Aluminum is intricately associated with the neuropathology of familial Alzheimer's disease
2021-04-09
(Press-News.org) Amsterdam, April 9, 2021 -- This study builds upon two earlier published studies (Mold et al., 2020, Journal of Alzheimer's Disease Reports) from the same group. The new data, also published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease Reports, demonstrate that aluminum is co-located with phosphorylated tau protein, present as tangles within neurons in the brains of early-onset or familial Alzheimer's disease (AD). "The presence of these tangles is associated with neuronal cell death, and observations of aluminum in these tangles may highlight a role for aluminum in their formation," explained lead investigator Matthew John Mold, PhD, Birchall Centre, Lennard-Jones Laboratories, Keele University, Staffordshire, UK.
The earlier research highlighted widespread co-localization of aluminum and amyloid-β in brain tissue in familial AD. The researchers used a highly-selective method of immunolabelling in the current study, combined with aluminum-specific fluorescence microscopy. Phosphorylated tau in tangles co-located with aluminum in the brain tissue of the same cohort of Colombian donors with familial AD were identified. "It is of interest and perhaps significance with respect to aluminum's role in AD that its unequivocal association with tau is not as easily recognizable as with amyloid-β. There are many more aggregates of aluminum with amyloid-β than with tau in these tissues and the latter are predominantly intracellular," remarked co-author, Professor Christopher Exley.
Per Dr. George Perry, Editor-in-Chief of Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, "Aluminum accumulation has been associated with Alzheimer's disease for nearly half a century, but it is the meticulously specific studies of Drs. Mold and Exley that are defining the exact molecular interaction of aluminum and other multivalent metals that may be critical to formation of the pathology of Alzheimer's disease."
"The new data may suggest that the association of aluminum with extracellular senile plaques precedes that with intracellular aggregates of tau. These relationships with both amyloid-β and tau may account for the high levels of aluminum observed in the brain tissue of donors with familial AD versus those without a diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease," said Dr Mold. "Tau and amyloid-beta are known to act in synergy to produce neurotoxicity in AD and our data provide new evidence for a role of aluminum in this process".
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-09
The properties of carbon-based nanomaterials can be altered and engineered through the deliberate introduction of certain structural "imperfections" or defects. The challenge, however, is to control the number and type of these defects. In the case of carbon nanotubes - microscopically small tubular compounds that emit light in the near-infrared - chemists and materials scientists at Heidelberg University led by Prof. Dr Jana Zaumseil have now demonstrated a new reaction pathway to enable such defect control. It results in specific optically active defects - so-called sp3 defects - which are more luminescent and can emit single photons, that is, particles of light. The efficient ...
2021-04-09
A new study using human genetics suggests researchers should prioritize clinical trials of drugs that target two proteins to manage COVID-19 in its early stages.
The findings appeared online in the journal Nature Medicine in March 2021.
Based on their analyses, the researchers are calling for prioritizing clinical trials of drugs targeting the proteins IFNAR2 and ACE2. The goal is to identify existing drugs, either FDA-approved or in clinical development for other conditions, that can be repurposed for the early management of COVID-19. Doing so, they say, will help keep people with the virus from being hospitalized.
IFNAR2 is the target ...
2021-04-09
PHILADELPHIA - Psychosocial stress - typically resulting from difficulty coping with challenging environments - may work synergistically to put women at significantly higher risk of developing coronary heart disease, according to a study by researchers at Drexel University's Dornsife School of Public Health, recently published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
The study specifically suggests that the effects of job strain and social strain -- the negative aspect of social relationships -- on women is a powerful one-two punch. Together they are associated with a 21% higher risk of developing coronary heart disease. Job strain ...
2021-04-09
There are millions of people who face the loss of their eyesight from degenerative eye diseases. The genetic disorder retinitis pigmentosa alone affects 1 in 4,000 people worldwide.
Today, there is technology available to offer partial eyesight to people with that syndrome. The Argus II, the world's first retinal prosthesis, reproduces some functions of a part of the eye essential to vision, to allow users to perceive movement and shapes.
While the field of retinal prostheses is still in its infancy, for hundreds of users around the globe, the "bionic eye" enriches the way they interact with the world on a daily basis. For instance, seeing outlines of objects enables them to move around unfamiliar environments with increased safety.
That is ...
2021-04-09
A new biosealant therapy may help to stabilize injuries that cause cartilage to break down, paving the way for a future fix or - even better - begin working right away with new cells to enhance healing, according to a new animal-based study by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Their research was published in Advanced Healthcare Materials.
"Our research shows that using our hyaluronic acid hydrogel system at least temporarily stops cartilage degeneration that commonly occurs after injury and causes pain in joints," said the study's senior author, Robert Mauck, PhD, a professor of Orthopaedic Surgery and the director of Penn Medicine's McKay Orthopaedic Research Laboratory. "In addition to pausing cartilage breakdown, we think that applying ...
2021-04-09
Experts have uncovered a new molecular reason why faecal transplants are highly effective in treating infections such as C. difficile (a nasty bacteria that can infect the bowel), which could lead to more targeted treatments for this and other similar diseases.
The study, published today in Gastroenterology, was led by experts from the University of Nottingham and Nottingham Trent University.
Clostridium difficile, also known as C. difficile or C. diff, is a bacterium that can infect the bowel and cause diarrhoea. The infection most commonly affects people who have recently been treated with antibiotics. It can spread easily to others.
A stool transplant - or to give it its full title "a faecal ...
2021-04-09
New York, NY (April 9, 2021) - Sets of genes associated with resistance to immunotherapy in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer of the bladder have been identified and validated by researchers at Mount Sinai. In a study published in Clinical Cancer Research, the team uncovered gene signatures representing adaptive immunity and pro-tumorigenic inflammation that were responsible for sensitivity or resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors, drugs that help the body's immune system recognize and attack cancerous cells.
"These findings enabled us to identify potential biomarkers in patients who are less likely to respond favorably to immune checkpoint inhibitors, as well as new combination therapeutic approaches that might overcome such resistance ...
2021-04-09
Nine out of ten Danes say that they will accept the COVID-19 vaccine when offered. This is the same level as before the AstraZeneca vaccine was paused.
This is shown by a questionnaire-based survey collected by Søren Dinesen Østergaard and co-authors. He is professor at the Department of Clinical Medicine at Aarhus University and affiliated with the Department of Affective Disorders at Aarhus University Hospital, Psychiatry.
"In February 2021, we asked a sample of Danes whether they were willing to be vaccinated against the coronavirus, and 89 per cent replied that they would. This picture was unchanged when the same people were asked again after the pausing of the AstraZeneca vaccine," says Søren Dinesen Østergaard. ...
2021-04-09
Throughout the last ice age, the climate changed repeatedly and rapidly during so-called Dansgaard-Oeschger events, where Greenland temperatures rose between 5 and 16 degrees Celsius in decades. When certain parts of the climate system changed, other parts of the climate system followed like a series of dominos toppling in succession. This is the conclusion from an analysis of ice-core data by a group of researchers that included postdoc Emilie Capron and associate professor Sune Olander Rasmussen from the Section for the Physics of Ice, Climate and Earth at the Niels Bohr ...
2021-04-09
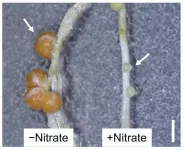
Tsukuba, Japan - Plants in the bean family (legumes) form nodules on their roots to take up nitrogen. Legumes will stop nodule production when nitrogen is plentiful (Figure 1), but precisely how nitrate presence controls nodule formation in these plants has been a mystery. Now, researchers from Japan have found that interactions between proteins and nitrate can induce and repress genes, controlling nodulation with potential applications in sustainable agriculture.
In a study published in April in The Plant Cell, a research team from the University of Tsukuba has shown that the different DNA-binding properties between proteins that establish nodule development determine if genes involved in symbiosis that govern nodulation turn on or off and that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Aluminum is intricately associated with the neuropathology of familial Alzheimer's disease