(Press-News.org) Concerns about climate change are driving a growing number of states, utilities, and corporations to set the goal of zeroing out power-sector carbon emissions. To date 17 states plus Washington, D.C. and Puerto Rico have adopted laws or executive orders to achieve 100% carbon-free electricity in the next couple of decades. Additionally, 46 U.S. utilities have pledged to go carbon free no later than 2050. Altogether, these goals cover about half of the U.S. population and economy.
These are ambitious targets, but a new look at the past 15 years in the electricity sector shows that large reductions in emissions are possible.
New research from the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) analyzes historical trends to examine how much progress the power sector has already made in reducing emissions. The study, "Halfway to Zero: Progress towards a Carbon-Free Power Sector," looks back at the 2005 Annual Energy Outlook from the Energy Information Administration (EIA), the U.S. government's official agency for data collection and analysis.
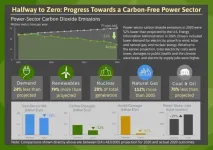
"Business-as-usual projections saw annual carbon dioxide emissions rising from 2,400 to 3,000 million metric tons (MMT) from 2005 to 2020," said Berkeley Lab scientist Ryan Wiser, lead author of the study. "But actual 2020 emissions fell to only 1,450 MMT. The U.S. cut power sector emissions by 52% below projected levels - we are now 'halfway to zero.'"
According to the study, relative to projected values, total consumer electricity costs were 18% lower; costs to human health and the climate were 92% and 52% lower, respectively; and the number of jobs in electricity generation was 29% higher.
Drivers of change
From technological advances to policy, the study identified the main drivers from the last 15 years that contributed to lower carbon emissions in the U.S. power sector. Total demand for electricity was almost exactly the same in 2020 as it was in 2005, and was 24% lower than projected fifteen years earlier. "This drop in demand was due in part to sectoral and economic changes, but also to greater energy efficiency driven by policies and technology advancement," said Wiser.
The researchers found that wind and solar power dramatically outperformed expectations, delivering 13 times more generation in 2020 than projected. This is also a result of technology development and state and federal policies, as prices plummeted for new wind and solar technologies. In addition, nuclear generation has largely held steady, tracking the past projections and helping to ensure no backsliding in carbon emission.
The study found that switching from coal to natural gas for power generation played a big role in lowering carbon emissions. Natural gas generation grew rapidly, driven by the shale gas revolution and low fuel prices.
The researchers also found that changes over the last 15 years had numerous other economic and environmental benefits. For example, total electric bills for consumers were 18% lower in 2020 than previously projected by EIA, for a total savings of $86 billion per year.
According to the study, reduced sulfur and nitrogen emissions led to lower health impacts, such as respiratory disease, with premature deaths falling from 38,000 to 3,100 per year. "Compared to the business-as-usual projection, not only did the nation significantly reduce its carbon footprint, but it did so while also reducing total energy bills and health burdens," said co-author and Berkeley Lab scientist Dev Millstein.
The study also found that while employment patterns shifted along with changes in the power sector, electricity supply is supporting 200,000 more jobs than might have been the case under the earlier projection.
Looking forward
While a look back shows that dramatic changes in emissions are possible over a 15-year span, the study points out that this does not guarantee the next 15 years will see similar progress.
Given advancements in wind, solar, and battery technologies, these resources are likely to play important near-term roles in further power-sector decarbonization. According to the study, a large share of the capacity needed to approach a zero-carbon power-sector target is already in the development pipeline: about 660 gigawatts (GW) of wind and solar have requested transmission access, more than half of what might be required to approach a zero-carbon power-sector target. Not all proposed projects will be built, but the scale indicates interest in development.
Wiser points out there are significant infrastructure requirements related to scaling up renewable energy. The power sector will have to ensure electricity delivery, reliability, and resilience; build new transmission infrastructure; change planning and grid operations; revise siting processes; and focus attention on impacted workers and communities.
Another major challenge is how to meet the last portion of demand, to ensure a reliable power supply when the wind doesn't blow and the sun doesn't shine. The study concludes that further research, development, and demonstration is needed for the numerous technologies that can fill this gap, such as longer-duration energy storage, hydrogen or synthetic fuels, bioenergy, fossil or biomass generation with carbon capture, nuclear energy, geothermal energy, and solar-thermal with storage.
"As the country maps out a plan for further decarbonization, experience from the past 15 years offers two central lessons," said Wiser. "First, policy and technology advancement are imperative to achieving significant emissions reductions. Second, our ability to predict the future is limited, and so it will be crucial to adapt as we gain policy experience and as technologies advance in unexpected ways."
INFORMATION:
-By Kiran Julin
Funding for this research was provided by the Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy.
Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest scientific challenges are best addressed by teams, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and its scientists have been recognized with 14 Nobel Prizes. Today, Berkeley Lab researchers develop sustainable energy and environmental solutions, create useful new materials, advance the frontiers of computing, and probe the mysteries of life, matter, and the universe. Scientists from around the world rely on the Lab's facilities for their own discovery science. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory, managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.
As the Rhode Island legislature considers designating the Northern Star Coral an official state emblem, researchers are finding that studying this local creature's recovery from a laboratory-induced stressor could help better understand how to protect endangered tropical corals.
A new study published today in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology, investigates antibiotic-induced disturbance of the coral (Astrangia poculata) and shows that antibiotic exposure significantly altered the composition of the coral's mucus bacterial microbiome, but that all the treated corals recovered ...
A new study published in Elementa by researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz and NOAA examines traditional aspects of seafood sustainability alongside greenhouse gas emissions to better understand the "carbon footprint" of U.S. tuna fisheries.
Fisheries in the United States are among the best managed in the world, thanks to ongoing efforts to fish selectively, end overfishing, and rebuild fish stocks. But climate change could bring dramatic changes in the marine environment that threaten seafood productivity and sustainability. That's one reason why researchers ...
Physicists from Swansea University are part of an international research collaboration which has identified a new technique for testing the quality of quantum correlations.
Quantum computers run their algorithms on large quantum systems of many parts, called qubits, by creating quantum correlations across all of them. It is important to verify that the actual computation procedures lead to quantum correlations of desired quality.
However, carrying out these checks is resource-intensive as the number of tests required grows exponentially with the number of qubits involved.
Researchers from the College of Science, working with colleagues from Spain ...
Biomedical scientists are increasingly using deconvolution methods, those used to computationally analyze the composition of complex mixtures of cells. One of their challenges is to select one method that is appropriate for their experimental conditions among nearly 50 available.
To help with method selection, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital have extensively evaluated 11 deconvolution methods that are based on RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data analysis, determining each method's ...
Almost all bacteria rely on the same emergency valves--protein channels that pop open under pressure, releasing a deluge of cell contents. It is a last-ditch effort, a failsafe that prevents bacteria from exploding and dying when stretched to the limit. If we understood how those protein channels worked, antibiotic drugs could be designed to open them on demand, draining a bacterium of its nutrients by exploiting a floodgate common to many species.
But these channels are tricky to operate in the lab. And how precisely they open and close, passing through a sub-conducting state and ending in a desensitized state under the influence of mechanical forces, remains poorly understood. Now, new research from ...
A study done in rooms where COVID-19 patients were isolated shows that the virus's RNA - part of the genetic material inside a virus - can persist up to a month in dust.
The study did not evaluate whether dust can transmit the virus to humans. It could, however, offer another option for monitoring COVID-19 outbreaks in specific buildings, including nursing homes, offices or schools.
Karen Dannemiller, senior author of the study, has experience studying dust and its relationship to potential hazards like mold and microbes.
"When the pandemic started, we really wanted to find a way that we could help ...
WHAT:
Many people who have COVID-19 make a full recovery and return to their baseline state of health; however, some people have symptoms or other sequelae weeks or months after initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These heterogeneous symptoms were the subject of the virtual "Workshop on Post-acute Sequelae of COVID-19" hosted on Dec. 2 and 4, 2020, by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), in collaboration with other institutes and centers of the National Institutes of Health. A paper published recently in Annals of Internal Medicine ...
Researchers have identified molecular signatures of the aging process in mice, publishing their results today in the open-access eLife journal.
Their analyses provide one of the most comprehensive characterisations of the molecular signatures of aging across diverse types of cells from different tissues in a mammal, and will aid future studies on aging and related topics.
Aging leads to the decline of major organs and is the main risk factor for many diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. While previous studies have highlighted different hallmarks of the aging process, the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms ...
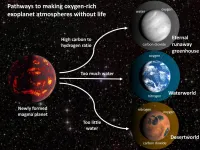
In the search for life on other planets, the presence of oxygen in a planet's atmosphere is one potential sign of biological activity that might be detected by future telescopes. A new study, however, describes several scenarios in which a lifeless rocky planet around a sun-like star could evolve to have oxygen in its atmosphere.
The new findings, published April 13 in AGU Advances, highlight the need for next-generation telescopes that are capable of characterizing planetary environments and searching for multiple lines of evidence for life in addition to detecting oxygen.
"This ...
After interviewing various stakeholders from public and private healthcare systems (in Lithuania and the US), researchers Dr Agne Gadeikiene, Prof Asta Pundziene, Dr Aiste Dovaliene from Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania designed a detailed structure revealing added value of remote healthcare services, i.e. telehealth. Adopting the concept of value co-creation common in business research to healthcare, the scientists claim that this is the first comprehensive analysis of this kind in the healthcare field involving two different healthcare systems.
According to the researchers, although in the US the consultations via phone with physician have been available for more than fifty ...