To combat gum disease, help oral bacteria evolve
For people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, exercise not only improves physiology, it may also improve their smile--by reducing gum disease.
2021-04-12
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan--Liver disease, from metabolic and bacterial causes, is a growing concern. What connects these dots? The gut, or more specifically, bacteria in the gut. Bacteria that cause inflammation in the mouth are transported through the digestive tract to the gut and liver, where they can cause liver inflammation. Lipopolysaccharides, important structural molecules in some bacteria, act as endotoxins, producing systemic effects that can manifest as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Now, a multidisciplinary team from the University of Tsukuba show that exercise could be used to improve the oral environment in people with NAFLD, potentially leading to a new treatment for the disease.
These researchers previously demonstrated that exercise benefits patients with NAFLD by reducing fat, inflammation, and scarring in the liver; improving the liver's response to and clearance of the endotoxin; and reducing gum disease. With the latest study in their series, they add another signpost to uncharted territory:
"We know that exercise has innumerable benefits to health overall and for these specific conditions," says corresponding author Professor Junichi Shoda. "With this study, we sought to characterize underlying mechanisms--that is, show how exercise alters physiology and how altered physiology induces changes in oral bacteria."
The researchers carried out biochemical and genetic analyses on saliva from overweight men with NAFLD and gum disease before and after 12-week exercise or diet programs. Men in both groups were able to lose fat mass, but those following dietary restrictions also lost muscle mass, whereas those following the exercise program gained muscle mass. "More importantly, we found that reductions in lactoferrin, lipopolysaccharide, and IgA concentrations were only evident in the men who followed the exercise regimen," Professor Shoda explains, "which suggested that the oral environment had been significantly altered by exercise."
The samples from the exercise group also showed increased bacterial diversity and changes in the relative constituent bacterial populations. In the overall population, more bacteria expressed genes related to environmental information processing, and less bacteria expressed genes related to genetic information processing and metabolism. In fact, bacteria expressed fewer genes for producing lipopolysaccharides.
"Therefore, it seems that, in people with both non-alcoholic liver disease and gum disease, exercise causes a biochemical shift in the environment of the mouth that favors the survival of less harmful bacteria," explains Professor Shoda.
A greater understanding of how to reduce the population or harmful effects of certain bacteria in patients with liver and periodontal disease could potentially lead to the development of new and improved treatment strategies for these diseases and other conditions thought to be influenced by bacteria, such as inflammatory bowel disease.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Effects of Exercise on the Oral Microbiota and Saliva of Patients with Non?Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease," was published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health at DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18073470
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-12
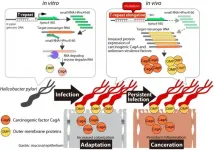
Osaka, Japan - Humans are exposed to many types of bacteria daily, the majority of which are harmless. However, some bacteria are pathogenic, which means they can cause disease. An extremely common pathogenic bacterial infection is Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in the stomach, where it can lead to chronic inflammation (gastritis), ulcers, and even cancer. A group of researchers from Osaka University have determined a specific molecular mechanism that H. pylori uses to adapt to growing in the human stomach for long periods of time.
In a report published in Nature Communications, this group found that a small RNA molecule called HPnc4160 plays a key role in how H. pylori invades the stomach ...
2021-04-12
Researchers at the University of Calgary and The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids), in Toronto, have discovered genetic risk factors for OCD that could help pave the way for earlier diagnosis and improved treatment for children and youth.
"Our group made the first finding of a genome-wide significant risk gene relevant to childhood OCD," says Dr. Paul Arnold, MD, PhD, co-principal investigator, a professor and director of The Mathison Centre for Mental Health Research & Education at the Cumming School of Medicine. "We've known that OCD runs in families, but we hadn't identified and validated specific genetic risks of OCD symptoms in children and youth until now."
The research drew on ...
2021-04-12
Inserting lightweight optimization code in high-speed network devices has enabled a KAUST-led collaboration to increase the speed of machine learning on parallelized computing systems five-fold.
This "in-network aggregation" technology, developed with researchers and systems architects at Intel, Microsoft and the University of Washington, can provide dramatic speed improvements using readily available programmable network hardware.
The fundamental benefit of artificial intelligence (AI) that gives it so much power to "understand" and interact with the world is the machine-learning step, in which ...
2021-04-12
Study: "Which U.S. Elementary Schoolchildren Are More Likely to Be Frequently Bullied?"
Authors: Paul Morgan (Pennsylvania State University), Adrienne D. Woods (Pennsylvania State University), Yangyang Wang (Pennsylvania State University), George Farkas (University of California, Irvine), Yoonkyung Oh (University of Texas Health Science Center), Marianne Hillemeier (Pennsylvania State University), Cynthia Mitchell (Pennsylvania State University)
This study was presented at the AERA 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting
Session: Friends, Enemies, and Bullies: Peer Relationships in Schools
Date/Time: Saturday, April 10, 10:40 a.m. - 12:10 p.m. ET
Main Findings:
Kindergarten children who frequently externalize problem behaviors (i.e., are aggressive or ...
2021-04-12
PULLMAN, Wash. - Humans cannot live on protein alone - even for the ancient indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest where salmon was once thought to make up as much as 90% of their diet.
In a new paper led by Washington State University anthropologist Shannon Tushingham, researchers document the many dietary solutions ancient Pacific Coast people likely employed to avoid "salmon starvation," a toxic and potentially fatal condition brought on by eating too much lean protein.
"Salmon was a critical resource for thousands of years throughout the Pacific Rim, but there were a lot of foods that were important," said Tushingham the lead author of the paper published online on April 8 in the American Journal of Physical Anthropology. "Native people were ...
2021-04-12
Cranfield University research using data from smart meters has found that household water consumption changed significantly after the start of the COVID-19 lockdown, shifting from predominantly higher usage early in the morning to multiple peaks and continued demand throughout the day.
The study used machine learning algorithms to analyse and identify patterns in hourly water consumption data from 11,528 households in the East of England from January to May 2020.
The research is the first of its kind in the UK to quantify network consumption and segment households ...
2021-04-12
The CDC recently declared racism as a threat to public health. But when it comes to dismantling white supremacy in public health, action must be taken beyond issuing statements declaring racism a public health crisis, says Sirry Alang, associate professor of sociology and health, medicine, and society at Lehigh University. A new analysis from Alang and colleagues examines the three core functions of public health -- assessment, policy development and assurance -- and the ten recently revised essential public health services (EPHSs) to offer strategies public health can follow to dismantle white supremacy.
The article, "White Supremacy and the Core Functions of Public ...
2021-04-12
Older adults with more harmful than healthy bacteria in their gums are more likely to have evidence for amyloid beta--a key biomarker for Alzheimer's disease--in their cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), according to new research from NYU College of Dentistry and Weill Cornell Medicine. However, this imbalance in oral bacteria was not associated with another Alzheimer's biomarker called tau.
The study, published in the journal Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring, adds to the growing evidence of a connection between periodontal disease (gum disease) and Alzheimer's. Periodontal disease--which affects 70 percent of adults 65 and older, ...
2021-04-12
WASHINGTON, April 12, 2021 -- Spiders are master builders, expertly weaving strands of silk into intricate 3D webs that serve as the spider's home and hunting ground. If humans could enter the spider's world, they could learn about web construction, arachnid behavior and more. Today, scientists report that they have translated the structure of a web into music, which could have applications ranging from better 3D printers to cross-species communication and otherworldly musical compositions.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2021 is being held online April 5-30. Live sessions will be hosted April 5-16, and on-demand and networking content will continue through April 30. The meeting ...
2021-04-12
DALLAS, April 12, 2021 -- Testing how well "good" cholesterol particles reduce inflammation may help predict who is at heightened risk to develop cardiovascular disease caused by narrowed arteries, according to research published today in the American Heart Association's flagship journal Circulation.
Assessing levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as "good cholesterol," are already a standard part of formulas used to predict cardiovascular risk. A new test of the anti-inflammatory function of HDL seems to provide additional information that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] To combat gum disease, help oral bacteria evolve
For people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, exercise not only improves physiology, it may also improve their smile--by reducing gum disease.