(Press-News.org) Supplementation of cocoa powder in the diet of high-fat-fed mice with liver disease markedly reduced the severity of their condition, according to a new study by Penn State researchers, who suggest the results have implications for people.
Cocoa powder, a popular food ingredient most commonly used in the production of chocolate, is rich in fiber, iron and phytochemicals reported to have positive health benefits, including antioxidant polyphenols and methylxanthines, noted study leader Joshua Lambert, professor of food science in the College of Agricultural Sciences.
"While it is typically considered an indulgence food because of its high sugar and fat content, epidemiological and human-intervention studies have suggested that chocolate consumption is associated with reduced risk of cardio-metabolic diseases including stroke, coronary heart disease and Type 2 diabetes," Lambert said. "So, it made sense to investigate whether cocoa consumption had an effect on non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease, which is commonly associated with human obesity."
This study has several strengths, Lambert explained. It used a commercially available cocoa product at a "physiologically achievable dose" -- meaning its equivalent could be duplicated by humans. "Doing the calculations, for people it works out to about 10 tablespoons of cocoa powder a day," he said. "Or, if you follow the directions on the Hershey's box of cocoa powder, that's about five cups of hot cocoa a day."
The high-fat-fed mouse is a well-established, diet-induced model of obesity, Lambert added. By waiting until mice were already obese before beginning cocoa treatment, researchers were able to test the protective effects of cocoa in a model that better simulates the current public health situation related to non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease.
That's important, Lambert pointed out, because a significant proportion of the world's population has preexisting obesity and non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease. "Given the high proportion of people in the United States and other parts of the world with obesity, there is a need to develop potentially effective dietary interventions rather than just preventive agents," he said.
For this study, researchers examined changes in fatty liver disease, markers of oxidative stress, antioxidant response and cell damage in high-fat-fed obese mice treated with a diet supplemented with 80 mg cocoa powder per gram of food -- roughly a pinch per quarter teaspoon -- for eight weeks.
In findings recently published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, the researchers reported that cocoa-treated mice gained weight at a 21% lower rate and had smaller spleen weights -- indicating less inflammation -- than the high-fat-fed control mice. At the end of the study, mice fed the cocoa-powder-supplemented diet had 28% less fat in their livers than the control mice. Cocoa-treated mice also had 56% lower levels of oxidative stress and 75% lower levels of DNA damage in the liver compared to high-fat-fed control mice.
The mechanisms by which cocoa imparts health benefits are not well understood, but previous studies in Lambert's lab showed that extracts from cocoa and some of the chemicals in cocoa powder can inhibit the enzymes that are responsible for digesting dietary fat and carbohydrate.
The result, he proposes, is that when mice get cocoa as part of their diet, these compounds in the cocoa powder prevent the digestion of dietary fat. When it can't be absorbed, the fat passes through their digestive systems. A similar process may occur with cocoa in humans, he hypothesizes.
In view of this new information about cocoa powder, Lambert is not recommending that obese people -- or anyone -- simply add five cups of hot cocoa to their daily routine and change nothing else in their diet. But he does advise, based on what he has learned in this study, to consider substituting cocoa for other foods, particularly high-calorie snack foods.
"This exchange is potentially beneficial, especially in combination with a healthy overall diet and increased physical activity," he said. "If you go to the gym and work out, and your reward is you go home and have a cup of cocoa, that may be something that helps get you off the couch and moving around."
INFORMATION:
Also involved in the research were Mingyao Sun, Yeyi Gu and Shannon Glisan, former graduate students in the Department of Food Science.
The research received technical support from the Penn State Genomics Core Facility and the Penn State Laboratory Animal Program. The National Institutes of Health, the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the Silvio and Edith Crespo Faculty Award partially funded this research. Blommer Chocolate Co., East Greenville, Pennsylvania, provided a gift of cocoa powder for the research.
TAMPA, Fla. (April 14, 2021)- The order in which your senses interact with food has a tremendous impact on how much you like it. That's the premise of a new study led by the University of South Florida (USF). The findings published in the Journal of Consumer Psychology show that food tastes better if you see it before smelling it.
Researchers came to this conclusion following four experiments involving cookies, fruit snacks and lemonade. In the first study, nearly 200 participants interacted with the food, each item wrapped in an opaque versus a transparent package. The ...
For centuries, ivory was often used to make art objects. But to protect elephant populations, the ivory trade was banned internationally in 1989. To restore ivory parts of old art objects, one must therefore resort to substitute materials - such as bones, shells or plastic. However, there has not been a really satisfactory solution so far.
TU Wien (Vienna) and the 3D printing company Cubicure GmbH, created as a spin-off of TU Wien, have now developed a high-tech substitute in cooperation with the Archdiocese of Vienna's Department for the Care of Art and Monuments and Addison Restoration: the novel material "Digory" consists of synthetic resin and calcium phosphate particles. It is processed in a hot, liquid state and hardened in the 3D printer with UV ...
International scientists from around the world are warning that chemical pollutants in the environment have the potential to alter animal and human behaviour.
A scientific forum of 30 experts formed a united agreement of concern about chemical pollutants and set up a roadmap to help protect the environment from behaviour altering chemicals. The conclusions of their work have been published today in a paper led by Professor Alex Ford, Professor of Biology at the University of Portsmouth, in Environmental Science and Technology. Until now the effect of chemical pollutants on wildlife has ...
Metabolic bone disease is a common complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and involves a broad spectrum of disorders of mineral metabolism that result in both skeletal and extra-skeletal consequences.
A new special issue of Calcified Tissue International brings together a comprehensive series of state-of-the-art reviews which discuss key issues in CKD and mineral and bone disorders, known as CKD-MBD. Authored by a multidisciplinary group of leading international experts, the wide-ranging reviews aim to improve the understanding and management of CKD-MBD, and advance interdisciplinary knowledge.
Professors ...
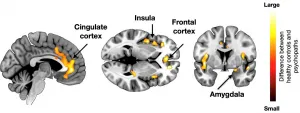
According to a Finnish study, the structure and function of the brain areas involved in emotions and their regulation are altered in both psychopathic criminal offenders and otherwise well-functioning individuals who have personality traits associated with psychopathy.
Psychopathy is a personality disorder characterised by persistent antisocial behaviour, impaired empathy, and bold, disinhibited and egotistical traits. However, similar antisocial traits are also common, yet less pronounced, with people who are well-off psychologically and socially. It is possible that the characteristics related to psychopathy form a continuum where only the extreme characteristics ...
Bern's ice core researchers were already able to demonstrate in 2008 how the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere has changed over the past 800,000 years. Now, using the same ice core from the Antarctic, the group led by Bernese climate researcher Hubertus Fischer shows the maximum and minimum values between which the mean ocean temperature has fluctuated over the past 700,000 years. The results of the reconstruction have just been published in the journal Climate of the Past.
The study's key findings: Mean ocean temperatures have been very similar over the last seven ice ages, averaging about 3.3 °C colder than the pre-industrial reference period, as already suggested by syntheses of deep water ...
It is an open question to what extent protection against reinfection persists after overcoming a SARS-CoV-2 infection. The "Rhineland Study", a population-based study conducted by DZNE in the Bonn area, is now providing new findings in this regard. Blood samples taken last year indicate that an important component of immunity - the levels of specific neutralizing antibodies against the coronavirus - had dropped in most of the study participants with a previous infection after four to five months. In some, antibody titers even fell below the detection limit. These results, published in the scientific journal "Nature Communications", lay the groundwork for planned follow-up studies.
Between April ...
Research breakthrough in understanding how neural systems process and store information.
A team of scientists from the University of Exeter and the University of Auckland have made a breakthrough in the quest to better understand how neural systems are able to process and store information.
The researchers, including lead author Dr Kyle Wedgwood from the University of Exeter's Living Systems Institute, have made a significant discovery in how a single cell can store electrical patterns, similar to memories.
They compared sophisticated mathematical modelling to lab-based experiments to determine how different parameters, such as how long it takes ...
In a new study, Dr. LU Xiankai and his colleagues from the South China Botanical Garden (SCBG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found that tropical forests can capture carbon dioxide (CO2) into soils and thus reduce emitted CO2. But how exactly do tropical forest soils capture atmospheric CO2?
Current knowledge of forest soil carbon sequestration mainly focuses on temperate and boreal forests, where most ecosystems are nitrogen-limited, and an increase in nitrogen supply can enhance net primary productivity (NPP) and subsequent soil carbon ...
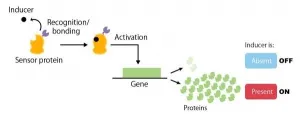
A group of researchers from Kobe University and Chiba University has successfully developed a flexible and simple method of artificially producing genetic switches for yeast, a model eukaryotic organism. The group consisted of Researcher TOMINAGA Masahiro*1, Associate Professor ISHII Jun*2 and Professor KONDO Akihiko*3 (of Kobe University's Graduate School of Science, Technology and Innovation/Engineering Biology Research Center), and Professor UMENO Daisuke et al. (of Chiba University's Graduate School of Engineering).
Genetic switches are gene regulatory networks that control gene expression. The researchers established a platform for ...