Efficient generations of complex vectorial optical fields with metasurfaces
2021-04-13
(Press-News.org) Light beams are widely used in photonics applications and attracted immense research interests. Compared to homogeneously polarized light beams, vectorial optical fields (VOFs) with tailored wave-fronts and inhomogeneous polarization distributions exhibits more advantages in applications comparing to their scalar-wave counterparts, thanks to the added degree of freedom (DOF) of polarization. By tailoring the polarization distributions, special VOFs such as flap-top beams and radially polarized beams can be generated, being highly favored in super-resolution microscopy, optical manipulations, etc.
Despite of great advances in applications, generation of such complex VOFs are far from satisfactory. Available methods based on conventional materials suffer from bulky size and low efficiency issues, due to the limited electromagnetic response of natural materials. And recently, metasurfaces have been widely used to generate VOFs in different frequency range, but mostly for far-field generation with certain limited polarization distributions (e.g. radial or azimuthal linear polarizations). In addition, complex VOFs in the near-field with arbitrary polarization distributions are so far rarely generated with metasurfaces.
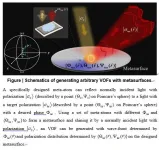
In a newly published paper in Light: Science & Application, Prof. Lei Zhou's group from Physics Department of Fudan University in China, proposed a generic approach to efficiently generate arbitrary VOFs based on metasurfaces exhibiting full-matrix yet inhomogeneous Jones-matrix distributions. To illustrate the feasibility and powerfulness of their strategy, they elucidated their concept based on model-level analytical calculations, and experimentally demonstrated a meta-device as a benchmark that can simultaneously deflect light and manipulate its polarization in controllable manner. Then, they further experimentally demonstrate the generations of far-field VOFs exhibiting a vortex wave front with an inhomogeneous polarization distribution and the generation of a near-field VOF with specially designed wave front and polarization distributions and even orbital angular momentum, i.e. a cylindrically polarized vortex surface plasmon wave. The excellent performance of realized meta-devices and the good agreement among the experimental results in NIR regime, the simulations and analytical calculations well validated their approach, making such meta-platform as an alternative avenue to generate complex VOFs. These scientists summarize their VOF generation platform:
"...we establish a generic strategy for designing ultra-thin meta-devices to efficiently generate arbitrary VOFs (including both far-field and near-field ones) as desired, and experimentally demonstrate the concept in the near-infrared (NIR) regime. The key idea is to assume the meta-device to exhibit an inhomogeneous full-matrix Jones matrix, thus possessing the control capabilities on both local spin and global wave-front of a light beam."
"...the strategy proposed is so generic that we can design VOF-generation meta-devices working for impinging lights with arbitrary incident angles and polarizations in both reflection and transmission geometries." They added.
"In summary, by exploiting the full degrees of freedoms provided by full-matrix inhomogeneous Jones matrix, we establish a general strategy to realize meta-devices to generate VOFs both in the near- and far-field, with any designed wave fronts and local polarization distributions. After illustrating our generic concept by both model-level analytical calculations and benchmark experiments on an anomalously-reflecting half-wave plate, we demonstrate the full capabilities of our approach by experimentally realizing two meta-devices...Our results offer a systematic approach to design ultra-compact optical devices to generate arbitrary VOFs under general conditions in different frequency domains, which are of great importance in both fundamental researches and photonic applications. Many future works can be expected along this line, such as extending the concept to transmission geometry, off-normal incidences, inhomogeneous amplitudes and arbitrary incident polarizations, and applying the generated VOFs to multi-channel communications, near-field sensing, optical trapping, and super-resolution imaging." the scientists forecast.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-13
In a study published in Applied Materials Today, researchers from Singapore have developed the largest range of silicone and epoxy hybrid resins for the 3D printing of wearable devices, biomedical equipment, and soft robotics. The range of tunable functionally graded materials, which displayed over five orders of magnitude of elastic modulus, demonstrated excellent interfacial toughness, higher precision in complex structures and better fabrication control for the integration of mechatronic components.
The multi-disciplinary team from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) highlighted the issue on the potential of soft robotics being limited in its robustness and ...
2021-04-13
Osaka, Japan - SARS-CoV-2 is the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. We know that mutations in the genome of SARS-CoV-2 have occurred and spread, but what effect do those mutations have? Current methods for studying mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 genome are very complicated and time-consuming because coronaviruses have large genomes, but now a team from Osaka University and Hokkaido University have developed a quick, PCR-based reverse genetics system for analyzing SARS-CoV-2 mutations.
This system uses the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and a circular polymerase extension reaction (CPER) to reconstruct the full-length cDNA of viral genome. This process does not involve the use of bacteria, which can introduce further ...
2021-04-13
In the 1930s, English climatologist, Sir Gilbert Walker, successfully predicted Indian summer monsoon rainfall (ISMR) based on the relationship between Southern Oscillation and ISMR connected by what is later-called Walker circulation, which is regarded as the first achievement of modern climate prediction with a clear physical mechanism. The Southern Oscillation was also recognized as the atmospheric component of El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
However, at the end of the 20th century, a research in Science led by Indian climatologist Krishna Kumar found the significant reverse relationship between ENSO and Indian rainfall has been ...
2021-04-13
Ammonia (NH3) is among the most important chemicals produced by humans and has a promising future in sustainable energy applications besides being used in fertilizer production. Unfortunately, so far, the only realistic way that exists to produce ammonia at an industrial scale is through the Haber-Bosch process. This technique, discovered in the 19th century, is very energy-intensive and environmentally unfriendly; about 2% of the yearly global CO2 emissions come from Haber-Bosch processes.
"Considering the threats posed by global warming, it is high time we swap to an ammonia synthesis route with zero CO2 emissions," says Professor Sangaraju Shanmugam from Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), Korea. ...
2021-04-13
What started out as a second-year physics project is making its way into Amazon Web Service's (AWS) quantum computing program.
University of Sydney science undergraduate Pablo Bonilla Ataides has tweaked some computing code to effectively double its capacity to correct errors in the quantum machines being designed in the emerging technology sector.
The simple but ingenious change to quantum error correcting code has grabbed the attention of quantum researchers at the AWS Center for Quantum Computing in Pasadena, California, and the quantum technology programs at Yale University and Duke University in the United States.
"Quantum technology is in its infancy, partly because we haven't ...
2021-04-13
CORVALLIS, Ore. - A new study by Oregon State University researchers found that shade provided by solar panels increased the abundance of flowers under the panels and delayed the timing of their bloom, both findings that could aid the agricultural community.
The study, believed to be the first that looked at the impact of solar panels on flowering plants and insects, has important implications for solar developers who manage the land under solar panels, as well as agriculture and pollinator health advocates who are seeking land for pollinator habitat restoration.
The findings, ...
2021-04-13
Durham, NC - When leukemia strikes an older person, it is in part due to the aging of his or her hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). These immature cells can develop into all types of blood cells, including white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets. As such, researchers have focused on rejuvenating HSCs as a way to treat leukemia.
A new study released today in STEM CELLS adds much to that level of knowledge by showing that the youthful function of rejuvenated HSCs upon transplantation depends in part on a young bone marrow "niche," which is the microenvironment surrounding stem cells that interacts with them to regulate their fate.
"The information revealed by our study tells us that the influence of this niche ...
2021-04-13
Ancient clues, in the shape of fossils and archaeological evidence of varying quality scattered across Australia, have formed the basis of several hypotheses about the fate of megafauna that vanished about 42,000 years ago from the ancient continent of Sahul, comprising mainland Australia, Tasmania, New Guinea and neighbouring islands.
There is a growing consensus that multiple factors were at play, including climate change, the impact of people on the environment, and access to freshwater sources.
Now, research led by Professor Corey Bradshaw of Flinders University and the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence of Australian Biodiversity and Heritage (CABAH) has used sophisticated mathematical modelling to assess how susceptible different species were to extinction - and what ...
2021-04-13
April 13th, 2021, Washington, D.C. - The severe health and economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic have disrupted food systems and upended livelihoods. Yet pandemic responses have demonstrated the power of well-crafted policies to blunt the impact of major shocks while laying the groundwork for stronger, more resilient food systems, according to the 2021 Global Food Policy Report, released today by the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI). The report provides lessons drawn from the current crisis that can help us transform food systems to reduce the impact of the ongoing pandemic, better prepare for future shocks, and address longstanding weaknesses and inequalities.
"We have known ...
2021-04-13
In the early time of optical design, people have to be proficient in aberration theory and perform a huge amount of numerical calculations, and thus mathematical skills and talents are very important. The emergence of electronic computers has freed people from heavy calculation tasks, and realized fast real ray tracing and been able to solve complex aberration equations. Since then, the application and development of optimization algorithms and optical design software have greatly improved the speed and effect of optical design. However, optical design still requires to solve or find an initial solution as the starting point of optimization, which will greatly determine the final result of optimization. Moreover, optimization is essentially ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Efficient generations of complex vectorial optical fields with metasurfaces