(Press-News.org) Glycine regulates neuronal activity in the brain
Glycine is the smallest amino acid - one of the building blocks of proteins. It acts also as a neurotransmitter in the brain, enabling neurons to communicate with each other and modulating neuronal activity. Many researchers have focused on increasing glycine levels in synapses to find an effective treatment for schizophrenia. This could be done using inhibitors targeting Glycine Transporter 1 (GlyT1), a protein that sits in neuronal cell membranes and is responsible for the uptake of glycine into neurons. However, the development of such drugs has been hampered because the 3D structure of GlyT1 was not known.
To determine the structure of GlyT1, researchers at the Danish Research Institute of Translational Neuroscience (DANDRITE), which is part of the Nordic EMBL Partnership for Molecular Medicine, F. Hoffmann-La END
Structural biology opens new perspectives for treating psychiatric disorders
Scientists have determined the structure of Glycine Transporter 1; the finding could open new avenues for developing therapeutics for psychiatric disorders
2021-04-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gained in translation: Subgenome fractionation determines hybrid vigor in maize
2021-04-06
The adage goes, "Two is better than one." Well, that might be true for endeavors involving human heads, but when it comes to ears, hybrid maize tends to have a superior advantage over the parental stocks in most cases. This phenomenon, called hybrid vigor or "heterosis," has been used by agriculturalists across ages to create higher-yielding, more resistant varieties of maize all over the world.
But what are the factors contributing to the increased hybrid vigor of maize? Several different genetic models have been proposed to explain heterosis in varied ...
No pain, no gain in exercise for peripheral artery disease
2021-04-06
Pain will lessen over time
Results include longer distance and walking time
8.5 million people in U.S., 250 million worldwide, have PAD
CHICAGO --- No pain means no gain when it comes to reaping exercise benefits for people with peripheral artery disease (PAD), reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
In people with peripheral artery disease, walking for exercise at an intensity that induces ischemic leg pain (caused by restricted blood flow) improves walking performance -- distance and length of time walking -- the study found. Walking at a slow pace that does not induce ischemic leg symptoms is no more effective than no exercise at all, the study showed.
This randomized trial is the first to show that a home-based walking exercise program ...
Gut microbiome plays role in autism
2021-04-06
Washington, D.C. - April 6, 2021 - A new study has demonstrated that autism spectrum disorder is related to changes in the gut microbiome. The findings are published this week in mSystems, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
"Longitudinally, we were able to see that within an individual, changes in the microbiome were associated with changes in behavior," said principal study investigator Catherine Lozupone, PhD, a microbiologist in the Department of Medicine, University of Colorado, Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado. "If we are going to understand the link between the gut microbiome and autism, we need more collaborative efforts across different regions and ...
A novel form of cellular logistics
2021-04-06
Biophysicists from Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have shown that a phenomenon known as diffusiophoresis, which can lead to a directed particle transport, can occur in biological systems.
In order to perform their biological functions, cells must ensure that their logistical schedules are implemented smoothly, such that the necessary molecular cargoes are delivered to their intended destinations on time. Most of the known transport mechanisms in cells are based on specific interactions between the cargo to be transported and the energy-consuming motor ...
Screening for skin disease on your laptop
2021-04-06
The founding chair of the Biomedical Engineering Department at the University of Houston is reporting a new deep neural network architecture that provides early diagnosis of systemic sclerosis (SSc), a rare autoimmune disease marked by hardened or fibrous skin and internal organs. The proposed network, implemented using a standard laptop computer (2.5 GHz Intel Core i7), can immediately differentiate between images of healthy skin and skin with systemic sclerosis.
"Our preliminary study, intended to show the efficacy of the proposed network architecture, holds promise in the characterization of SSc," reports Metin Akay, John S. Dunn Endowed Chair Professor of biomedical engineering. ...
Alien raindrops surprisingly like rain on Earth
2021-04-06
WASHINGTON--Raindrops on other planets and moons are close to the size of raindrops on Earth despite having different chemical compositions and falling through vastly different atmospheres, a new study finds. The results suggest raindrops falling from clouds are surprisingly similar across a wide range of planetary conditions, which could help scientists better understand the climates and precipitation cycles of other worlds, according to the researchers.
Raindrops on Earth are made of water, but other worlds in our solar system have precipitation made of more unusual stuff. On Venus, ...
New perspective to understand and treat a rare calcification disease
2021-04-06
As part of an international collaboration, researchers from ELTE Eötvös Loránd University developed a new animal model to study a rare genetic disease that can lead to blindness at the age of 40-50. The new model could open up new perspectives in our understanding of this metabolic disease and will also help to identify new potential drug candidates, according to the recent study published in Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is a rare genetic disease with symptoms that usually manifest in adolescence or in early adulthood. The symptoms are caused by the appearance of hydroxyapatite crystal deposits in the subcutaneous connective tissue and retina ...
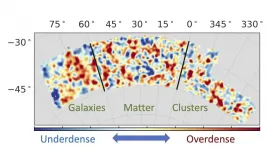
Dark Energy Survey physicists open new window into dark energy
2021-04-06
The universe is expanding at an ever-increasing rate, and while no one is sure why, researchers with the Dark Energy Survey (DES) at least had a strategy for figuring it out: They would combine measurements of the distribution of matter, galaxies and galaxy clusters to better understand what's going on.
Reaching that goal turned out to be pretty tricky, but now a team led by researchers at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University and the University of Arizona have come up with a solution. Their analysis, published April 6 in Physical Review ...
For breastfeeding moms, COVID-19 vaccinations may also protect babies
2021-04-06
Nursing mothers who receive a COVID-19 vaccine may pass protective antibodies to their babies through breast milk for at least 80 days following vaccination, suggests new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
"Our study showed a huge boost in antibodies against the COVID-19 virus in breast milk starting two weeks after the first shot, and this response was sustained for the course of our study, which was almost three months long," said first author Jeannie Kelly, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology. "The antibodies levels were still high at the end of our study, so the protection likely extends even longer."
Based ...
Accelerated cellular aging associated with mortality seen in depressed individuals
2021-04-06
Cells from individuals with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) were found to have higher than expected rates of methylation at specific sites on their DNA, when compared to cells from healthy individuals without MDD, according to a study by a multidisciplinary team of UC San Francisco scientists, in collaboration with others. Methylation is a process by which DNA is chemically modified at specific sites, resulting in changes in the expression of certain genes. Methylation of particular sets of genes, called "DNA methylation clocks," typically change in predictable ways as people ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Structural biology opens new perspectives for treating psychiatric disordersScientists have determined the structure of Glycine Transporter 1; the finding could open new avenues for developing therapeutics for psychiatric disorders