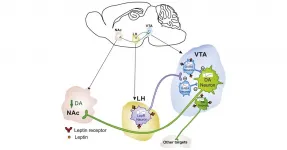
Philadelphia, April 6, 2021 - Since the discovery of leptin in the 1990s, researchers have wondered, how does leptin, a hormone made by body fat, suppress appetite? Despite tremendous gains in the intervening three decades, many questions still remain. Now, a new study in mice describes novel neurocircuitry between midbrain structures that control feeding behaviors that are under modulatory control by leptin. The study appears in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier.
John Krystal, MD, Editor of Biological Psychiatry, said of the findings, "Omrani and colleagues shed light on how, in non-obese animals, leptin puts the brakes on overeating."
Leptin acts as a critical link between the body and the brain, providing information about metabolic ...
2021-04-06
In addition to smoothing out wrinkles, researchers have found that the drug Botox can reveal the inner workings of the brain. A new study used it to show that feedback from individual nerve cells controls the release of dopamine, a chemical messenger involved in motivation, memory, and movement.
Such "self-regulation," the researchers say, stands in contrast to the widely held view that the release of dopamine -- known as the "feel good" hormone -- by any cell relied on messages from nearby cells to recognize that it is releasing too much of the hormone.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, ...
2021-04-06
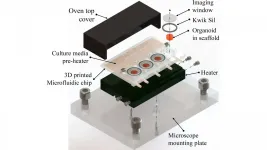
WASHINGTON, April 6, 2021 -- Scientists from MIT and the Indian Institute of Technology Madras have grown small amounts of self-organizing brain tissue, known as organoids, in a tiny 3D-printed system that allows observation while they grow and develop. The work is reported in Biomicrofluidics, by AIP Publishing.
Current technology for real-time observation of growing organoids involves the use of commercial culture dishes with many wells in a glass-bottomed plate placed under a microscope. The plates are costly and only compatible with specific microscopes. They do not allow for the flow or replenishment of a nutrient medium to the growing tissue.
Recent advances have used a technique known as microfluidics, where a nutrient ...
2021-04-06
WASHINGTON, April 6, 2021 -- Cryocoolers are ultracold refrigeration units used in surgery and drug development, semiconductor fabrication, and spacecraft. They can be tubes, pumps, tabletop sizes, or larger refrigerator systems.
The regenerative heat exchanger, or regenerator, is a core component of cryocoolers. At temperatures below 10 kelvins (-441.67 degrees Fahrenheit), performance drops precipitously, with maximum regenerator loss of more than 50%.
In their paper, published in Applied Physics Letters, by AIP Publishing, researchers at the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences used ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] People with HIV at high risk for intimate partner violence
Intimate partner violence found to be associated with riskier behaviors associated with elevated transmission of HIV, increased depression and anxiety, and poor adherence to HIV treatment, scientists report in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine