Dark Energy Survey physicists open new window into dark energy
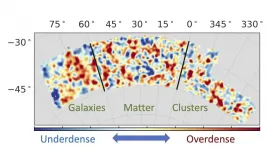
For the first time, DES scientists can combine measurements of the distribution of matter, galaxies, and galaxy clusters to advance our understanding of dark energy.
2021-04-06
(Press-News.org) The universe is expanding at an ever-increasing rate, and while no one is sure why, researchers with the Dark Energy Survey (DES) at least had a strategy for figuring it out: They would combine measurements of the distribution of matter, galaxies and galaxy clusters to better understand what's going on.
Reaching that goal turned out to be pretty tricky, but now a team led by researchers at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University and the University of Arizona have come up with a solution. Their analysis, published April 6 in Physical Review Letters, yields more precise estimates of the average density of matter as well as its propensity to clump together - two key parameters that help physicists probe the nature of dark matter and dark energy, the mysterious substances that make up the vast majority of the universe.
"It is one of the best constraints from one of the best data sets to date," says Chun-Hao To, a lead author on the new paper and a graduate student at SLAC and Stanford working with Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology Director Risa Wechsler.
An early goal
When DES set out in 2013 to map an eighth of the sky, the goal was to gather four kinds of data: the distances to certain types of supernovae, or exploding stars; the distribution of matter in the universe; the distribution of galaxies; and the distribution of galaxy clusters. Each tells researchers something about how the universe has evolved over time.
Ideally, scientists would put all four data sources together to improve their estimates, but there's a snag: The distributions of matter, galaxies, and galaxy clusters are all closely related. If researchers don't take these relationships into account, they will end up "double counting," placing too much weight on some data and not enough on others, To says.
To avoid mishandling all this information, To, University of Arizona astrophysicist Elisabeth Krause and colleagues have developed a new model that could properly account for the connections in the distributions of all three quantities: matter, galaxies, and galaxy clusters. In doing so, they were able to produce the first-ever analysis to properly combine all these disparate data sets in order to learn about dark matter and dark energy.
Improving estimates
Adding that model into the DES analysis has two effects, To says. First, measurements of the distributions of matter, galaxies and galaxy clusters tend to introduce different kinds of errors. Combining all three measurements makes it easier to identify any such errors, making the analysis more robust. Second, the three measurements differ in how sensitive they are to the average density of matter and its clumpiness. As a result, combining all three can improve the precision with which the DES can measure dark matter and dark energy.
In the new paper, To, Krause and colleagues applied their new methods to the first year of DES data and sharpened the precision of previous estimates for matter's density and clumpiness.
Now that the team can incorporate matter, galaxies and galaxy clusters simultaneously in their analysis, adding in supernova data will be relatively straightforward, since that kind of data is not as closely related with the other three, To says.
"The immediate next step," he says, "is to apply the machinery to DES Year 3 data, which has three times larger coverage of the sky." This is not as simple as it sounds: While the basic idea is the same, the new data will require additional efforts to improve the model to keep up with the higher quality of the newer data, To says.
"This analysis is really exciting," Wechsler said. "I expect it to set a new standard in the way we are able to analyze data and learn about dark energy from large surveys, not only for DES but also looking forward to the incredible data that we will get from the Vera Rubin Observatory's Legacy Survey of Space and Time in a few years."
INFORMATION:
The research was a collaborative effort within the Dark Energy Survey and was supported by the National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy's Office of Science.
SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio- and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
Nursing mothers who receive a COVID-19 vaccine may pass protective antibodies to their babies through breast milk for at least 80 days following vaccination, suggests new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
"Our study showed a huge boost in antibodies against the COVID-19 virus in breast milk starting two weeks after the first shot, and this response was sustained for the course of our study, which was almost three months long," said first author Jeannie Kelly, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology. "The antibodies levels were still high at the end of our study, so the protection likely extends even longer."
Based ...
2021-04-06
Cells from individuals with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) were found to have higher than expected rates of methylation at specific sites on their DNA, when compared to cells from healthy individuals without MDD, according to a study by a multidisciplinary team of UC San Francisco scientists, in collaboration with others. Methylation is a process by which DNA is chemically modified at specific sites, resulting in changes in the expression of certain genes. Methylation of particular sets of genes, called "DNA methylation clocks," typically change in predictable ways as people ...
2021-04-06
During the early phase of the pandemic, approximately 40% of the COVID-19 literature was shared as preprints - freely available manuscripts that are shared prior to peer-review. In a new study publishing in the open access journal PLOS Biology, researchers led by Dr Jonathon Coates (Queen Mary University of London), Dr Nicholas Fraser (Leibniz Information Centre for Economics, Germany) and Dr Liam Brierley (University of Liverpool) explore the crucial role of preprint servers in hosting COVID-19 related science and how these preprints have been used to disseminate knowledge of COVID-19, leading to cultural shifts in journalistic and policy practices.
There has been a rapid and incredible scientific response to the COVID-19 pandemic, with research ...
2021-04-06
Innovation and advances in technology have facilitated agricultural activity in recent years, as traditional irrigation techniques have been supplanted by pressure-basedones, improving water efficiency but increasing energy dependence. This drives up the Agriculture sector's energy costs, some of the highest in the European Union.
With the aim of increasing the energy efficiency of irrigation, researchers at the Hydraulics and Irrigation Group with the María de Maeztu Unit of Excellence,at the Department of Agronomy of the University of Cordoba (DAUCO), Juan Antonio Rodríguez Díaz and Jorge García Morillo, have field-tested a low-cost technology that takes advantage of the excess pressure on the grid to generate energy. This ...
2021-04-06
It is difficult to imagine our daily life without lithium-ion batteries. They dominate the small format battery market for portable electronic devices, and are also commonly used in electric vehicles. At the same time, lithium-ion batteries have a number of serious issues, including: a potential fire hazard and performance loss at cold temperatures; as well as a considerable environmental impact of spent battery disposal.
According to the leader of the team of researchers, Professor in the Department of Electrochemistry at St Petersburg University END ...
2021-04-06
Ambient air pollution is a global public health crisis, causing more than 4.9 million premature deaths per year around the world. In Africa, it has surpassed AIDS as the leading cause of premature death. According to one study, air pollution--specifically, fine particulate matter (PM2.5)--may cause at least as many as 780,000 premature deaths annually in Africa and worsen a significant number of diseases, including asthma, lung cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Kinshasa, capital of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Brazzaville, capital of the Republic of Congo, are both large metropolises. However, neither Kinshasa (population 14. 3 million) nor Brazzaville (population 2.4 million) have had comprehensive air quality monitoring programs. ...
2021-04-06
Scientists at UCL have used artificial intelligence (AI) to identify three new multiple sclerosis (MS) subtypes. Researchers say the groundbreaking findings will help identify those people more likely to have disease progression and help target treatments more effectively.
MS affects over 2.8 million people globally and 130,000 in the UK, and is classified into four* 'courses' (groups), which are defined as either relapsing or progressive. Patients are categorised by a mixture of clinical observations, assisted by MRI brain images, and patients' symptoms. These observations guide the timing and choice of treatment.
For this study, published in Nature Communications, researchers wanted to find out if there were any - as yet unidentified - patterns ...
2021-04-06
HOUSTON - (April 6, 2021) - Runoff from Houston's 2016 Tax Day flood and 2017's Hurricane Harvey flood carried human waste onto coral reefs more than 100 miles offshore in the Flower Garden Banks National Marine Sanctuary, according to a Rice University study.
"We were pretty shocked," said marine biologist Adrienne Correa, co-author of the study in Frontiers in Marine Science. "One thing we always thought the Flower Garden Banks were safe from was terrestrial runoff and nutrient pollution. It's a jolt to realize that in these extreme events, it's not just the salt marsh or the seagrass that we need to worry about. Offshore ecosystems can be affected too."
The Flower Garden Banks sit atop several salt domes near the edge ...
2021-04-06
Mitochondria, known as the powerhouses within human cells, generate the energy needed for cell survival. However, as a byproduct of this process, mitochondria also produce reactive oxygen species (ROS). At high enough concentrations, ROS cause oxidative damage and can even kill cells. An overabundance of ROS has been connected to various health issues, including cancers, neurological disorders, and heart disease.
An enzyme called manganese superoxide dismutase, or MnSOD, uses a mechanism involving electron and proton transfers to lower ROS levels in mitochondria, thus preventing oxidative damage and maintaining cell health. More than a quarter of known enzymes also rely on electron and proton transfers to facilitate cellular activities ...
2021-04-06
Boron nitride is a technologically interesting material because it is very compatible with other two-dimensional crystalline structures. It therefore opens up pathways to artificial heterostructures or electronic devices built on them with fundamentally new properties.
About a year ago, a team from the Institute of Physics at Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Wuerzburg in Bavaria, Germany, succeeded in creating spin defects, also known as qubits, in a layered crystal of boron nitride and identifying them experimentally.
Recently, the team led by Professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Dark Energy Survey physicists open new window into dark energy
For the first time, DES scientists can combine measurements of the distribution of matter, galaxies, and galaxy clusters to advance our understanding of dark energy.