(Press-News.org) Abstract #LB008
HOUSTON -- A preclinical study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center shows an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting surface protein MT1-MMP can act as a guided missile in eradicating osteosarcoma tumor cells without damaging normal tissues. This technology, using precision therapy targeting of cell-surface proteins through a Bicycle toxin conjugate (BTC), shows encouraging results for the treatment of osteosarcoma.
Findings from the study were presented today by Yifei Wang, M.D., a postdoctoral fellow of Pediatrics Research, at the virtual American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2021. The study was led by Richard Gorlick, M.D., chair and division head of Pediatrics at MD Anderson.
Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone tumor in adolescents and young adults. The outcome of patients with osteosarcoma has not improved in the last several decades ?¬ since the implementation of adjuvant chemotherapy. For patients who are unable to tolerate the side effects of chemotherapy, few alternative treatments are available. While novel immunotherapies have shown promising efficacy in hematologic malignancies, like leukemia and lymphoma, little progress has been made in recent years for osteosarcoma.
"It's a novel approach for osteosarcoma and we now have the opportunity to explore new treatment options," Gorlick said. "This discovery represents a paradigm shift that will help us to move forward more rapidly. I anticipate that there will be an influx of other drugs that can be tested, and because the drugs are targeted to a particular surface protein, they are potentially more effective and have fewer side effects."
In this study, researchers developed an integrated bioinformatic approach using proteomic and transcriptomic data compiled from the profiling data of osteosarcoma cell lines, mouse models, hundreds of patient tumor samples and thousands of normal human tissues. This approach identified surface proteins that are highly expressed on the osteosarcoma cell surface, but not in the normal tissues. Results from the analytical laboratory technique confirmed specific proteins could be targeted therapeutically by ADC or BTC.
The team had previously identified four surface proteins, MT1-MMP, MRC2, CD276 and LRRC15, that were highly expressed on the cell surface of osteosarcoma, but not in the normal human tissues. An earlier evaluation of CD276 and LRRC15 targeted ADC showed encouraging antitumor activity, validating the research team's approach.
In this study, researchers focused on MT1-MMP as a drug target, validating the expression of the target in patient samples. They then tested an MT1-MMP targeted BTC, BT1769, in preclinical osteosarcoma mouse models. The drug proved to be highly active in the preclinical test, with 50% of the mice showing a 100% improved response.
"We are excited by these results because this target and drug have not been previously reported in osteosarcoma," Wang said. "This is the first in a series of other proteins that have been identified by the same method."
If successful in clinical trials, this research may bring new opportunities for the treatment of osteosarcoma, with higher efficacy and minimal toxicity exposure. Gorlick and his lab also are working with MD Anderson's Therapeutics Discovery team on new approaches for targeting antibodies.
INFORMATION:
This work was funded by National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Cancer Institute (NCI) (5U01CA199221-06), Swim Across America, The Foster Foundation, the Terry Fox Foundation, an Osteosarcoma Institute Translational and Preclinical grant, and the Barbara Epstein Foundation. MD Anderson Cancer Center's Proteomics Facility was funded in part by NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant (P30CA016672), NIH High End Instrumentation program grant (1S10OD012304-01), and Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas Core Facility Grant (RP130397). NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant (P30CA016672) also supported the Clinical Trials Office and the Bioinformatics Shared Resource.
In addition to Gorlick and Wang, MD Anderson authors include Jonathan Gill, M.D., Michael Roth, M.D., Douglas Harrison, M.D., Pooja Hingorani, M.D., Zhachui Xu, Xiangjun Tian, Ph.D., Jing Wang, Ph.D., Rossana Lazcano Segura, M.D., Alexander Lazar, M.D., Wendong Zhang, Zhongting Zhang, Zhaohui Xu, Sylvester Jusu and Sankaranarayanan Kannan, DPHIL. Other authors include Edward A. Kolb, M.D., of Nemours Alfred I. duPont Hospital for Children; Raushan Kurmasheva, Ph.D., and Peter Houghton, Ph.D., of Greehey Children's Cancer Research Institute; Eric Earley and Stephen Erickson of RTI International; Malcolm A. Smith, M.D., Ph.D., of National Cancer Institute; and Tara Gelb, Philip Huxley, Johanna Lahdenranta and Gemma Mudd of Bicycle Therapeutics. A full list of author disclosures can be found here.
Blood taken from a small group of children before the COVID-19 pandemic contains memory B cells that bind SARS-CoV-2 and weakly cross-react with other coronaviruses, a new study finds, while adult blood and tissue showed few such cells. "Further study of the role of cross-reactive memory B cell populations... will be important for ongoing improvement of vaccines to SARS-CoV-2, its viral variants, and other pathogens," the authors say. As the COVID-19 pandemic has continued, children have often exhibited faster viral clearance and lower viral antigen loads than adults; whether B cell repertoires against SARS-CoV-2 (and other pathogens) differ between children and ...
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Nitrogen is an element basic for life -- plants need it, animals need it, it's in our DNA -- but when there's too much nitrogen in the environment, things can go haywire. On Cape Cod, excess nitrogen in estuaries and salt marshes can lead to algal blooms, fish kills, and degradation of the environment.
In a study published in Environmental Research Letters, scientists at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) Ecosystems Center examine ways to reduce the nitrogen footprint of smaller institutions, like the MBL, by focusing on a bottom-up approach.
"This bottom-up approach is all about balancing the needs of various stakeholders to come up with the best, ...
When winter storms threaten to make travel dangerous, people often turn to salt, spreading it liberally over highways, streets and sidewalks to melt snow and ice. Road salt is an important tool for safety, because many thousands of people die or are injured every year due to weather related accidents. But a new study led by Sujay Kaushal of the University of Maryland warns that introducing salt into the environment--whether it's for de-icing roads, fertilizing farmland or other purposes--releases toxic chemical cocktails that create a serious and growing global threat to our freshwater supply and human health.
Previous studies by Kaushal and his team showed that added salts in the environment can interact with soils and infrastructure to release a cocktail of metals, ...
Researchers have genetically engineered a probiotic yeast to produce beta-carotene in the guts of laboratory mice. The advance demonstrates the utility of work the researchers have done to detail how a suite of genetic engineering tools can be used to modify the yeast.
"There are clear advantages to being able to engineer probiotics so that they produce the desired molecules right where they are needed," says Nathan Crook, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at North Carolina State University. "You're not just delivering drugs or nutrients; you are effectively manufacturing the drugs or nutrients on site."
The study focused ...
Spanking may affect a child's brain development in similar ways to more severe forms of violence, according to a new study led by Harvard researchers.
The research, published recently in the journal Child Development, builds on existing studies that show heightened activity in certain regions of the brains of children who experience abuse in response to threat cues.
The group found that children who had been spanked had a greater neural response in multiple regions of the prefrontal cortex (PFC), including in regions that are part of the salience network. These areas of the brain respond to cues in the environment that tend ...
Energy flows through a system of atoms or molecules by a series of processes such as transfers, emissions, or decay. You can visualize some of these details like passing a ball (the energy) to someone else (another particle), except the pass happens quicker than the blink of an eye, so fast that the details about the exchange are not well understood. Imagine the same exchange happening in a busy room, with others bumping into you and generally complicating and slowing the pass. Then, imagine how much faster the exchange would be if everyone stepped back and created a safe bubble for the pass to happen unhindered.
An international collaboration of scientists, including UConn Professor of Physics Nora Berrah and post-doctoral researcher ...
New York, NY - Major depressive disorder is highly prevalent, with one in five people experiencing an episode at some point in their life, and is almost twice as common in women than in men. Antidepressants are usually given as a first-line treatment, including during pregnancy, either to prevent the recurrence of depression, or as acute treatment in newly depressed patients. Antidepressant use during pregnancy is widespread and since antidepressants cross the placenta and the blood-brain barrier, concern exists about potential long-term effects of intrauterine antidepressant exposure in the unborn child.
Using the Danish National Registers to follow more than 42,000 singleton babies born ...
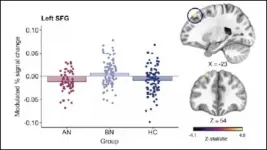
Stress alters brain activity in self-inhibition areas yet doesn't trigger binge-eating, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
People who binge-eat, a hallmark symptom of several eating disorders, can feel out of control and unable to stop, and often binge after stressful events. This led scientists to theorize stress impairs the brain regions responsible for inhibitory control -- the ability to stop what you are about to do or currently doing -- and triggers binge-eating.
Westwater et al. tested this theory by using fMRI to measure the brain activity of women with anorexia, bulimia, or without ...
A unique residential study has concluded that, contrary to perceived wisdom, people with eating disorders do not lose self-control - leading to binge-eating - in response to stress. The findings of the Cambridge-led research are published today in the Journal of Neuroscience.
People who experience bulimia nervosa and a subset of those affected by anorexia nervosa share certain key symptoms, namely recurrent binge-eating and compensatory behaviours, such as vomiting. The two disorders are largely differentiated by body mass index (BMI): adults affected by anorexia nervosa tend to have BMI of less than 18.5 kg/m2. More than 1.6 million people in ...
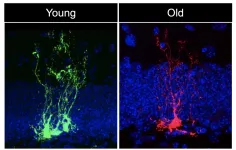
In a new study published in Cell Stem Cell, a team led by USC Stem Cell scientist Michael Bonaguidi, PhD, demonstrates that neural stem cells - the stem cells of the nervous system - age rapidly.
"There is chronological aging, and there is biological aging, and they are not the same thing," said Bonaguidi, an Assistant Professor of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, Gerontology and Biomedical Engineering at the Keck School of Medicine of USC. "We're interested in the biological aging of neural stem cells, which are particularly vulnerable to the ravages of time. This has implications for the normal cognitive decline that ...