Metabolic changes in fat tissue in obesity associated with adverse health effects
No similar link found in muscle tissue
2021-04-09
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Obesity Research Unit of the University of Helsinki have found that obesity clearly reduces mitochondrial gene expression in fat tissue, or adipose tissue. Mitochondria are important cellular powerplants which process all of our energy intake. If the pathways associated with breaking down nutrients are lazy, the changes can often have health-related consequences.
A total of 49 pairs of identical twins discordant for body weight participated in the study conducted at the University of Helsinki: their body composition and metabolism were studied in detail, and biopsies from adipose and muscle tissue were collected. Multiple techniques for analysing the genome-wide gene expression, the proteome and the metabolome were used in the study.
The study was recently published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine.
According to the findings, the pathways responsible for mitochondrial metabolism in adipose tissue were greatly reduced by obesity. Since mitochondria are key to cellular energy production, their reduced function can maintain obesity. For the first time, the study also compared the effects of obesity specifically on the mitochondria in muscle tissue in these identical twin pairs: muscle mitochondria too were found to be out of tune, but the change was less distinct than in adipose tissue.
The study provided strong evidence of a connection between the low performance of adipose tissue mitochondria and a proinflammatory state. Furthermore, the findings indicate that metabolic changes in adipose tissue are associated with increased accumulation of fat in the liver, prediabetic disorders of glucose and insulin metabolism as well as cholesterol.
"If mitochondria, the cellular powerplants, are compared to the engine of a car, you could say that the power output decreases as weight increases. A low-powered mitochondrial engine may also generate toxic exhaust fumes, which can cause a proinflammatory state in adipose tissue and, consequently, the onset of diseases associated with obesity," says Professor Kirsi Pietiläinen from the Obesity Research Unit, University of Helsinki.
"What was surprising was that the mitochondrial pathways in muscle had no association with these adverse health effects," Pietiläinen adds.
Obesity also affected amino acid metabolism
In the study, changes in mitochondrial function were also seen in amino acid metabolism. The metabolism of branched-chain amino acids, which are essential to humans, was weakened in the mitochondria of both adipose tissue and muscle tissue.
"This finding was of particular significance because the reduced breakdown of these amino acids and the resulting heightened concentration in blood have also been directly linked with prediabetic changes and the accumulation of liver fat in prior twin studies," says Pietiläinen.
Obesity, with its numerous associated diseases, is a common phenomenon that is continuously increasing in prevalence. While lifestyle influence the onset of obesity, genes also have a significant role.
"Identical twins have the same genes, and their weight is usually fairly similar. In fact, studying twins is the best way to investigate the interplay between genes and lifestyle. In spite of their identical genome, the genes and even mitochondria of twins can function on different activity levels. We utilised this characteristic in our study when looking into the effects of weight on tissue function," Pietiläinen says.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-09
WASHINGTON, April 9, 2021 -- For the millions of people worldwide who have sickle cell disease, there are only a few treatment options, which include risky bone marrow transplants, gene therapy or other treatments that address a subset of symptoms. Today, researchers will describe the discovery of a small molecule with the potential to address the root cause of sickle cell disease by boosting levels of fetal hemoglobin, a healthy form that adults normally do not make. The drug could be formulated into a convenient daily tablet.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2021 is being held online April 5-30. Live sessions will be hosted April 5-16, and on-demand and networking content will continue through ...
2021-04-09
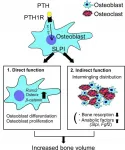
Osaka, Japan - Despite what some people think, bone is not merely a passive component of the body. The skeleton is structurally dynamic and responds to life's physical stresses with continual equilibration between bone mass loss and reformation. This ensures healing and remodeling in tune with the ebb and flow of calcium and phosphorus in the bloodstream. Now, researchers at Osaka university have identified a molecule--secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI)--that helps mediate this critical balance, which could be used in the development of new treatments for bone diseases such as osteoporosis.
Skeletal tissue changes are orchestrated ...
2021-04-09
Exercise and a healthy diet in childhood leads to adults with bigger brains and lower levels of anxiety, according to new UC Riverside research in mice.
Though diet and exercise are consistently recommended as ways to promote health, this study is the first to examine the long-lasting, combined effects of both factors when they are experienced early in life.
"Any time you go to the doctor with concerns about your weight, almost without fail, they recommend you exercise and eat less," said study lead and UCR physiology doctoral student Marcell Cadney. "That's why it's surprising most studies only look at diet or exercise separately. In this study, we wanted to include both."
The researchers determined that early-life exercise generally reduced anxious behaviors ...
2021-04-09
Obesity is linked to heavier periods and may be caused by delayed repair of the womb lining, according to a study published in the Journal of Endocrinology. Using a combined approach, assessing both women and mice, the study suggests an association between higher body weight and greater menstrual blood loss that may result from increased inflammation in the womb lining, delaying its repair. Although the study did not examine whether weight loss or anti-inflammatory medications may be useful in treating women with obesity and heavy periods, this is a step towards developing more successful ...
2021-04-09
Below the verdant surface and organic rich soil, life extends kilometers into Earth's deep rocky crust. The continental deep subsurface is likely one of the largest reservoirs of bacteria and archaea on Earth, many forming biofilms - like a microbial coating of the rock surface. This microbial population survives without light or oxygen and with minimal organic carbon sources, and can get energy by eating or respiring minerals. Distributed throughout the deep subsurface, these biofilms could represent 20-80% of the total bacterial and archaeal biomass ...
2021-04-09
Early results show that a new combination drug therapy is safe and effective against advanced skin cancer in patients who were not able to have their tumors surgically removed.
The drug combination is among the first, researchers say, to demonstrate the potential value of a live common cold virus, a coxsackievirus, to infect and kill cancer cells.
The Phase I study, led by a researcher at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, is also among the first to show how such oncolytic viruses can safely boost the action of widely used cancer therapies that help the body's immune defense system detect and kill cancer ...
2021-04-09
An international team working at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) used a unique X-ray instrument to learn new things about lithium-rich battery materials that have been the subject of much study for their potential to extend the range of electric vehicles and the operation of electronic devices.
The researchers focused their investigations on a material called lithium manganese oxide (Li2MnO3), the extreme example of so-called "lithium-rich" materials, containing the largest amount of lithium possible within this family of materials. A recently developed tenet of the ...
2021-04-09
A dementia diagnosis turns the world upside down, not only for the person affected but also for their relatives, as brain function gradually declines. Those affected lose their ability to plan, remember things or behave appropriately. At the same time, their motor skills also deteriorate. Ultimately, dementia patients are no longer able to handle daily life alone and need comprehensive care. In Switzerland alone, more than 150,000 people share this fate, and each year a further 30,000 new cases are diagnosed.
To date, all attempts to find a drug to cure this disease ...
2021-04-09
As demonstrated by multiple studies over the years, women who breastfeed have a lower risk for developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes when compared to those who don't or can't. However, the mechanisms by which these risks are reduced for lactating women are still not fully understood.
Duke Appiah, Ph.D., an assistant professor of public health at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center and director of the university's master's program in public health, said the presence of excess fat, specifically visceral and pericardial fat could help explain this finding. Using that hypothesis, Appiah and a team of researchers recently completed a study titled, "The ...
2021-04-09
Dengue risk is exacerbated in highly populated areas of Brazil after extreme drought because of improvised water containers housing mosquitoes, suggests a new study in Lancet Planetary Health.
The research was led by the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine's (LSHTM) Centre on Climate Change & Planetary Health and Centre for the Mathematical Modelling of Infectious Diseases. Using advanced statistical modelling techniques, the team predicted the timing and intensity of dengue risk in Brazil from extreme weather patterns.
The risk of dengue ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Metabolic changes in fat tissue in obesity associated with adverse health effects
No similar link found in muscle tissue