Study links structural brain changes to behavioral problems in children who snore
2021-04-13
(Press-News.org) WHAT:
A large study of children has uncovered evidence that behavioral problems in children who snore may be associated with changes in the structure of their brain's frontal lobe. The findings support early evaluation of children with habitual snoring (snoring three or more nights a week). The research, published in Nature Communications, was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and nine other Institutes, Centers, and Offices of the National Institutes of Health.
Large, population-based studies have established a clear link between snoring and behavioral problems, such as inattention or hyperactivity, but the exact nature of this relationship is not fully understood. While a few small studies have reported a correlation between sleep apnea--when pauses in breathing are prolonged--and certain brain changes, little is known about whether these changes contribute to the behaviors seen in some children with obstructive sleep-disordered breathing (oSDB), a group of conditions commonly associated with snoring that are characterized by resistance to breathing during sleep.
To address this knowledge gap, researchers led by Amal Isaiah, M.D., D.Phil., of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, capitalized on the large and diverse dataset provided by the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study, a long-term study of child health and brain development in the United States. The team of researchers mined this wealth of data from more than 11,000 9- and 10-year-old children to examine the relationships among snoring, brain structure, and behavioral problems.
Confirming the results of previous work, their statistical analysis revealed a positive correlation between habitual snoring and behavioral problems, with the children who most frequently snored generally exhibiting worse behavior according to an assessment completed by parents. The findings further showed that snoring is linked to smaller volumes of multiple regions of the brain's frontal lobe, an area involved in cognitive functions such as problem solving, impulse control, and social interactions. The statistical analysis also suggested that the brain differences seen in children who snore may contribute to behavioral problems, but additional work on how snoring, brain structure, and behavioral problems change over time is needed to confirm a causal link.
This study's findings point to oSDB as a potential reversible cause of behavioral problems, suggesting that children routinely be screened for snoring. Children who habitually snore may then be referred for follow-up care. Such care may include assessment and treatment for conditions that contribute to oSDB, such as obesity, or evaluation for surgical removal of the adenoids and tonsils.
The ABCD Study, the largest of its kind in the United States, is tracking nearly 12,000 youth as they grow into young adults. Investigators regularly measure participants' brain structure and activity using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, and collect psychological, environmental, and cognitive information, as well as biological samples. The goal of the study is to define standards for normal brain and cognitive development and to identify factors that can enhance or disrupt a young person's life trajectory.
INFORMATION:
The Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study and ABCD Study are service marks and registered trademarks, respectively, of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Article
Isaiah A, et al. Associations between frontal lobe structure, parent-reported obstructive sleep disordered breathing and childhood behavior in the ABCD dataset. Nature Communications. DOI: 10.15154/1520518 (2021).
WHO:
Gayathri J. Dowling, Ph.D., director of the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study, at NIDA is available for interviews.
About the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA): NIDA is a component of the National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIDA supports most of the world's research on the health aspects of drug use and addiction. The Institute carries out a large variety of programs to inform policy, improve practice, and advance addiction science. For more information about NIDA and its programs, visit http://www.drugabuse.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-13
Ammonoids, ancestors of today's octopus, squid and cuttlefish, bobbed and jetted their way through the oceans for around 340 million years beginning long before the age of the dinosaurs. If you look at the fossil shells of ammonoids over the course of that 340 million years, you'll notice something striking--as time goes on, the wavy lines inside the shell become more and more complex, eventually becoming frilled almost like the edges of kale leaves.
Fossil of Menuites oralensis with external shell removed to reveal intricate suture patterns.
These ...
2021-04-13
Children who regularly snore have structural changes in their brain that may account for the behavioral problems associated with the condition including lack of focus, hyperactivity, and learning difficulties at school. That is the finding of a new study conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), which was published today in the journal Nature Communications.
The research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and nine other Institutes, Centers, and Offices of the National Institutes of Health.
To conduct study, the researchers examined MRI images collected from more than 10,000 children aged 9 to 10 years enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development ...
2021-04-13
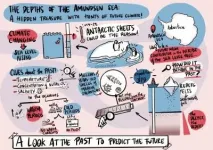
Past Global Changes Horizons is a scientific review of why the study of Earth's history is important, and uses comics, pictures, and drawings that support short papers with strong messages about past sciences and how to prepare for a changing future. Articles cover different environments across the planet, from caves to oceans, and from Antarctica to the Rift valley in Africa.
Each of the 18 contributions addresses a scientific question and includes appealing and understandable figures or images, without sacrificing scientific rigor. Tips and suggestions for further research and discussion topics are also included, meaning Horizons is ...
2021-04-13
Growing more legumes, like beans and lentils, is potentially a more sustainable and nutritious approach to European agriculture, shows a new study in END ...
2021-04-13
PITTSBURGH, April 13, 2021 - What can vaccine proponents, clinicians and public health communicators learn from "anti-vaxxers?" A lot, according to new guidance for pro-vaccination social media events written by University of Pittsburgh health scientists.
The five-part guidelines, published today in the journal Vaccine, arose from an analysis of a grassroots pro-vaccination campaign organized last year by popular physician and social media personality Zubin Damania, M.D., colloquially known as "ZDoggMD." Unexpectedly, more than three-quarters of the tweets associated with the ...
2021-04-13
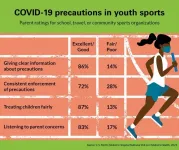
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- For young athletes, the new normal on soccer fields and basketball courts means temperature checks before practice, wearing masks through games and a sparse in-person fan base.
But that hasn't kept children and teens from playing. Close to a fourth of parents say their child has participated in school, travel, or community sports during the fall or winter months, according to the C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health at the University of Michigan.
And while the majority of parents give their child's sports organization high marks for communication about safety protocols, one in four rate their sports ...
2021-04-13
Hamilton, ON (April 13, 2021) - Ontario doctors are still hesitant to prescribe medical cannabis to patients suffering long-term pain 20 years after it was first introduced, says a new study carried out at McMaster University.
Physicians surveyed said their main concerns relate to possible ill-effects and a lack of understanding regarding their effectiveness as painkillers.
Of particular concern among doctors were potentially harmful effects on cognitive development, a possible worsening of existing mental illnesses in patients and the drug's effects in older adults, which may include dizziness or drowsiness.
Meanwhile, the ...
2021-04-13
As the foremost economic zone in China, the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region has recently been experiencing more frequent haze events, resulting in dramatic damages to human and ecosystem health.
Anthropogenic aerosol emissions play a key role in affecting the formation of haze events. However, aside from local sources of pollution, some studies have found that external and preceding climate drivers, such as Arctic sea ice and subtropical western Pacific sea surface temperature, are also influential factors. However, most research has mainly been confined to analyzing the effects on haze pollution in the Northern Hemisphere, with few considering the Southern Hemisphere.
"We found that the December sea surface temperature ...
2021-04-13
Scientists found six sex chromosomes in the Odorrana swinhoana frog species endemic in Taiwan, giving new insights into how complex XY systems evolve.
The discovery was a surprise to the international research team led by Associate Professor Ikuo Miura of Hiroshima University's Amphibian Research Center. In 1980, the first reported instance of multiple sex chromosome systems in amphibians was found in the Taiwanese brown frog Raina narina -- a synonym for O. swinhoana -- which had a male-specific translocation between two chromosomes. Its sex chromosomes could be described as ?X1Y1X2Y2-?X1X1X2X2.
The ...
2021-04-13
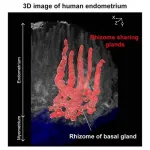
Niigata, Japan- New insights into the three-dimensional (3D) morphology of the human uterine endometrium could advance our understanding of the mechanisms of endometrial regeneration and fertilized egg implantation while clarifying the pathogenesis of menstrual disorders, infertility and endometrium-related diseases such as adenomyosis, endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer.
The endometrial glands are comprised of complicated winding and branching structures, and conventional 2D imaging techniques have been unable to adequately assess their shape. This limitation has prevented elucidation of the mechanisms of endometrial regeneration during the menstrual cycle and the location of endometrial progenitor cells. Recent developments in 3D tissue-clearing imaging ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study links structural brain changes to behavioral problems in children who snore