UZH researchers find new measure to predict stress resilience
2021-04-15
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Zurich show that increased sensitivity in a specific region of the brain contributes to the development of anxiety and depression in response to real-life stress. Their study establishes an objective neurobiological measure for stress resilience in humans.
Some people don't seem to be too bothered when it comes to handling stress. For others, however, prolonged exposure to stress can lead to symptoms of anxiety and depression. While stress resilience is a widely discussed concept, it is still very challenging to predict people's individual response to increased levels of stress. Lab experiments can only go so far in replicating the chronic stress many people experience in their day-to-day lives, as stress simulated in the lab is always limited in exposure time and intensity.
It is possible, however, to observe a group of medical students who are all about to face real-life stress for an extended period - during their six-month internship in the emergency room. This is precisely the real-life situation on which a team of researchers involving Marcus Grueschow and Christian Ruff from the UZH Zurich Center for Neuroeconomics and Birgit Kleim from the Department of Psychology and the University Hospital of Psychiatry Zurich based their study.
Stress as a response to cognitive conflict and loss of control
Before starting their internship, the subjects were given a task that required them to process conflicting information. This conflict task activates the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine (LC-NE) system, a region of the brain associated with regulating our response to stress and resolving conflict. However, the intensity of LC-NE activation - often referred to as the "firing rate" - varies from one person to the next.
Subjects with a higher LC-NE responsivity showed more symptoms of anxiety and depression following their emergency room internships. "The more responsive the LC-NE system, the more likely a person will develop symptoms of anxiety and depression when they're exposed to prolonged stress," Marcus Grueschow summarizes their findings.
Objective measure predicting stress resilience
With their study, the scientists have identified an objective neurobiological measure that can predict a person's stress response. This is the first demonstration that in humans, differences in LC-NE responsivity can be used as an indicator for stress resilience. "Having an objective measure of a person's ability to cope with stress can be very helpful, for example when it comes to choosing a profession. Or it could be applied in stress resilience training with neuro-feedback," Marcus Grueschow explains.
This does not mean that aspiring doctors or future police officers will all have to have their brain scanned. "There might be an even more accessible indicator for stress resilience," Christian Ruff says. Research with animals suggests that stimulation of the LC-NE system correlates with pupil dilation. "If we could establish the same causal link between pupil dilation and the LC-NE system in humans, it would open up another avenue," he adds.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-15
Technologies to remove CO2 from the atmosphere, such as reforestation or bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), are an indispensable part in most scenarios to limit climate change. However, excessive deployment of such technologies would carry risks such as land conflicts or enhanced water scarcity due to a high demand for bioenergy crops. To tackle this trade-off, a team of researchers from Potsdam and Berlin has now identified requirements for a dynamic, long-term carbon price pathway to reduce the demand for CO2 removal technologies and thus effectively limit long-term ...
2021-04-15
ROCHESTER, Minn. - Though researchers have long known that several physiological and anatomical changes occur during pregnancy that can contribute to kidney stone formation, evidence of the link has been lacking. But now Mayo Clinic researchers believe they have that evidence.
An observational study that reviewed the medical records for nearly 3,000 female patients from 1984 to 2012 finds that pregnancy increases the risk of a first-time symptomatic kidney stone. The risk peaks close to delivery and then improves by one year after delivery, though a modest risk of developing kidney stones continues beyond ...
2021-04-15
The COVID-19 disease due to infection by the SARS-CoV2 virus has changed the behavior patterns of humanity by becoming a pandemic of international scope. To date, more than 136 million people have suffered from the disease and more than 2.9 million of them have lost their lives. It is important to remember that the symptoms of the infection vary widely in the population, from individuals who do not present any symptoms to those who need admission to intensive care units with emergency assisted ventilation. It is largely unknown what factors are responsible for this range of very ...
2021-04-15
Sophia Antipolis - 15 April 2021: An observational study in nearly 20,000 individuals has found that greater intake of red and processed meat is associated with worse heart function. The research is presented at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
"Previous studies have shown links between greater red meat consumption and increased risk of heart attacks or dying from heart disease," said study author Dr. Zahra Raisi-Estabragh of Queen Mary University of London, UK.2,3 "For the first time, we ...
2021-04-15
More than 30 years ago, wilderness areas - natural areas that have not been considerably modified by humans - were identified as priorities of conservation and protection actions. Only recently has there been a push to define how to measure wilderness, with a focus on intact habitats. The integrity of natural ecosystems has also been recognized by the UN Convention on Biological Diversity as an important goal in the post-2020 global biodiversity framework. "We know intact habitat is increasingly being lost and the values of intact habitat have been demonstrated for both biodiversity and people," says Dr Andrew Plumptre from the Key Biodiversity Areas Secretariat in Cambridge, ...
2021-04-15
A new study in SLEEP, published by Oxford University Press, demonstrates the significant benefits of later school start times for middle and high school students' sleep schedules.
Sleep is essential to a student's overall health, social development, and academic achievement, yet lack of sleep is common among children and adolescents. Biological changes to sleep cycles during puberty make falling asleep early difficult for adolescents. This, coupled with early school start times, means that students often end up with insufficient sleep.
Approximately 28,000 elementary, middle, and high school students and parents completed surveys annually, ...
2021-04-15
Young adults must step up their exercise routines to reduce their chances of developing high blood pressure or hypertension - a condition that may lead to heart attack and stroke, as well as dementia in later life.
Current guidelines indicate that adults should have a minimum of two-and-a-half hours of moderate intensity exercise each week, but a new study led by UCSF Benioff Children's Hospitals reveals that boosting exercise to as much as five hours a week may protect against hypertension in midlife - particularly if it is sustained in one's thirties, forties and fifties.
In the study publishing in American Journal ...
2021-04-15
Geneva, 15th April 2021 - When it was shown launching out of the sea to snatch birds from the air in the first episode of the BBC's Blue Planet II, the Seychelles giant trevally, or 'karang ledan' as it is called in Creole, became world-famous. Typically eating fish, not birds, this reef predator is critical for maintaining healthy balanced ecosystems. 'The giant trevally is a popular, sought-after prize fish in Seychelles, particularly in the big-game sportfishing industry. Seychelles has a reputation for being one of the best trevally destinations in the world. The species is also caught in the handline fishery,' explains Helena Sims, the Save Our Seas Foundation's Seychelles ambassador. Sims, with more than a decade of conservation experience, ...
2021-04-15
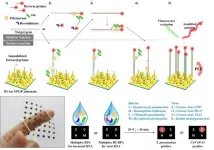
Researchers in South Korea developed a plasmonic isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) array chip, the world's first plasmoinc isothermal PCR technology which can detect 8 types of pathogens (4 bacteria and 4 viruses) that cause acute respiratory infectious diseases in 30 minutes, led by Dr. Sung-Gyu Park and Dr. Ho Sang Jung of the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS, President Jung-Hwan Lee) and by Dr. Min-Young Lee and Dr. Ayoung Woo of Samsung Medical Center. KIMS is a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT.
* PCR(Polymerase Chain Reaction): A test method to amplify and detect nucleic acids target
The current detection technology for COVID-19 is impossible ...
2021-04-15
Despite surgery and subsequent treatment with chemotherapy and radiation, the majority of patients experience recurrence of malignant brain tumours. Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, and the Medical University of Graz, Austria, have shown in cells in culture that an ion pump can deliver drugs more accurately, which gives less severe adverse effects in chemotherapy. The results have been published in Advanced Materials Technologies.
"This is the first time an ion pump has been tested as a possible method to treat malignant brain tumours. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] UZH researchers find new measure to predict stress resilience