(Press-News.org) It is more complicated than copy and paste, but digital twins could be way of future manufacturing according to researchers from the University of Kentucky. They developed a virtual environment based on human-robot interactions that can mirror the physical set up of a welder and their project. Called a digital twin, the prototype has implications for evolving manufacturing systems and training novice welders. They published their work in the IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica (Volume 8, Issue 2, February 2021).
"This human-robot interaction working style helps to enhance the human users' operational productivity and comfort; while data-driven welder behavior analysis benefits further novice welder training," said paper author YuMing Zhang, James R. Boyd Professor in electrical engineering at the University of Kentucky.
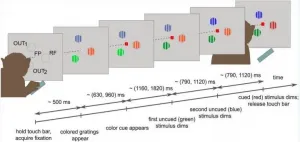
The researchers had a human demonstrate welder operations using a manual welding torch and a motion tracker. Their movements are transmitted to a machine that is actually welding. Sensors in the physical welding environment feedback data to the human. The physical environment, and incoming data, is accessible via an augmented virtual reality in which the human can make adjustments accordingly.
"In current developed digital twins, humans are the observers of the physical systems --information flow is one way," Zhang said. "For processes where intelligence from humans is needed, like precise welding, human-robot interaction needs to be integrated with the digital twins such that the humans' operative ability can be enhanced and the roles they play transmit from observers to dominators."
The researchers also tracked the behavior of six welders with different experience levels in the digital twin system. All welders were able to complete the same welding task, to varying levels of satisfaction. Analysis revealed the distinct patterns in the skilled and unskilled welders' operating behaviors and, ultimately, their work.
"The successful pattern recognition in skilled welder operations should help accelerate novice welder training," Zhang said.
The digital twin environment could, for example, provide a safe space for novice welders to practice techniques without the risk of dangerous or costly damages, as the system could be trained to recognize potentially harmful patterns and shut down.
"In future work, we plan to investigate efficient novice welder training based on this developed human-robot interactive welding with the recognized patterns from skilled welders and also upgrade the system to support multi-robot collaboration such that some more complex welding operations can be completed by this system," Zhang said. "As such, the system applicability can be increased greatly."
INFORMATION:
Reference
Q. Y. Wang, W. H. Jiao, P. Wang, and Y. M. Zhang, "Digital twin for human-robot interactive welding and welder behavior analysis," IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sinica, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 334-343, Feb. 2021.
http://www.ieee-jas.net/en/article/doi/10.1109/JAS.2020.1003518
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica aims to publish high-quality, high-interest, far-reaching research achievements globally, and provide an international forum for the presentation of original ideas and recent results related to all aspects of automation.
The first Impact Factor of IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica is 5.129, ranking among Top 17% (11/63, SCI Q1) in the category of Automation & Control Systems, according to the latest Journal Citation Reports released by Clarivate Analytics in 2020. In addition, its latest CiteScore is 8.3, and has entered Q1 in all three categories it belongs to (Information System, Control and Systems Engineering, Artificial Intelligence) since 2018.
Why publish with us: Fast and high quality peer review; Simple and effective online submission system; Widest possible global dissemination of your research; Indexed in SCIE, EI, IEEE, Scopus, Inspec. JAS papers can be found at http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/mostRecentIssue.jsp?punumber=6570654 or http://www.ieee-jas.net
To effectively perform any daily task, the human brain needs to process information from the outside world using various cognitive functions. This cognitive processing passes through a dense interconnected network of cells whose physiology is specialized. The interconnected cell network needs to perform this processing of information efficiently and interact cooperatively to provide us, in real time, with useful instructions for living.
Research published on 23 March in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America challenges recent scientific advances seeking to find out how cognitive control and sensory information relate to the cortical machinery ...
New research has for the first time compared images of the protein spikes that develop on the surface of cells exposed to the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine to the protein spike of the SARS-CoV-19 coronavirus. The images show that the spikes are highly similar to those of the virus and support the modified adenovirus used in the vaccine as a leading platform to combat COVID-19.
The SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19, has a large number of spikes sticking out of its surface that it uses to attach to, and enter, cells in the human body. These spikes are coated in sugars, known as ...
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, as part of an international collaboration of scientists through the Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes Consortium, have analysed the whole genomes of tumour samples from over 2,600 patients with different types of cancer. They identified a high prevalence of genetic diversity within individual tumours, which they further characterised. Their findings confirm that, even at late stages of development, tumour evolution is driven by changes that benefit the cancer.
When cancer cells divide, errors occur in the process of copying their DNA. These copying errors mean that different tumours can be made up of cells presenting a wide range of genetic diversity. This variation is a challenge for doctors as a treatment that ...
Digitalisation can support transitions towards a more sustainable society if technologies and processes are designed in line with suitable criteria. This requires a systemic focus on the risks and benefits of digital technologies across the three dimensions of sustainable development: the environment, society, and the economy. This is the conclusion of a study prepared by a team of researchers at the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) in Potsdam. Applying this precautionary approach to digitalisation requires the active involvement of developers, users, and regulators.
Digitalisation ...
ALS is a progressive neurological disease that attacks the nerves that interact with the body's muscles. The disease typically leads to complete paralysis of the body, robbing patients of their ability to walk, speak, eat and breathe.
Researchers studied ALS patients and healthy elderly volunteers living in Malta who took part in an ongoing study aiming at identifying genetic and environmental risk factors. Malta is a sovereign microstate in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and is home to a geographically and culturally isolated population. Recently, Maltese ALS patients were found to have a unique genetic makeup compared to ...
Bishop Peder Winstrup died in 1679, and is one of the most well-preserved human bodies from the 1600s. Researchers at Lund University in Sweden may now have solved the mystery of why a foetus was hidden in his coffin in Lund Cathedral. DNA from the bishop and the foetus, along with kinship analyses, has shown that the child was probably the bishop's own grandson.
Something is protruding between Bishop Peder Winstrup's two calves. The X-ray reveals small bones. Could it be an animal? When the image is studied more closely, the osteologists from Lund University can see faint signs of what is to become ...
A novel way to pinpoint and illuminate bone damage promises to make X-rays more efficient at diagnosing bone and other injuries, Flinders University researchers say.
The new technique, looking at potential biomedical applications of an ancient inorganic salt-based aggregation induced emission (AIE) radio-luminescence material, could open new frontiers in medicine including X-ray dosimetry, bioimaging and advanced applications such as optogenetics, says Professor Youhong Tang, from Flinders University's College of Science and Engineering.
The review article, published by Professor Tang, postdoctoral student Dr Javad Tavokoli, colleagues in Hong Kong and Australian technology company Micro-X and, examined the potential of the AIEgen luminogens ...
Sweden's acclaimed research on uterine transplants has taken a new step forward: into the field of health economics. Now, for the first time, there is a scientifically based estimate of how much implementing the treatment costs.
The current research is based on the nine uterine transplants from living donors carried out in 2013, under the leadership of Mats Brännström, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, and Chief Physician at Sahlgrenska University Hospital.
The transplants were performed within the scope of the world's first systematic, scientifically based study in the field. After ...
If relatives of people with mental illness become better at accepting the difficult emotions and life events they experience - which is what training in compassion is about - their anxiety, depression and stress is reduced. These are the results of a new study from the Danish Center for Mindfulness at Aarhus University.
Being a relative of a person with a mental illness can be very burdensome. It can feel like a great responsibility, and many people struggle with feelings of fear, guilt, shame and anger. A new study from the Danish Center for Mindfulness shows that eight weeks of training in compassion can significantly improve the well-being of relatives.
Compassion is a human quality that is anchored in the recognition of and desire to relieve ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Dermatomyositis is an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy that has been regarded as an autoimmunity-based disorder, although its pathogenesis remains unclear. In this study, researchers from the University of Tsukuba used a mouse model to identify a mechanism by which dermatomyositis may develop in humans. The animal model and findings can be used to better understand the disease and develop disease-specific treatments.
Dermatomyositis belongs to a group of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies that are associated with the presence of specific autoantibodies in patient sera. Multiple myositis-specific autoantibodies, which target proteins ubiquitously expressed in the nucleus or cytoplasm, have been described. One ...